Content Organization
Learn how to keep your content organized for a better user experience, improved SEO, and easier content management.
 Keeping content on your website organized is an important area of content management.
Keeping content on your website organized is an important area of content management.
In this tutorial, we’ll cover the following:
- Why Keeping Your Web Content Organized Is Important
- First Things First – Planning Your Website For Better Content Organization
- Built-In Organization Features Of The WordPress CMS
- Making Content Management Easier With Plugins
Why Keeping Your Content Organized Is Important
“Order is Heaven’s First Law”
Having a manageable website is not only “heavenly” but keeping your website’s content organized also provides your business with the following benefits:
- Save Time – Having a “smart” way to organize your content can save a lot of time adding, managing, and updating content on your site. In this lesson, we’ll show you smart methods and tools that let you easily manage content published on multiple areas of your website from one central location.
- Improve User Experience – A website that users can quickly and easily navigate to find the content they are looking for creates a better user experience. It helps them to engage with more of your content, keeps them longer on your site, encourages repeat visits, and increases the likelihood that they will tell others about your site.
- Boost SEO – Having a well-organized content structure is also part of good SEO practices and helps search engines like Google to better understand and index your content, which can rank your content higher and deliver more organic traffic.
First Things First – Planning Your Website For Better Content Organization
Good content organization starts at the website planning phase, before your website is built
Ideally, your website was or will be built using a Content Management System (CMS). While there are various content management systems available to choose from, the platform that we recommend using is WordPress.
This website (ContentManagementCourse.com), for example, runs on WordPress.
As you will see from the examples used in this lesson, using a CMS platform like WordPress provides a massive advantage when it comes to keeping your content organized, because a CMS is designed to make managing content easier.
What If My Website Doesn’t Run On WordPress?
If your existing website does not run on WordPress, you can ask a web developer to set up a WordPress blog on your domain.
For example, if your website runs on the domain https://yourcompanysite.com, you can set up a blog on a subdirectory of your domain, like https://yourcompanysite.com/blog.
WordPress is highly customizable, so you can easily match your blog’s look and feel with your website’s design and layout to create a seamless web presence.
You can then use your blog for content marketing activities and link your blog content to your existing website’s pages. For example, if your main website is an eCommerce store, you can promote your products on your blog and send visitors to your store’s product pages to purchase.
![]()
Check this tutorial if you don’t know whether your website runs on WordPress or not: How To Tell If It’s A WordPress Site
Built-In Organization Features Of The WordPress CMS
From here on, we’ll assume that your website or blog is powered by WordPress.
WordPress offers many powerful built-in features to help you manage and keep your content organized. Let’s go through some of these features:
Organize Your Web Content with Categories
Post categories help keep your website and your content organized, improve SEO to boost your search engine rankings, and make it easier for site visitors to find what they are looking for.
- For a detailed step-by-step tutorial on how to set up and use categories in your posts, see this tutorial: Using WordPress Post Categories
- Categories and tags (see below) are normally assigned to WordPress Posts, not Pages, so this tutorial will focus on posts (if you are unsure about the difference, see this tutorial on WordPress Posts Vs WordPress Pages).
Plan Your Categories
Although WordPress is flexible enough to let you add new categories on the fly, it’s more difficult to keep your content organized as you add more content if you haven’t planned out your categories (and subcategories) properly beforehand.
If you need help with website or content planning, see these website planning tutorials and this guide on keeping your website manageable and organized.
Improve WordPress SEO With Post Categories
Here is the simplest and easiest way to improve WordPress SEO with post categories:
- Set up permalinks to include categories, and
- Install and configure an SEO plugin.
Include Categories In Your Permalinks
Permalinks are a feature of WordPress that lets you set up search-engine-friendly URLs (for more details, see this tutorial on how to set up and use WordPress permalinks).
When configuring your permalinks, make sure that post categories are included in the URLs.
