Content Backup Strategy
This section looks at implementing an effective content backup strategy for your business.
 If content plays any part in the success and growth of your business, website, or digital presence, then we recommend developing and implementing an effective content backup strategy.
If content plays any part in the success and growth of your business, website, or digital presence, then we recommend developing and implementing an effective content backup strategy.
This will ensure that, if anything should happen to your business, to your website, or to your digital presence, your content can be fully restored quickly and easily.
This section looks at implementing an effective content backup strategy – what needs backing up, how often to back up, and cost-effective backup tools and methods.
Content Backups Goals And Objectives
The goals and objectives of performing regular content backups include:
- Protect against data loss: This goal aims to protect your business against data loss due to hardware failure, software corruption, or other unforeseen events. Examples include regularly creating backups of website files, using backup software or services, and storing backups in multiple locations.
- Ensure business continuity: This goal focuses on ensuring that your business can continue to operate in the event of data loss. Examples include having a disaster recovery plan in place, regularly testing backups to ensure they can be restored, and ensuring backups are easily accessible in case of an emergency.
- Meet compliance requirements: This goal aims to meet any legal or regulatory requirements for data retention and backup. Examples include adhering to industry-specific regulations such as HIPAA or SOX, and keeping backups for a certain period of time to meet legal requirements
- Easily revert to a previous version: This goal focuses on providing the ability to easily revert to a previous version of your website in case of errors or issues. Examples include creating point-in-time backups, keeping multiple versions of backups, and having the ability to easily restore backups.
- Save time and resources: This goal aims to save time and resources by automating the backup process and reducing the need for manual intervention. Examples include using backup software or services that automate the backup process, setting up scheduled backups, and utilizing incremental backups to minimize data transfer.
- Secure backups: This goal focuses on ensuring that backups are secure and protected from unauthorized access. Examples include encrypting backups, using secure protocols for data transfer, and using secure storage for backups.
- Monitor and test backups: This goal aims to regularly monitor and test backups to ensure they are working correctly. Examples include regularly testing backups to make sure they can be restored, monitoring backup logs for errors, and setting up alerts for backup failures.
- Store backups in multiple locations: This goal focuses on ensuring that backups are stored in multiple locations to protect against data loss due to physical disasters. Examples include storing backups on the cloud, on external hard drives, and on a separate server.
Your Content Backup Strategy
Having a content backup strategy is all about answering this question…
“How would we feel if something happened to our business, our website, or our digital presence?”
With this answer…
“Peace of mind.”
People take out health insurance, life insurance, business insurance, income insurance, home insurance, car insurance, etc. for “peace of mind.”
This is no different. If your content is important to your business, then you need content insurance to give you peace of mind.
Having an effective content backup system in place will ensure that your content can be restored fully, quickly, and easily should anything unpredictable or unexpected happen to your business or content.
The challenge is that in order to implement an effective content backup system that can fully restore your content quickly and easily, your business first needs to implement the following systems:

Content Documentation System
Your content documentation system includes planning and documenting all the processes, procedures, policies, guidelines, workflows, and checklists used to create all the content used in your business.
This ensures that if something disastrous were to happen and you have no backups, your business can assess what content it needs to recreate.
We cover this in more detail in the Content Documentation lesson.
Content Organization System
Your content organization system includes planning and deciding where all of your documentation will be stored.
This ensures that in the case of an emergency, you can quickly and easily retrieve all of your stored content.
We cover this in more detail in the Content Organization lesson.
Content Backup System
If the goal of your content backup strategy is to have “complete peace of mind,” then your content backup system must be comprehensive and take into account all business-related content generated from every area of the business, stored everywhere, including external servers and applications, internal company drives, and user devices.
