Content Curation
 Content curation is the strategic process of discovering, gathering, and organizing relevant information from diverse sources to present it in a meaningful and cohesive manner.
Content curation is the strategic process of discovering, gathering, and organizing relevant information from diverse sources to present it in a meaningful and cohesive manner.
In this lesson, we provide a comprehensive overview of content curation and how to use content curation to manage your content production more effectively.
Understanding Content Curation
What is Content Curation?
Content curation is a method for creating valuable and engaging content by gathering, organizing, and presenting information from various sources in a meaningful and coherent way.
It goes beyond simple sharing and involves selecting, filtering, and adding value to content before presenting it to a specific audience.
Content curation involves sifting through the vast amount of information available online and selecting only the most relevant and valuable content for your audience.
Content curators act as information custodians, sifting through vast amounts of data to provide valuable insights, trends, or knowledge tailored to the interests and needs of their audience.
This practice not only helps build credibility but also fosters audience engagement by offering a curated experience that is both informative and targeted.
Why is Content Curation Important?
In today’s digital age, where information overload is a common issue, the ability to filter and organize content effectively has become more important than ever.
As a content curator, you play the role of a trusted resource for your audience, providing them with valuable and relevant information that helps them make informed decisions.
One of the key reasons why content curation is important is that it helps you build credibility and establish yourself as an authority in your niche. By consistently sharing high-quality content that resonates with your audience, you can position yourself as a go-to source for valuable insights and information. This, in turn, can help you attract a loyal following and build trust with your audience.
Content curation also helps you save time and resources. Instead of creating every piece of content from scratch, you can leverage existing content that is already available online. By curating content from reputable sources and adding your own unique perspective, you can provide value to your audience without having to invest a significant amount of time and effort.
Additionally, content curation can help you stay up-to-date with the latest trends and developments in your industry. By regularly curating and sharing relevant content, you can demonstrate your expertise and keep your audience informed about important news and updates.
Overall, content curation is a valuable skill that can help you build credibility, save time, and stay informed. By incorporating content curation into your content marketing strategy, you can provide value to your audience and establish yourself as a trusted authority in your niche.
The Benefits of Content Curation
The key benefits of content curation include:
- Save time and resources. Instead of creating all your content from scratch, you can leverage existing content from reputable sources and add your insights and commentary to enhance its value. This not only saves you time but also allows you to focus on other aspects of your business.
- Build authority in your niche. By curating content, you can provide your audience with high-quality, high-value information, build credibility and trust with your audience, and position yourself as an expert in your niche.
- Stay up-to-date with the latest trends and developments in your industry. By curating content from a variety of sources, you can keep your finger on the pulse of what’s happening in your niche and share timely and relevant information with your audience.
Types Of Curated Content
Content curation is a multifaceted practice, encompassing various approaches to present information cohesively. Diverse content curation strategies also offer flexibility in presenting information, catering to different preferences, and enhancing the overall user experience.
Types of curated content include:
1. Aggregation
- This involves consolidating the most pertinent content on a particular topic into a singular location.
- Widely adopted, this form serves as the foundation for many available content curation services.
2. Distillation
- Strips away extraneous details from a topic, distilling it down to its fundamental concept.
- Aims to simplify by highlighting key points essential for the audience’s understanding at a specific stage of the consumer journey.
3. Elevation
- Curators extrapolate general insights or trends from an extensive pool of content.
- This approach seeks to formulate hypotheses, ideas, or theories by identifying common threads in multiple content pieces.
4. Mashups
- Involves blending diverse content types to generate a fresh and original perspective.
- For instance, uncovering relevant content pieces within the same industry and connecting previously unnoticed correlations to present a new viewpoint.
5. Chronology
- Takes a historiographical approach to content curation, mapping content pieces along a storyline or timeline.
- Demonstrates the evolution of a concept or theory through a sequential arrangement of content, showcasing the contributions of individual pieces toward the endpoint.
Content Curation vs Content Repurposing
Content curation differs from content repurposing in the following ways:
1. Definition
- Content Curation: Involves sourcing, selecting, and sharing existing content from various outlets to provide value to your audience.
- Content Repurposing: Refers to updating or changing existing content into a different form or format to cater to a different audience or purpose.
2. Process
- Content Curation: Involves discovering and organizing relevant content created by others.
- Content Repurposing: Requires modifying or adapting existing content, often by presenting it in a new format or targeting a different audience.
3. Objective
- Content Curation: Aims to provide a curated collection of valuable information to your audience.
- Content Repurposing: Focuses on extending the life of content by adapting it for different platforms or audiences.
4. Creation vs. Adaptation
- Content Curation: Utilizes existing content without modification, focusing on selection and organization.
- Content Repurposing: Involves modifying, updating, or presenting existing content in a new way to serve a different purpose or audience.
Quick Guide To Content Curation
Below is a quick overview of the content curation process:
- Understand Content Curation: Content curation involves selecting and sharing high-quality digital content that resonates with your target audience.
- Identify Your Audience and Goals: Define your target audience and understand their interests and preferences to curate relevant content.
- Select Reliable Sources: Identify reputable sources that align with your niche or industry. Use social media management tools to find these.
- Use Content Curation Tools: Various content curation tools, including AI content research tools are available that can aid in finding curated content (see the Resources section below). Leverage these tools to streamline the curation process and discover valuable content.
- Organize and Share Content Categorize curated content to make it easily accessible. Share it on various platforms, adding your insights or commentary to provide value.
- Monitor Engagement: Track audience engagement using analytics tools. Adjust your curation strategy based on the content that resonates the most with your audience.