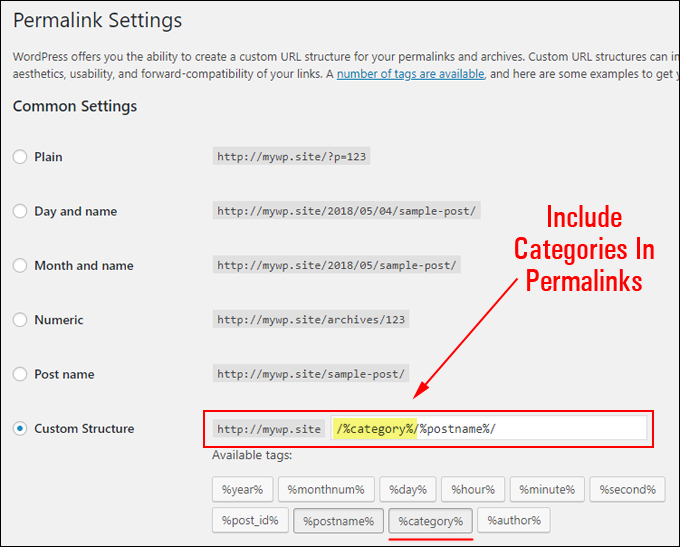
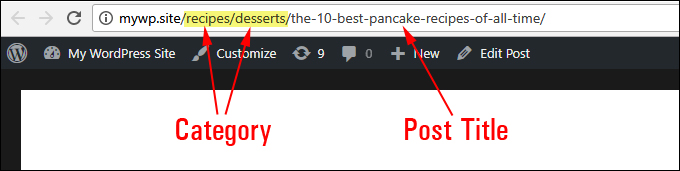
This will automatically display search-engine-friendly URLs with your categories (and subcategories) and in your post title keywords.
Use An SEO Plugin
Installing an SEO plugin helps to improve your content SEO and optimize your post categories, category archive pages, etc.
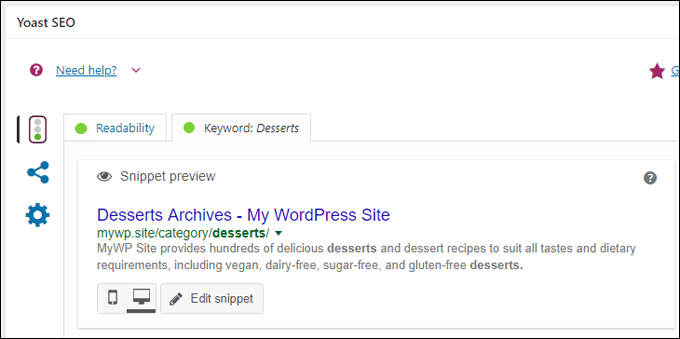
Adding category descriptions will also display on some WordPress themes and can also help to boost your content’s SEO.
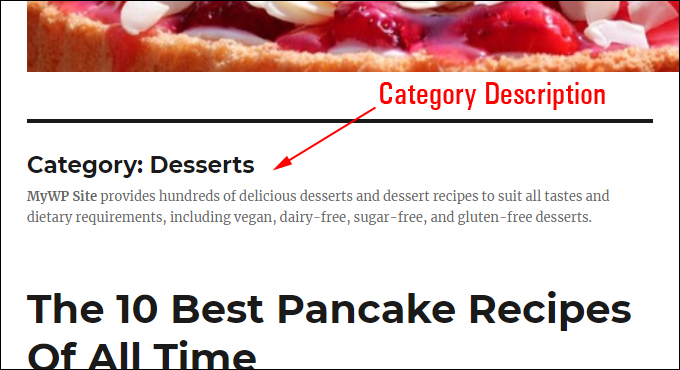
Once your permalinks and SEO plugin settings are configured for your post categories, WordPress will then automatically start delivering you the SEO benefits of using search engine-friendly URLs, such as better content indexing.
Improve User Navigation With Post Categories
Post categories can be used to improve user navigation on your WordPress site in different pages and different sections of your site, such as site maps, menus, sidebar widgets, archive pages, and even your RSS feeds.
For example, here are some of the ways you can help users navigate your content using post categories:
Categories Widget
Adding a categories widget to your sidebar lets users find related content assigned to a category.
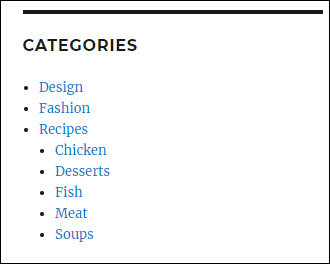
When users click on a category link on the categories widget, they are taken to a category archive page.