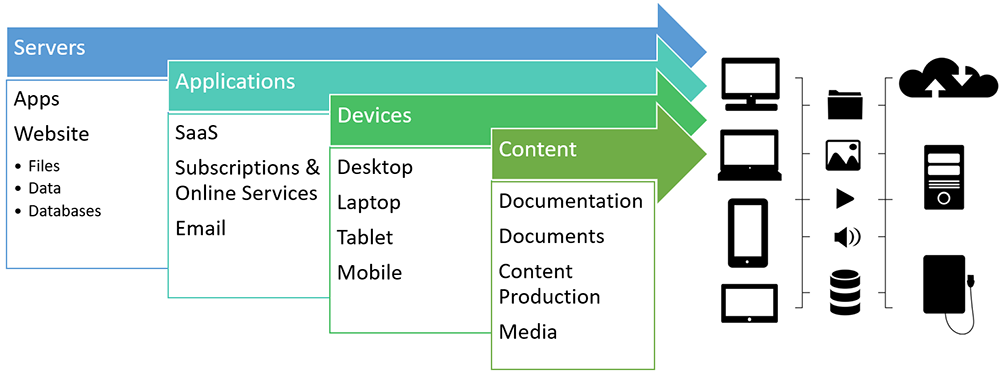
In essence, this involves making an inventory of what needs to be backed up in each of the following areas:
Servers
Most of your public-facing content will be stored on servers.
This includes your website and all of its files, data, databases, and applications.
Many webhosting services include daily, weekly, or monthly server backups (full or incremental) depending on your webhosting plan. Some even include hourly backups, which are useful for sites that process large amounts of data, eCommerce sites, etc.
Typically, these backups are run automatically and managed by your webhosting company.
When creating your content backup strategy, contact your web host and ask them or review how data and files on your servers are backed up, how often, how data, files, and content can be restored, etc., and include this in your documentation.
Applications
Many applications, services, and tools used for work productivity, content production, and content promotion are run on cloud-based platforms (i.e. Software as a Service, or SaaS).
This makes the companies running these services responsible for keeping your account secure and your content backed up.
When creating your content backup strategy, make an inventory of all the services and applications that host your content externally, make a note of their backup processes and policies, and find out if it’s possible to export or back up your content and data files to your own backup solutions, so you can safeguard and protect your content.
Devices
Content such as business documentation and company-branded media files (e.g. logos, banners, etc.) should be stored on devices accessed through company accounts.
Sometimes, however, these files can end up being stored on personal devices, such as laptops and mobile devices of staff members.
It’s important, therefore, to assess and review where all of your business documentation is being stored and implement correct policies and procedures so that content isn’t lost if a team member leaves their role or loses their laptop or mobile phone.
Once you have done this, add this information to your backup plan.
Content
While your website content will typically be stored on a server and your business may choose to store other content on external applications or services, there are loads of internal documents that are probably being stored on internal drives, user devices, and other locations.
This content includes documents for external distribution (e.g. marketing brochures, pdf guides, reports, lists, drafts, revisions, etc.), content for internal communications (e.g. emails), etc.
It’s important to make sure that a record of this content is also uploaded to company folders, services, and accounts listed in your backup plan.
Back-Up Your Backups
Human error, malicious activity, technical errors, and natural disasters can lead to serious loss of data.
As stated earlier, if the plan is to achieve “complete peace of mind,” then your content backup strategy must not only include a system for backing all content from all areas of the business stored on all devices across the organization but also maintain regular backups of your backups.
Having multiple backups of backups stored across different locations is the ultimate strategy for mitigating and protecting your company’s content and data.
What Is An Offsite Storage Solution?
An offsite storage solution involves storing your website data and backups in a different physical location from your primary site.
This can be achieved through services that keep your data in secure data centers away from your main operations, offering protection against local disasters like fires or floods.
Why Use A Secure Data Storage Solution?
Storing your data backups on your computer hard drive can present a serious risk if your computer crashes or dies due to excessive use, or malicious viruses.
Using a secure offsite, remote, or cloud data storage solution for your website backups and files is a practical and sensible way to ensure that your valuable data can be recovered quickly if something happens to your computer.