Example of Content Curation: Curating a Marketing Trends Roundup
- Define the Theme: Choose a theme, such as “Emerging Marketing Trends in 2024.”
- Select Your Sources: Utilize diverse sources like blogs, articles, and podcasts.
- Perform Comprehensive Search: Scour reputable platforms for up-to-date information. Explore examples from various industries, like those highlighted in this article.
- Add Value: Study the examples of curated content from Codecademy’s career paths page, Selzy’s email marketing resource, and SEO Notebook’s newsletter in this article.
- Organize and Attribute: Compile the curated content, giving credit to the original sources. Ensure proper attribution to maintain credibility.
- Add Visual Appeal: Enhance the presentation with visual elements. Incorporate statistics, infographics, and images.
- Provide Expert Insights: Include quotable quotes from industry experts found during the curation process.
- Publish and Share: Schedule the curated content in advance, following content curation best practices (see below)
Content Curation Best Practices
Effective content curation requires strategic thinking. The essential practices listed below wll help you develop a more strategic approach to curating content and enhance your content sharing:
1. Know Your Audience
- Align curated content with your audience’s needs and your brand perception.
- Before sharing, assess its relevance and value for your target customers.
- Reference your content strategy and buyer personas for guidance.
2. Credit Your Sources
- Always acknowledge and link to the original creators.
- Avoid presenting curated content as your own to maintain brand integrity.
- Tag creators using @ on platforms like X(Twitter) or Instagram.
- If sharing from multiple sources, provide a preview and link to the full piece, crediting all sources.
3. Add Your Insights
- Enhance shared content with your thoughts to provide additional value.
- A brief sentence or two introducing the share can be impactful.
- Consider creating an image with a relevant quote to captivate your audience.
4. Schedule in Advance
- Save time by scheduling curated and original content in advance.
- Use social media management tools like to plan, analyze performance, and identify content gaps.
- Ensure timely posting, avoiding last-minute rushes for campaign posts.
5. Offer a Diverse Content Mix:
- Maintain a balanced content calendar with various content types, including curated posts.
- Aim for a 40% original and 60% curated content ratio.
- Prioritize high-quality, actionable, and fully original content to attract and engage your audience.
Remember, content curation complements your original content and contributes to a well-rounded social media strategy.
Curating Content Effectively
Create a Content Curation Strategy
The first step to curating content effectively is to create a content curation strategy.
Creating a content curation strategy is essential for effectively curating content that resonates with your target audience.
By following a structured approach, you can ensure that the content you share is relevant, valuable, and engaging.
Let’s explore the key steps involved in creating a content curation strategy that works for you.
1. Define your goals: Before you start curating content, it’s important to clearly define your goals. Are you looking to increase brand awareness, drive website traffic, or establish thought leadership in your industry? By identifying your objectives, you can tailor your content curation strategy to achieve the desired outcomes.
2. Know your audience: Understanding your target audience is crucial for effective content curation. Take the time to research their interests, preferences, and pain points. This will help you curate content that is relevant and valuable to them, increasing engagement and building trust.
3. Identify your sources: Once you know your goals and audience, it’s time to identify sources for curating content. This may include industry publications, blogs, social media influencers, and news websites. By diversifying your sources, you can ensure a steady stream of high-quality content to share with your audience.
4. Curate with purpose: When curating content, it’s important to do so with purpose. Choose content that aligns with your brand values and supports your overall goals. Consider adding your own commentary or insights to provide additional value to your audience.
5. Measure and optimize: Finally, it’s crucial to measure the impact of your content curation efforts. Monitor key metrics such as engagement rates, website traffic, and lead generation to determine what is working and what can be improved. Use this data to optimize your content curation strategy for continued success.
By following these steps, you can create a content curation strategy that drives results and helps you connect with your audience on a deeper level. Remember, content curation is not just about sharing content – it’s about providing value and building relationships with your audience.
Find Quality Content
When curating content, use the process below to help you find quality content.
Identify Your Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is crucial in content curation. Knowing who you are creating content for will help you tailor your curation efforts to meet their needs and preferences. When you have a clear understanding of your target audience, you can curate content that resonates with them, engages them, and ultimately drives them to take action.
To identify your target audience, start by defining the demographics of your ideal audience. Consider factors such as age, gender, location, income level, education level, and interests. This will help you create a detailed profile of your target audience and guide your content curation efforts.
Next, consider the psychographics of your audience. Psychographics refer to the attitudes, beliefs, values, and behaviors of your target audience. Understanding these factors will help you create content that speaks to their motivations, desires, and pain points.
It is also important to conduct market research to gather insights into your target audience. Use surveys, interviews, and social media analytics to gather information about your audience’s preferences, habits, and challenges. This will help you create content that addresses their needs and interests.
Once you have identified your target audience, create buyer personas to represent different segments of your audience. These personas will help you visualize and humanize your audience, making it easier to create content that resonates with them.
By understanding who your audience is, what they care about, and what motivates them, you can create curated content that engages and inspires them. Take the time to research and define your target audience to ensure that your content curation efforts are effective and impactful.
Utilize Content Curation Tools
As a content curator, you are responsible for finding, organizing, and sharing relevant and valuable content with your audience. However, with the sheer volume of information available online, it can be overwhelming to manually curate content.
This is where content curation tools come into play. These tools can help streamline the content curation process, making it easier and more efficient for you to find and share high-quality content. By utilizing these tools, you can save time, stay organized, and ensure that you are consistently providing your audience with valuable content.
For popular content curation tools that you can use, go here: Content Research Tools
When choosing a content curation tool, it’s important to consider your specific needs and goals. Look for a tool that aligns with your content curation strategy and workflow. Additionally, make sure the tool is user-friendly and offers the features you need to effectively curate content for your audience.