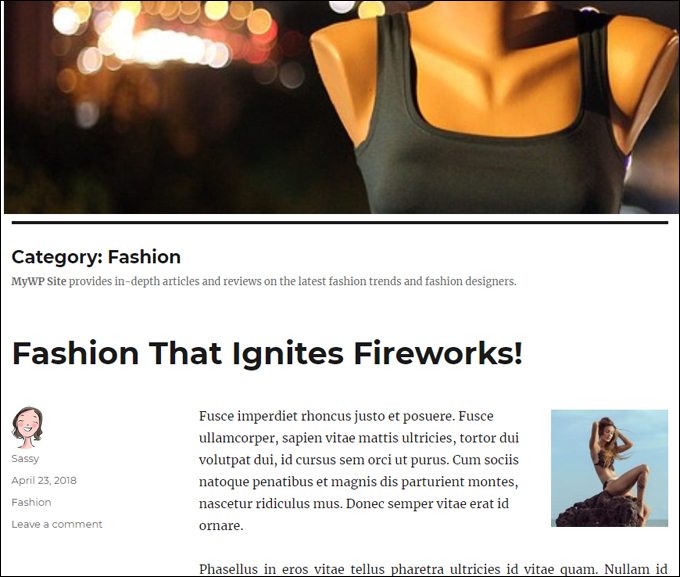
Category Archive Pages
Category archive pages group together all the posts assigned to a category.
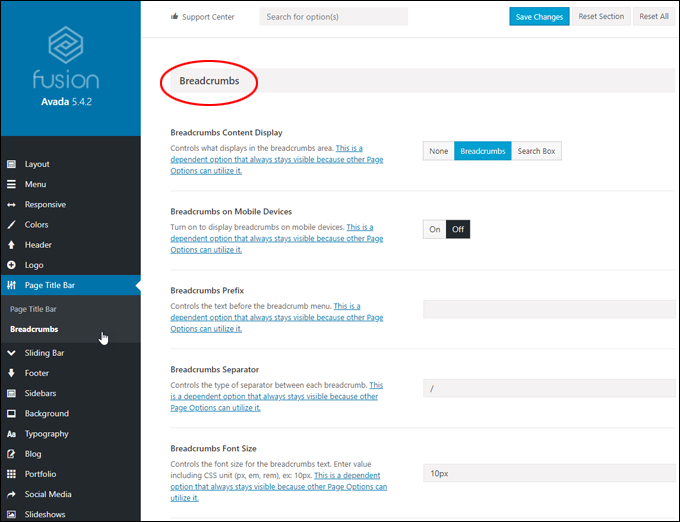
Breadcrumb Navigation Links
Breadcrumb navigation links display on some WordPress themes. Displaying categories in breadcrumb navigation links helps to improve user navigation and SEO.
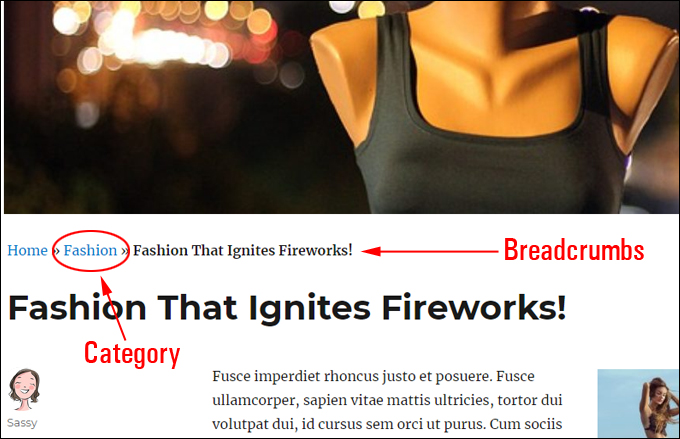
Clicking on the category section of the breadcrumb link will take users to the category archive page.
You can display breadcrumbs on your pages using SEO plugins or choose a WordPress theme that supports breadcrumb navigation links, like the Avada theme.
Organize Your Content With Tags
Using tags is another effective way to keep your web content organized.
Tags are like categories but where categories tend to be a broader method of organizing your content, tags are more granular.
For example, your post may be filed under a single category but referenced using several tags.
Tag clouds are often used in blog navigation areas (like the sidebar) to help users find what they are looking for.