For example, if your website is compromised by a cyberattack, having an offsite backup ensures you can restore the site to a previous, uncorrupted state quickly, avoiding prolonged downtime and potential loss of revenue.
Additionally, offsite storage solutions often provide scalable options that can grow with your business, offering cost savings compared to maintaining your own backup infrastructure.
Which Type Of Storage Solution Should You Use?
There are different types of storage solutions you can consider using.
For example:
- Offsite Storage:
- Definition: Physical storage of data in a location separate from your main site.
- Example: Backing up your WordPress site to an external hard drive kept in a different building.
- Remote Storage:
- Definition: Accessing data stored at a distant location via the internet.
- Example: Using a remote server to access and store files that are not physically close to you, such as through a company’s distant data center.
- Cloud Storage:
- Definition: Data stored on virtual servers hosted on the internet by third-party providers.
- Example: Services like Google Drive or Dropbox, where data is stored in the cloud and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
For more information on this, visit our File Transfer Tools tutorial, or see this article: How To Back Up Your Backups For Bulletproof Protection
How Often Should You Back Up Content?
The ideal backup interval depends on how often new content is added to your system and how valuable the content is.
If you run a high-volume eCommerce website, for example, you may want to back up your transaction data (and accompanying external sales data, communications, etc.) hourly.
If new content is regularly added to your website, then your website should get backed up at least daily (or nightly).
You may choose to back up files and content used for content planning, content production, or content promotion (e.g. media files, outline or draft documents, etc.) weekly or monthly.
The same applies to company documentation such as guides, policies, templates, etc. Depending on how often these documents are updated, you may want to create a monthly, quarterly, or semi-annual backup schedule.
The bottom line is that backup intervals must suit your business and help to eliminate the risk of losing important content, files, or data should anything unexpected happen.
Where To Backup Content
Your organization’s content will either reside internally or externally.
Content stored internally (documents, files, data, applications, etc.) is typically backed up using solutions like remote or cloud backup services and external drives.
As stated earlier, backing up content stored or hosted externally is the responsibility of the service providers. If you can export your data from these services, then add those export files to your internal data backup system.
For information on business cloud storage backup services, backing up your computer devices, and WordPress backup plugins, see the articles and tutorials listed in the “References” section at the end of this lesson.
Create A Content Backup Strategy Document
Your Content Backup Strategy document includes your content documentation and organization systems, a list of where all your content is being backed up to, their corresponding backup schedules, and who is responsible for performing these backups.
For this reason, we recommend focusing first on creating and implementing a Content Documentation System and Content Organization System.
Your Content Backup System then becomes the process of regularly backing up these systems.
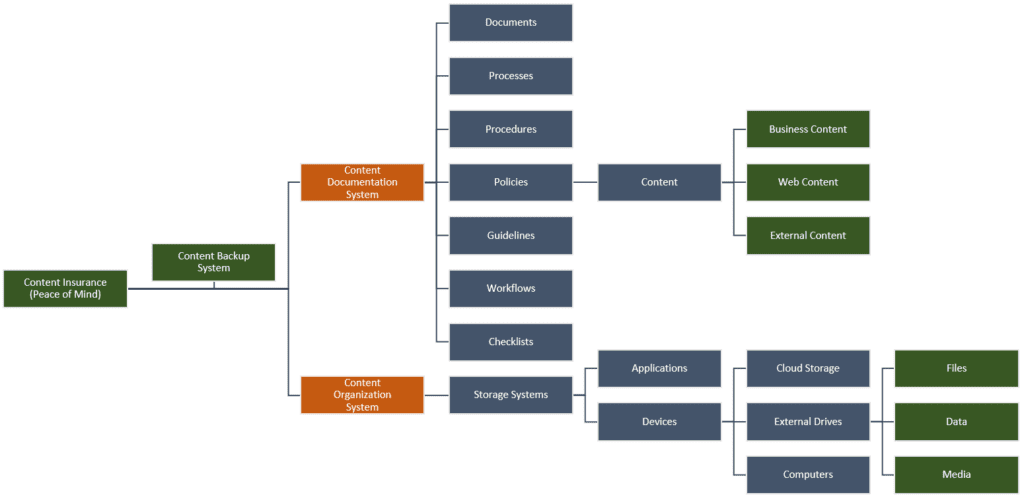
Content Backup Checklist
Use the checklist below to ensure you have a complete content backup system for backing up the following:
- Server Backup
- Server applications
- Website files
- Website data
- Databases
- Applications
- SaaS (e.g. work productivity tools, content production software, content promotion services)
- Subscriptions
- Externally-hosted services
- Device Backup (Desktop, Laptop, Tablet, Mobile)
- Programs and applications
- Files
- Data
- Content Backup
- Documentation (including logins, passwords, licenses, etc.)