By incorporating content curation tools into your workflow, you can take your content curation efforts to the next level. These tools can help you stay organized, save time, and ensure that you are consistently providing your audience with valuable and relevant content.
Understand Copyright Laws
Understanding Copyright Laws is essential for anyone engaging in content curation. Copyright laws are in place to protect the intellectual property of creators, ensuring that they receive recognition and compensation for their work. As a content curator, it is crucial to be aware of these laws to avoid infringement and legal issues.
One key aspect of copyright laws to understand is that original works are automatically copyrighted upon creation. This means that any content you come across, whether it be written, visual, or audio, is protected by copyright unless stated otherwise. It is important to respect the rights of creators and obtain permission before using their work in your curated content.
Fair use is a concept within copyright laws that allows for the limited use of copyrighted material without permission from the creator. However, there are specific guidelines that must be followed to qualify for fair use, such as using the material for educational purposes, commentary, or parody. It is important to familiarize yourself with these guidelines to ensure that your curated content falls within the boundaries of fair use.
When curating content, always credit the original creator and provide a link back to the source. This not only shows respect for the creator but also helps to build credibility and trust with your audience. Additionally, consider using content that is licensed under Creative Commons, which allows for more lenient use of copyrighted material with proper attribution.
By understanding and following copyright laws, you can create curated content that is both ethical and legal. Stay informed on the latest developments in copyright laws to ensure that your content curation practices are up to date and compliant.
Organize Your Curated Content
Now that you have gathered a wealth of valuable content through your curation efforts, it’s time to focus on organizing it effectively. Organizing your curated content is crucial for maximizing its impact and making it easily accessible for your audience.
One of the first steps in organizing your curated content is to categorize it based on themes or topics. This will help you create a clear structure for your curated content and make it easier for your audience to navigate through the information.
You can use tools like a content management system or spreadsheets to create a system for organizing your curated content.
Next, consider the format in which you want to present your curated content. Do you want to create blog posts, infographics, or videos? By determining the format in advance, you can tailor your organization approach to fit the needs of that specific format.
It’s also important to establish a schedule for when you will release your curated content. Consistency is key in content curation, so make sure you have a plan in place for when and how often you will share your curated content with your audience.
Additionally, consider creating a tagging system for your curated content. Tags can help you easily search and retrieve specific pieces of content when needed. This can save you time and make it simpler to repurpose your curated content in the future.
By organizing your curated content effectively, you can enhance its value and make it more impactful for your audience. Take the time to establish a clear structure, determine the format, create a schedule, and implement a tagging system to streamline your content curation process.
Add Value to Curated Content
Adding value to curated content is essential in order to make it unique and valuable to your audience. Simply collecting and sharing content from various sources is not enough – you need to add your own insights, opinions, and expertise to make it stand out.
One way to add value to curated content is to provide context. Explain why you chose to include a particular piece of content, how it relates to your overall message, and what your audience can learn from it. This helps your audience understand the significance of the content and how it fits into the bigger picture.
Another way to add value is to offer your own commentary. Share your thoughts, opinions, and personal experiences related to the curated content. This not only helps to establish your expertise in the niche but also adds a personal touch that can resonate with your audience on a deeper level.
Additionally, you can add value by organizing and presenting curated content in a way that is easy to digest and navigate. This could involve categorizing content by topic, creating summaries or key takeaways, or even creating visual aids such as infographics or charts to enhance understanding.
Ultimately, adding value to curated content is about creating a unique and valuable experience for your audience. By providing context, sharing your insights, and organizing content effectively, you can set yourself apart as a trusted source of curated content in your niche. Remember, the goal is not just to share content, but to add value and make a meaningful impact on your audience.
Promoting Your Curated Content
Share Curated Content on Social Media
Sharing curated content on social media is a crucial step in maximizing the reach and impact of your curated collection.
When sharing curated content on social media, it is important to tailor your posts to the specific platform you are using. Each social media platform has its own unique audience and posting style, so make sure to customize your content accordingly. For example, on X(Twitter), you will need to keep your posts short and concise, while on Instagram, you can use visually appealing images to capture your audience’s attention.
Another important aspect of sharing curated content on social media is to add your own commentary or insights to the post. This not only adds value to the content you are sharing but also helps to establish your expertise in the field. By sharing your thoughts on the curated content, you can engage your audience and spark discussions around the topic.
Additionally, make sure to schedule your posts at optimal times to reach the largest audience possible. Use social media management tools to plan your posts in advance and ensure that they are posted at times when your followers are most active.
Overall, sharing curated content on social media is a powerful way to showcase your expertise, engage with your audience, and drive traffic to your curated collection. By following these best practices, you can maximize the impact of your curated content and build a strong online presence in the world of content curation.
Engage with Your Audience
Engaging with your audience is a crucial aspect of content curation. It is not enough to simply find and share interesting content; you must also interact with your audience to build a loyal following and create meaningful connections. In this subchapter, we will discuss some strategies for engaging with your audience effectively.
One of the most important ways to engage with your audience is to listen to their feedback. Pay attention to the comments and messages you receive on your curated content, and take the time to respond thoughtfully. This shows your audience that you value their input and are interested in what they have to say. It also helps you to build relationships with your followers and create a sense of community around your curated content.
Another way to engage with your audience is to ask for their input. Encourage your followers to share their opinions, thoughts, and ideas on the content you curate. This can be done through polls, surveys, or simply by asking open-ended questions in your posts. By involving your audience in the curation process, you show them that their opinions matter and help to make them feel like they are a part of your content curation journey.