So, if a user clicks on a tag in a tag cloud…
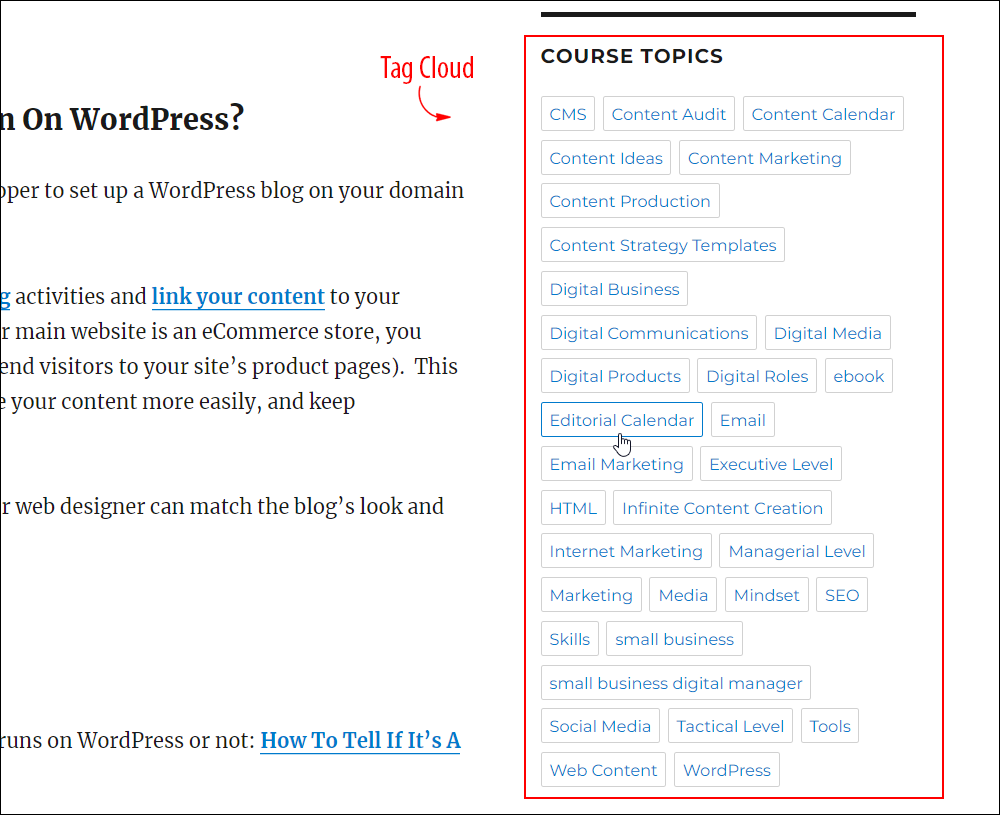
They are presented with a “tag archive” page listing all the posts filed using that tag…
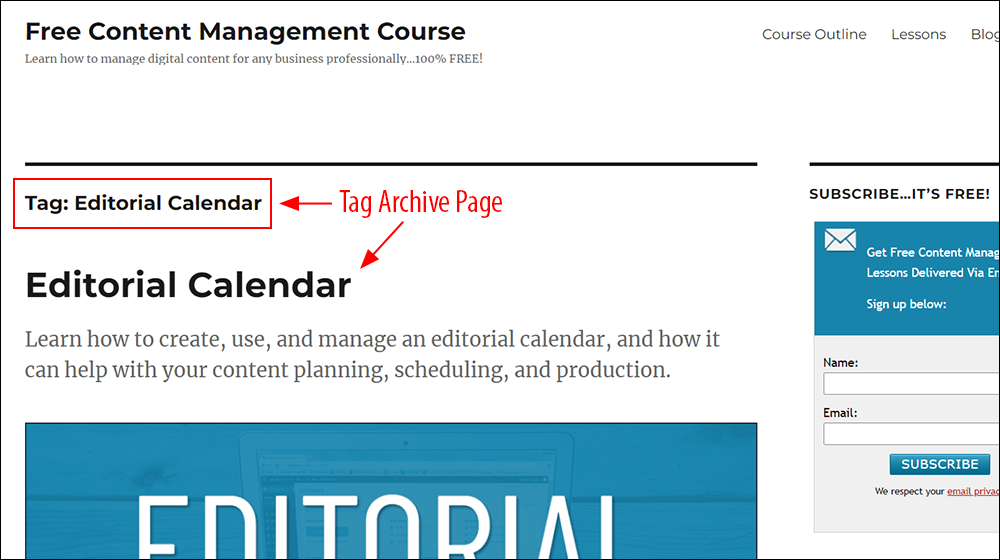
Learn more about using tags in WordPress.