- Documents (e.g. PDF guides, downloadable files, etc.)
- Website (files, data, content revisions, etc.)
- Media (e.g. images, videos, audio, slide presentations, etc.)
Content Backups – FAQs
Here are frequently asked questions about content backups:
What is a content backup?
A content backup refers to the process of copying and archiving website data so that it can be restored in the event of data loss, whether accidental or due to a cyber attack.
Why are backups important in content management?
Backups are crucial as they ensure that your digital content is safeguarded against data loss, corruption, or system failures, thus maintaining business continuity.
How often should I backup my website content?
The frequency of backups depends on the volume of content changes and the critical nature of your data. Daily backups are common, but more frequent backups might be necessary for highly dynamic sites.
What should be included in a content backup?
A comprehensive backup should include all website files, databases, images, and any additional resources used by the website such as plugins or custom code.
Where should I store my backups?
It is best practice to store backups in multiple locations, including both on-site and off-site storage solutions. Cloud storage services are also a popular and secure option.
How can I ensure my backups are secure?
Secure your backups by using encryption, strong access controls, and ensuring that any physical or cloud storage providers comply with industry-standard security practices.
What is the difference between incremental and full backups?
A full backup copies all selected data, whereas an incremental backup only copies data that has changed since the last backup, which can save storage space and reduce backup time.
How do I restore from a backup?
Restoring from a backup typically involves accessing your backup storage, selecting the appropriate backup, and using your CMS or a specialized tool to restore the data to your live environment.
Can automated tools help with content backups?
Yes, many CMS platforms have plugins or built-in features that automate the backup process, scheduling backups at regular intervals and storing them in predefined locations.
What common issues should I be aware of with content backups?
Potential issues include incomplete backups, backups failing to run as scheduled, data corruption during backup, and inadequate testing of backup integrity.
Summary
Trying to keep track of all the content flowing in, out, and through your organization is complex and challenging.
However, it is important to have a Content Backup strategy in place, so that if a disaster ever strikes your business, you can restore your content fully, quickly, and easily, and return to business as usual.
Action Steps
- Review your Content Documentation and Content Organization systems.
- Review the backup processes for all content stored on servers, applications, user devices, etc.
- Choose backup intervals to suit your business that will eliminate the risk of losing important content, files, or data should anything unexpected happen to your business, website, or digital presence.
- Automate as much of the backup process as you can, including uploading backup and export files of all your content to secure cloud storage solutions or external drives.
- Create and implement a content backup system for all of the above that includes making backups of your backups.
- Document all of the above in your Content Backup Strategy Document.
Resources
References
- The Best Cloud Backup Services For Business
- How To Create A Computer Backup System
- Best WordPress Backup Plugins
- How To Back Up WordPress Files Using Backup Wizard
- How To Back Up Your Backups For Bulletproof Protection
Next Steps
- Return to the Content Management Overview course module
- View the Course Outline
***
Image: Cloud Storage