Finally, don’t forget to show your personality and be authentic in your interactions with your audience. People are more likely to engage with content that feels genuine and relatable, so don’t be afraid to let your personality shine through in your curated content. Share personal stories, jokes, or insights that show your audience who you are and what you stand for.
By engaging with your audience in a meaningful way, you can build a loyal following, create a sense of community, and ultimately grow your influence as a content curator. So don’t be afraid to reach out, listen, and connect with your audience – they will appreciate it, and your curated content will be all the better for it.
Measure the Success of Your Curated Content
Measuring the success of your curated content is crucial in determining the effectiveness of your curation efforts. By analyzing key metrics, you can gain valuable insights into what is resonating with your audience and what can be improved upon. Here are some ways to measure the success of your curated content:
1. Engagement Metrics: One of the most important indicators of success is the level of engagement your curated content is receiving. This includes metrics such as likes, shares, comments, and click-through rates. By tracking these metrics, you can see which pieces of content are generating the most interest and adjust your curation strategy accordingly.
2. Traffic and Conversion Rates: Another key metric to track is the amount of traffic your curated content is driving to your website or landing pages. By monitoring your conversion rates, you can see how effective your curated content is at converting leads into customers. This can help you determine which types of content are most effective at driving conversions and focus on creating more of that content.
3. Brand Awareness: Measuring the impact of your curated content on brand awareness is also important. This can be done through metrics such as social media mentions, brand sentiment, and search engine rankings. By monitoring these metrics, you can see how your curated content is helping to increase brand visibility and reputation.
4. Feedback and Surveys: Gathering feedback from your audience through surveys or direct communication can provide valuable insights into the success of your curated content. By asking for feedback on the relevance, quality, and usefulness of your curated content, you can make informed decisions on how to improve your curation strategy.
Overall, by monitoring these key metrics and gathering feedback from your audience, you can measure the success of your curated content and make data-driven decisions to improve your curation efforts. Remember, success is not just about quantity but also about the quality and relevance of your curated content.
Overcoming Common Content Curation Challenges
Dealing with Information Overload
We are constantly bombarded with information from all directions. Whether it’s social media updates, news articles, or emails, it can be overwhelming to try and keep up with everything. This is where the importance of content curation comes into play.
As someone who is interested in content curation, you understand the value of sorting through the vast amount of information available online to find the most relevant and valuable content for your audience. However, even for seasoned curators, dealing with information overload can be a challenge.
One of the key strategies for managing information overload is to establish clear goals and priorities for your content curation efforts. By defining what you hope to achieve through your curation, you can focus your efforts on finding the content that aligns with these goals.
Another important aspect of dealing with information overload is to establish a routine for consuming and curating content. This could involve setting aside specific times each day to review new content, or using tools and technologies to help streamline the curation process.
It’s also important to be selective about the sources of information you rely on for your curation. By focusing on high-quality, reputable sources, you can ensure that the content you share with your audience is accurate and valuable.
Ultimately, dealing with information overload is an ongoing process that requires constant refinement and adjustment. By staying organized, setting clear goals, and being selective about your sources, you can effectively manage the deluge of information and create curated content that truly resonates with your audience.
Maintaining Consistency in Content Curation
Consistency is key when it comes to content curation. It’s not just about finding great content to share with your audience; it’s also about ensuring that you are consistently providing value and engaging your audience on a regular basis.
One of the most important things you can do to maintain consistency in your content curation is to create a content calendar. This will help you plan out your content in advance, ensuring that you are consistently posting and sharing content with your audience. A content calendar can also help you stay organized and avoid last-minute scrambling to find content to share.
Another tip for maintaining consistency in your content curation is to establish a posting schedule. Whether you are posting daily, weekly, or monthly, it’s important to stick to a consistent schedule so that your audience knows when to expect new content from you. This will help you build trust and credibility with your audience.
Additionally, it’s important to stay up to date with the latest trends and news in your industry. By staying informed, you can ensure that you are curating relevant and timely content for your audience. This will help you stay ahead of the curve and position yourself as a thought leader in your niche.
Overall, maintaining consistency in your content curation efforts is essential for building a loyal and engaged audience. By creating a content calendar, establishing a posting schedule, and staying informed about industry trends, you can ensure that you are consistently providing value to your audience and growing your online presence.
Avoiding Plagiarism in Curated Content
When it comes to content curation, one of the most important things to keep in mind is avoiding plagiarism. Plagiarism is the act of using someone else’s work or ideas without giving them proper credit. Not only is plagiarism unethical, but it can also have serious consequences for you and your reputation as a content curator.
To avoid plagiarism in your curated content, there are a few key things to keep in mind. First and foremost, always make sure to properly cite your sources. This means including a link to the original content or providing a clear attribution to the original author. By giving credit where credit is due, you can avoid any accusations of plagiarism.
Another important way to avoid plagiarism in curated content is to put the information you gather into your own words. Even if you are summarizing or quoting from a source, it is important to rephrase the information in a way that is unique to you. This not only helps to avoid plagiarism but also adds value to your curated content by providing your own perspective and insights.
Lastly, it is important to always double-check your work for any instances of potential plagiarism. There are many online tools available that can help you check for plagiarism in your content before you publish it. By taking the time to review and revise your curated content, you can ensure that it is original and free from any plagiarism.
Avoiding plagiarism in curated content is essential for maintaining your credibility as a content curator. By properly citing your sources, putting information into your own words, and double-checking for plagiarism, you can create high-quality curated content that is both informative and ethical.
Advanced Content Curation Techniques
Collaborate with Other Content Curators
Collaborating with other content curators can be a game-changer in your content curation journey. By working together with like-minded individuals who share your passion for discovering and sharing valuable content, you can amplify your impact and reach a wider audience.