Organize Your Content With Menus
Another useful way to organize your web content for site visitors is using menus.
WordPress comes with a powerful built-in feature that lets you easily create different custom menus using drag and drop and add these to different locations on your site (e.g. header, footer, sidebar).
For example, you can create and display your main menu on the header section containing only links to important sections of your website.

And create different menus with other useful links for your site’s sidebar or footer areas, like the course outline we have added to the right-hand side of this website.
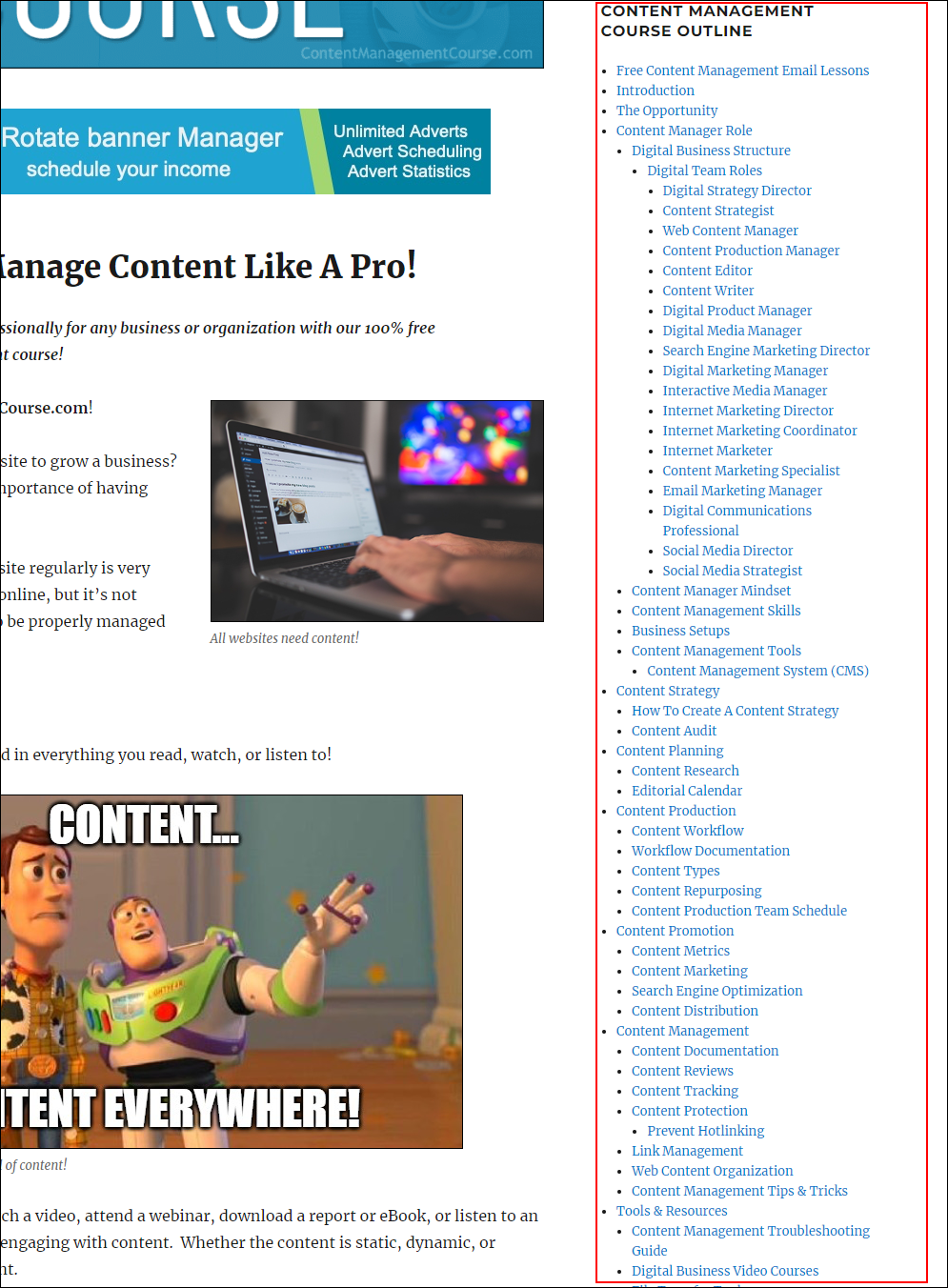
The WordPress menu feature allows you to build an unlimited number of menus with nested submenus and combine links from posts, pages, categories, external URLs, and more, all using drag and drop.