One of the key benefits of collaborating with other content curators is the opportunity to tap into their unique perspectives and expertise. Each curator brings their own set of skills and knowledge to the table, which can help you discover new content sources, angles, and ideas that you may not have come across on your own.
By pooling your resources and sharing insights, you can create a more comprehensive and diverse range of curated content that will resonate with a larger audience.
Collaborating with other content curators also allows you to leverage each other’s networks and followers. By cross-promoting each other’s curated content, you can introduce your work to new audiences and gain exposure to potential followers who may be interested in your content.
This can help you grow your own following and establish yourself as a trusted source of curated content within your niche.
To start collaborating with other content curators, reach out to individuals or groups who share your interests and values. Establishing a mutually beneficial partnership based on trust and respect is key to a successful collaboration.
You can co-create curated content, host joint events or webinars, or simply share each other’s work on social media platforms.
Remember, collaboration is not about competition but about building a supportive community of content curators who can learn from each other and grow together. By working together, you can elevate your content curation skills and make a bigger impact in your niche.
Automate Your Content Curation Process with AI
Content curation is the process of finding, organizing, and sharing relevant content with your audience. However, manually curating content can be time-consuming and overwhelming.
This is where artificial intelligence (AI) comes in to revolutionize the way you curate content.
AI-powered content curation can automate and enhance processes related to managing vast amounts of digital content, ensuring efficient organization and delivery of relevant content to the right audiences.
How AI Transforms Content Curation
AI algorithms revolutionize content curation by analyzing extensive data from sources like social media, news, blogs, and customer feedback. They identify patterns and preferences, allowing for the automation of content sorting and personalization. This reduces manual effort and enhances user experience by delivering tailored content.
AI tools can help you automate the content curation process, making it more efficient and effective. These tools use algorithms to sift through vast amounts of information, helping you discover the most relevant and valuable content for your audience.
Many AI tools also cite their sources when compiling content from your prompts, effectively doing most of the content curation “heavy-lifting” for you.
Benefits of AI in Content Curation
- Efficiency and Accuracy: AI algorithms can process and interpret large volumes of data quickly, saving time and minimizing human error.
- Personalization: One benefit of using AI for content curation is its ability to provide personalized content recommendations based on user preferences and behaviors. AI algorithms can analyze data such as user interactions, browsing history, and social media activity to recommend content that is tailored to each individual’s interests. This personalized approach can help you understand user behavior and preferences, engage your audience more effectively and increase overall user satisfaction.
- Resource Optimization: Automating repetitive tasks allows human curators to focus on strategic activities and boost their productivity.
- Competitive Advantage: AI can help you stay ahead of the curve by monitoring trends and predicting future content opportunities. By analyzing patterns and data from various sources, AI tools can identify emerging topics and opportunities for content creation. This proactive approach can give your business a competitive edge in your industry and help to position it as a thought leader.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges:
- Bias and Ethical Concerns: AI algorithms can perpetuate biases present in their training data. Ensuring diverse and unbiased datasets is crucial.
- Balancing AI and Human Expertise: Human curators add unique insights and creativity. A balanced approach combining AI and human judgment will ensure high-quality content curation.
Best Practices for Implementing AI in Content Curation
- Select Suitable AI Tools: Evaluate AI tools based on organizational goals, content types, and audience needs.
- Train and Refine Algorithms: Continuous monitoring and refining of AI algorithms based on user feedback ensures optimal performance.
- Integrate Human Expertise: Leverage both AI’s analytical capabilities and human curators’ creativity for enhanced content curation.
Future Trends in AI and Content Curation
- Enhanced Personalization: Advanced AI algorithms will offer more granular content personalization, improving user engagement.
- Predictive Analytics: AI-driven predictive analytics will enable proactive content curation, anticipating user needs and preferences.
AI-powered content curation offers significant advantages in terms of efficiency, personalization, and resource optimization. By automating your content curation process and leveraging AI, you can streamline your workflow, better engage your audience, improve the quality of your content, and save time and resources.
However, addressing ethical concerns and balancing AI with human expertise is essential. By adopting best practices, your business can leverage AI to create meaningful and engaging content experiences.
Personalize Your Curated Content
As you continue on your content curation journey, it’s important to consider how you can personalize the content you share with your audience.
Personalization is a key aspect of creating a unique and engaging experience for your followers. By tailoring your curated content to fit the interests and preferences of your audience, you can increase engagement, build trust, and establish yourself as a thought leader in your niche.
One way to personalize your curated content is to understand your audience’s preferences and interests. Take the time to research and analyze the demographics, behaviors, and preferences of your target audience. Use this information to curate content that resonates with their interests and provides value to them. By understanding what your audience is looking for, you can create curated content that is relevant and engaging.
Another way to personalize your curated content is to add your own unique perspective and voice to the content you share. Don’t just share content for the sake of sharing it; instead, add your own insights, opinions, and commentary to make the content more valuable and interesting to your audience. By adding your personal touch to the curated content you share, you can establish yourself as an authority in your niche and build a stronger connection with your audience.
Remember, personalizing your curated content doesn’t mean creating content from scratch. It’s about finding the right balance between sharing valuable content from others and adding your own unique touch to make it more engaging and relevant to your audience. By personalizing your curated content, you can create a more memorable and impactful content experience for your followers.
Tip: Many email marketing tools allow you to personalize your content and target segmented audiences.
Creating Your Ultimate Content Curation Plan
Set Goals for Your Content Curation
Setting goals for your content curation is essential to ensure that you are curating content that aligns with your objectives. Without clear goals in mind, your content curation efforts may lack direction and purpose.
The first step in setting goals for your content curation is to define what you hope to achieve through your curation efforts. Are you looking to increase website traffic, engage with your audience, or establish yourself as an authority in your niche? By clearly defining your goals, you can tailor your content curation strategy to support these objectives.
Once you have identified your goals, it is important to establish specific and measurable targets. For example, if your goal is to increase website traffic, you may set a target of increasing your monthly page views by a certain percentage. Setting specific targets will help you track your progress and assess the effectiveness of your content curation efforts.
It is also important to set realistic goals that are achievable within a reasonable timeframe. Setting overly ambitious goals can lead to frustration and demotivation if they are not met. Start with smaller, achievable goals and gradually increase the difficulty as you gain confidence in your content curation skills.
Finally, regularly review and adjust your goals as needed. The content curation landscape is constantly evolving, so it is important to be flexible and adapt your goals to reflect changes in your industry or audience preferences. By setting clear, achievable goals for your content curation efforts, you can ensure that your curated content is purposeful and effective in achieving your objectives.
Establish a Content Curation Schedule
Creating a consistent and effective content curation schedule is essential for successfully curating content that resonates with your audience. By establishing a schedule, you can ensure that you are consistently providing valuable and relevant content to your followers.
Here are some tips to help you create a content curation schedule that works for you:
1. Identify your audience: Before you can create a content curation schedule, you need to have a clear understanding of who your audience is and what type of content they are interested in. Take the time to research your target audience and identify their preferences, interests, and needs.
2. Set goals: Determine what you want to achieve with your content curation efforts. Are you looking to increase engagement, drive traffic to your website, or establish thought leadership in your niche? Setting clear goals will help you create a schedule that aligns with your objectives.
3. Choose the right tools: There are many content curation tools available that can help you streamline the process of finding and sharing content. Research and choose the tools that work best for you and your specific needs. (See the Resources section below for links to tools).
4. Create a content calendar: Once you have identified your audience, set goals, and chosen your tools, it’s time to create a content calendar. A content calendar will help you plan and organize your content curation efforts, ensuring that you are consistently sharing valuable content with your audience.
5. Be consistent: Consistency is key when it comes to content curation. Make sure that you stick to your content calendar and regularly share content with your audience. Consistency will help you build trust with your followers and establish yourself as a reliable source of information in your niche.
Establishing a content curation schedule takes time and effort, but the benefits are well worth it. By following these tips, you can create a schedule that works for you and helps you achieve your content curation goals.
Evaluate and Adjust Your Content Curation Plan
Evaluating and adjusting your content curation plan is a crucial step in ensuring the success of your content strategy.
Firstly, you should review the performance metrics of your curated content. Analyze metrics such as engagement rates, click-through rates, and social shares to determine which types of content are resonating with your audience. This will help you understand what is working well and what needs improvement.
Next, consider the relevance of the content you are curating. Are you providing valuable, up-to-date information that is aligned with the interests of your target audience? It is essential to regularly assess the relevance of your curated content to ensure that it continues to meet the needs and preferences of your audience.
Another important aspect to evaluate is the diversity of your content sources. Are you sourcing content from a wide range of reputable sources, or are you relying too heavily on a few sources? Diversifying your sources can help you provide a more balanced and comprehensive view of the topics you are curating.
Finally, don’t forget to regularly review and adjust your content curation schedule. Are you posting content at the right times and frequencies to maximize engagement? Experiment with different posting schedules and monitor the results to find the optimal posting times for your audience.
By regularly evaluating and adjusting your content curation plan based on these key factors, you can ensure that your curated content remains relevant, engaging, and valuable to your audience.
Remember, content curation is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring and optimization to achieve the best results.
Content Curation – FAQs
Here are frequently asked questions about content curation:
What is content curation?
Content curation is the process of collecting, contextualizing, and sharing information that is relevant to a specific audience or topic. It involves sorting through large amounts of content and presenting the best pieces in a meaningful and organized way.
How does content curation differ from content creation?
Content curation involves gathering and sharing existing content from external sources, whereas content creation is about producing new content. Curation is used to enhance a content strategy by adding value through perspective and context.
Why is content curation important?
Content curation helps establish authority and expertise, keeps followers engaged with regular updates, and supplements original content without the additional resources needed for content creation. It can also help target content to specific audiences effectively.
What are the key considerations for effective content curation?
Key considerations include understanding your audience’s needs, selecting high-quality and relevant content, adding unique insights, and maintaining ethical standards such as proper attribution and respect for intellectual property.
What are some best practices for content curation?
Best practices include using reliable sources, curating content that aligns with your brand’s values, regularly updating curated collections, and using tools to streamline the curation process. Engaging with the content by adding personal insights or additional context is also crucial.
What tools can help with content curation?
There are several tools available for content curation, including Feedly for RSS feeds, Pocket for saving articles, and social media tools (e.g. Hootsuite) for scheduling and sharing curated content. These tools help curators save time and organize content efficiently.
How can content curation benefit learning and development?
In learning and development, content curation can provide learners with a variety of perspectives and expert insights, help keep learning materials up-to-date, and aid in building a continuous learning culture by making a wide range of resources accessible.
What is AI content curation?
AI content curation involves using artificial intelligence to gather, organize, and present relevant digital content from various sources. It helps to streamline the process of delivering high-quality content to target audiences.
How does AI content curation work?
AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and select content based on relevance, quality, and user preferences. These systems often use machine learning to improve their curation over time.
What are the benefits of AI content curation?
Benefits include increased efficiency, personalized content delivery, improved audience engagement, reduced manual effort, and the ability to process large volumes of information quickly.