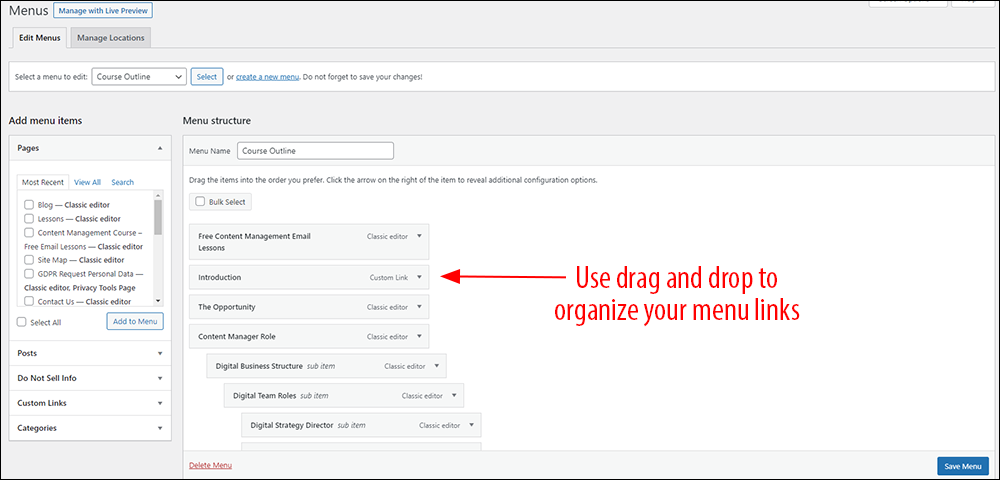
Menus built with WordPress also update dynamically, so if you change the title of your post, the text displayed on your menu link will also be automatically updated (you can also override this by giving the link a custom name).
Use the menu feature of WordPress to keep the content on your site’s navigation areas organized and improve your site’s user experience.
Learn more about using menus in WordPress.
Organize Your Content With Widgets
Widgets are another powerful organizing feature of WordPress. They allow you to move entire blocks of content around your site without touching code using drag and drop.
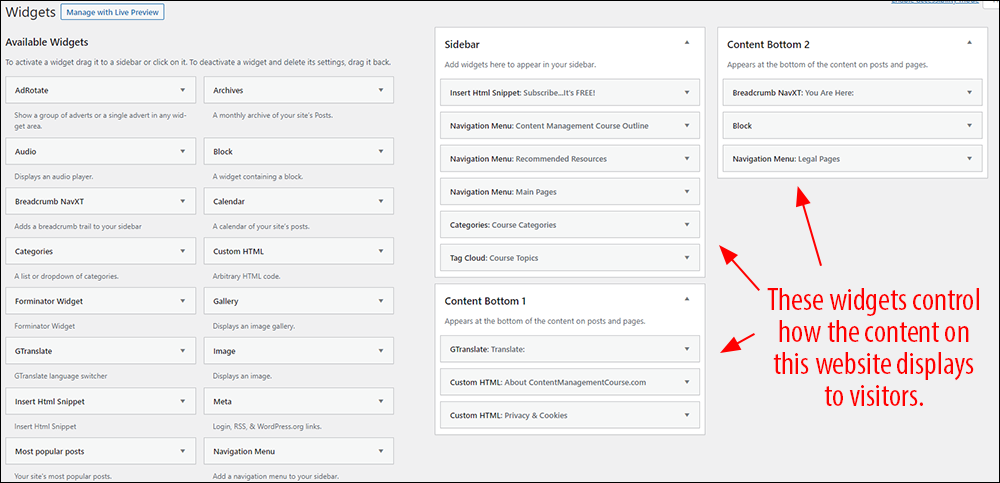
Note: WordPress eventually plans to phase widgets out because the platform has been evolving to use a new technology called “blocks” (see next section below).