What are the disadvantages of AI content curation?
Disadvantages can include high initial setup costs, potential biases in algorithms, dependency on accurate data inputs, and the need for ongoing maintenance and updates.
What are the pros and cons of AI content curation?
- Pros: Efficiency, personalization, scalability, and enhanced engagement.
- Cons: Cost, complexity, potential biases, and maintenance needs.
What trends are shaping AI content curation?
Key trends include the integration of natural language processing (NLP), increased use of predictive analytics, enhanced user personalization, and the growing importance of ethical AI practices.
How can businesses leverage AI content curation effectively?
Businesses can leverage AI content curation by using it to deliver targeted content, enhance customer experiences, optimize content marketing strategies, and streamline internal knowledge management.
What should be considered when choosing an AI content curation tool?
Considerations include the tool’s scalability, integration capabilities, accuracy, ease of use, cost, and the level of support and training provided by the vendor.
What is the difference between AI content generation and AI content curation?
AI content generation involves creating new content using AI, while AI content curation focuses on selecting and organizing existing content from various sources.
How does AI content curation improve audience engagement?
By delivering personalized and relevant content, AI content curation helps keep the audience engaged and interested, leading to higher levels of interaction and satisfaction.
Resources
- Content Research Tools
- AI Content Research Tools
- Social Media Tools
- WordPress Content Plugins
- Content Curation Tools For WordPress Users
References
The content in the above lesson was curated from various sources, including the following:
- How To Curate Content: A Beginner’s Guide To Content Curation
- The Complete Guide To Content Curation
- Content Curation Guide
- Ultimate Guide To Content Curation
- Developing An Effective Content Curation Strategy
- How to Create a Curated Blog Post [+ Free Blog Post Templates]
- Great Content Curation Examples
- Extend The Life Of Your Content Marketing With Curation And Repurposing
***
Image: Resumes


 Creating content for your business is an essential aspect of digital marketing.
Creating content for your business is an essential aspect of digital marketing.
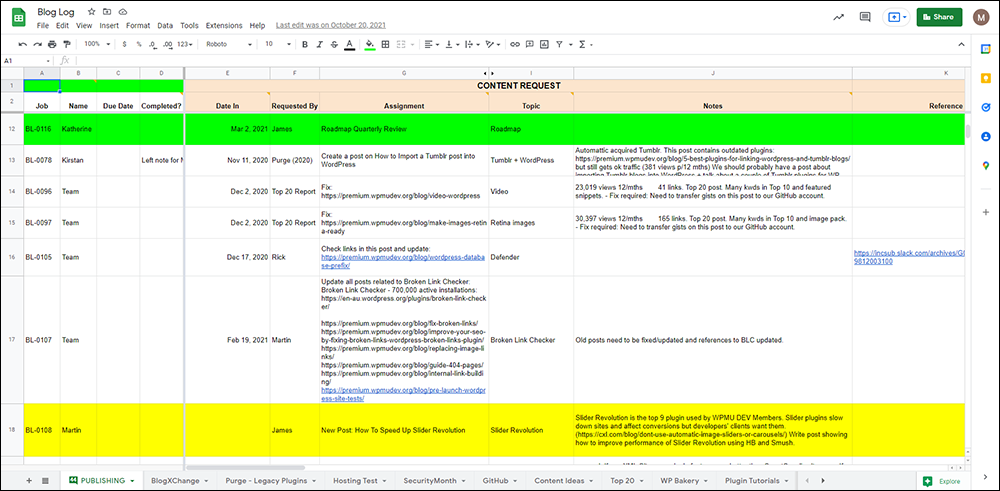
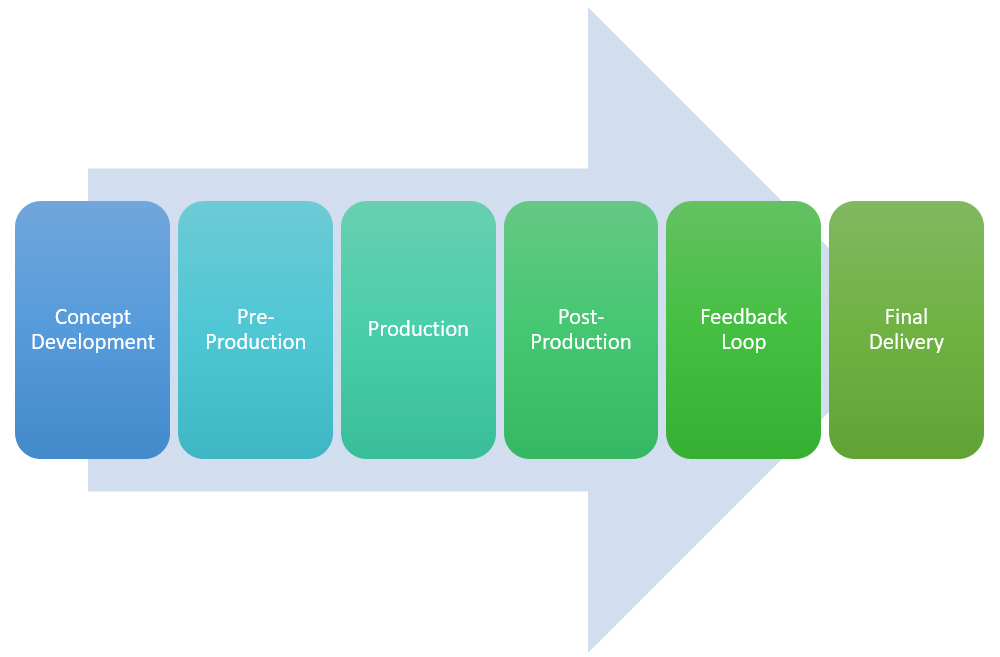
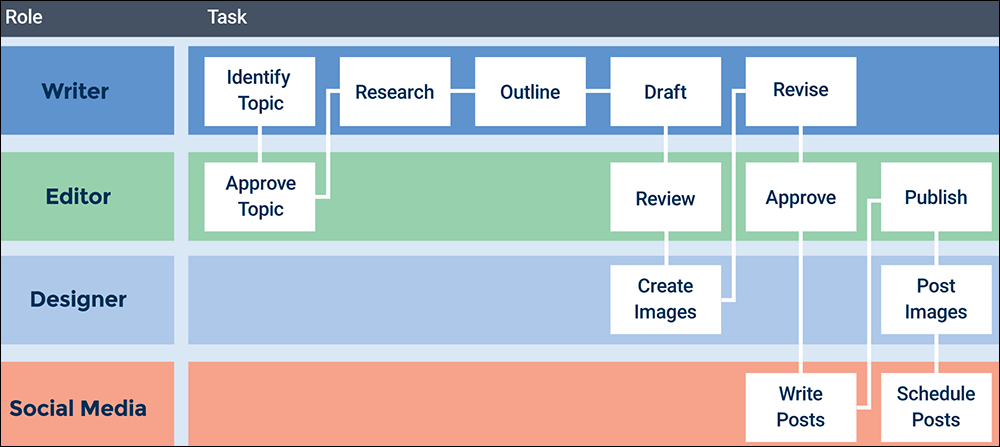
 Keeping content projects on track and on time requires organizing and managing processes with specific tasks, done in a specific order, by team members assigned to specific roles.
Keeping content projects on track and on time requires organizing and managing processes with specific tasks, done in a specific order, by team members assigned to specific roles.




 Documenting your
Documenting your 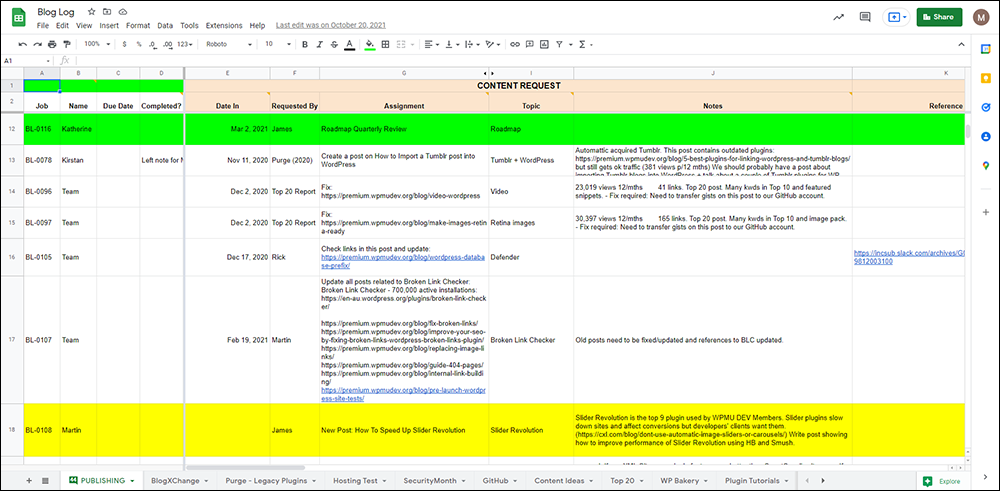











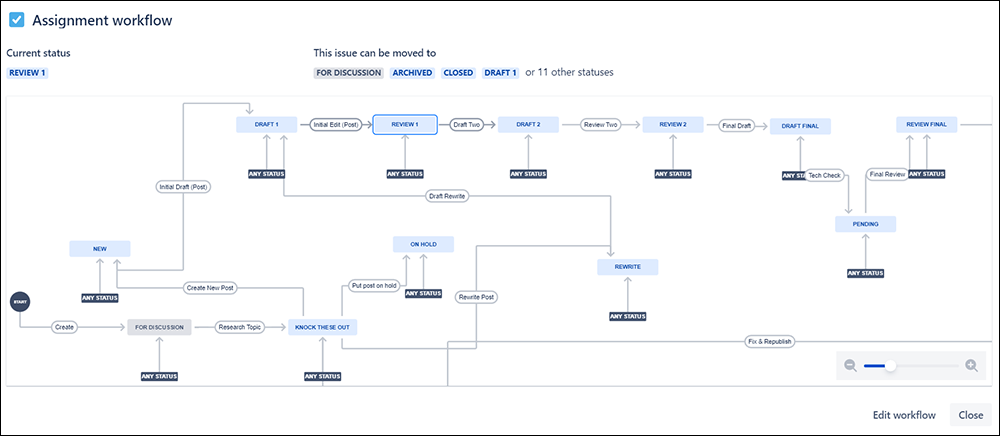


















 Content production management involves overseeing the creation, distribution, and strategic implementation of content to engage and inform audiences effectively.
Content production management involves overseeing the creation, distribution, and strategic implementation of content to engage and inform audiences effectively.













 Creating high-quality content on a regular basis involves a significant investment of time and resources.
Creating high-quality content on a regular basis involves a significant investment of time and resources.

 The type of content your business or organization decides to create will depend on its
The type of content your business or organization decides to create will depend on its 












 An efficient
An efficient