Learn more about using widgets in WordPress.
Organize Your Content With Blocks
WordPress 5.0 introduced a new technology called “blocks” at the end of 2018.
As the name suggests, blocks let you insert content and functionality wherever you like on your site by adding and rearranging different types of blocks.
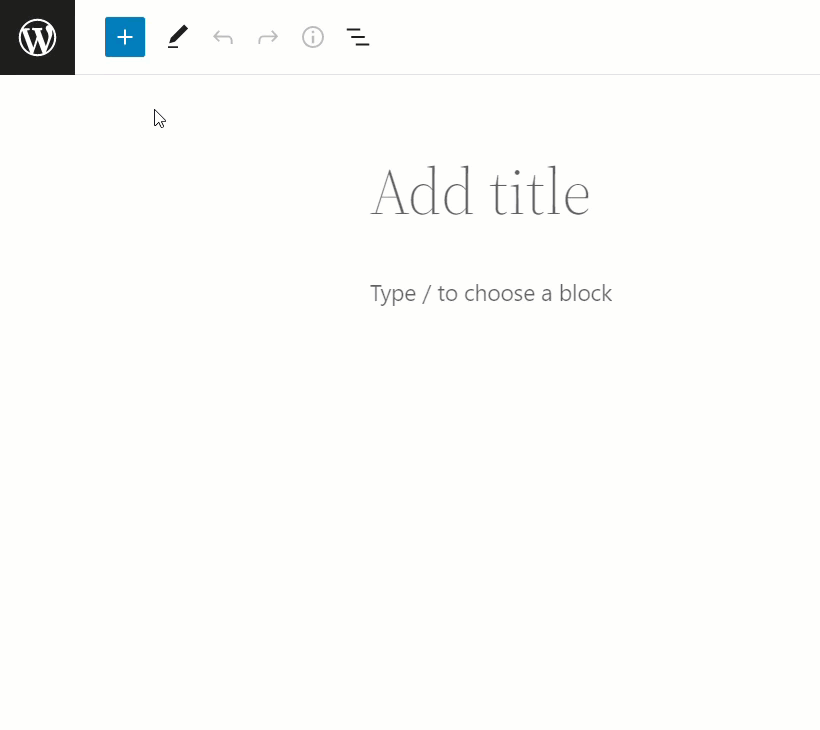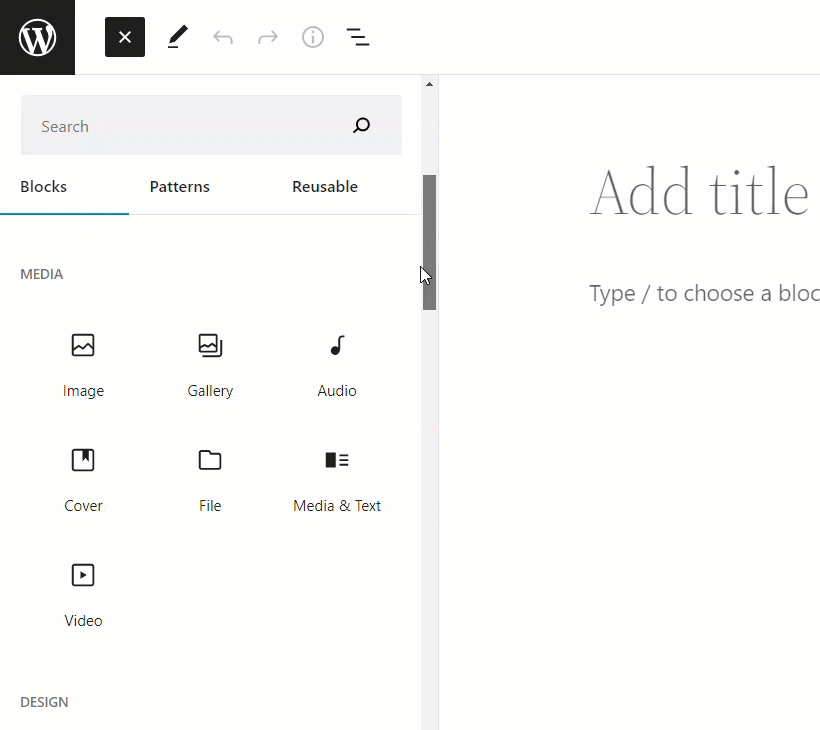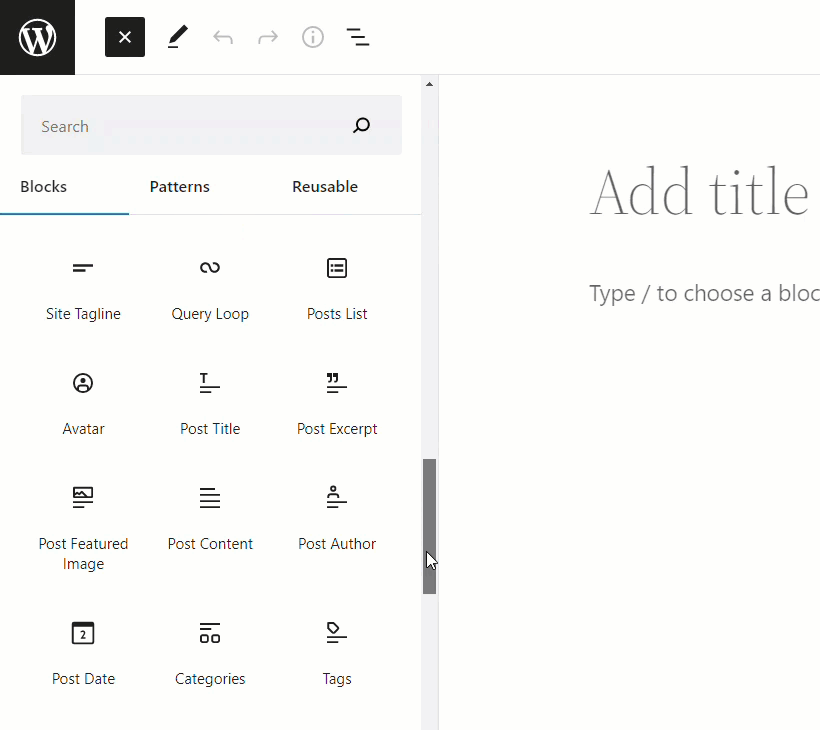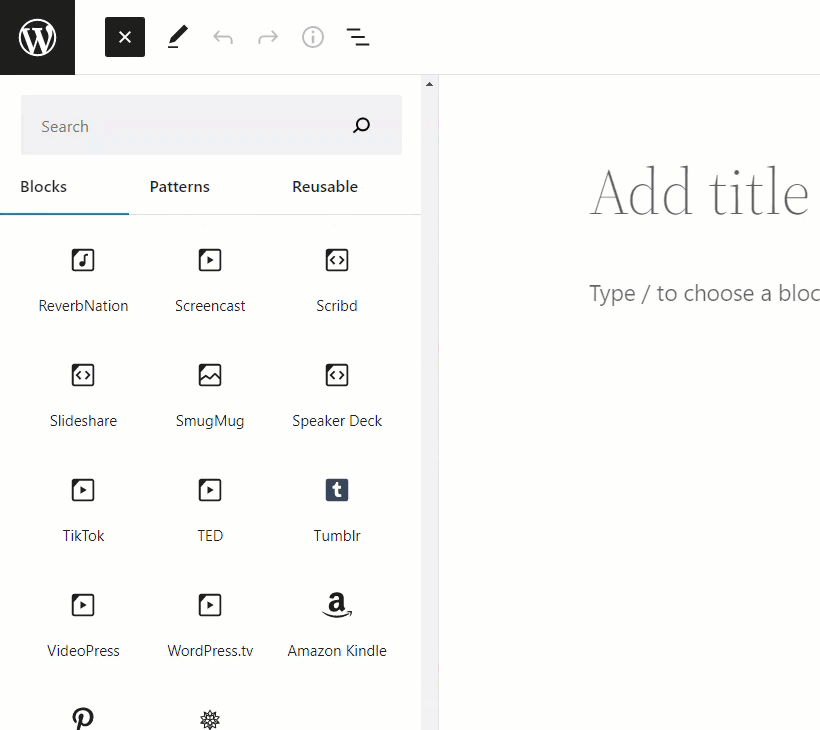
With content-related blocks (e.g. text block, image block, video block, etc.) you can manage the content from within the block…
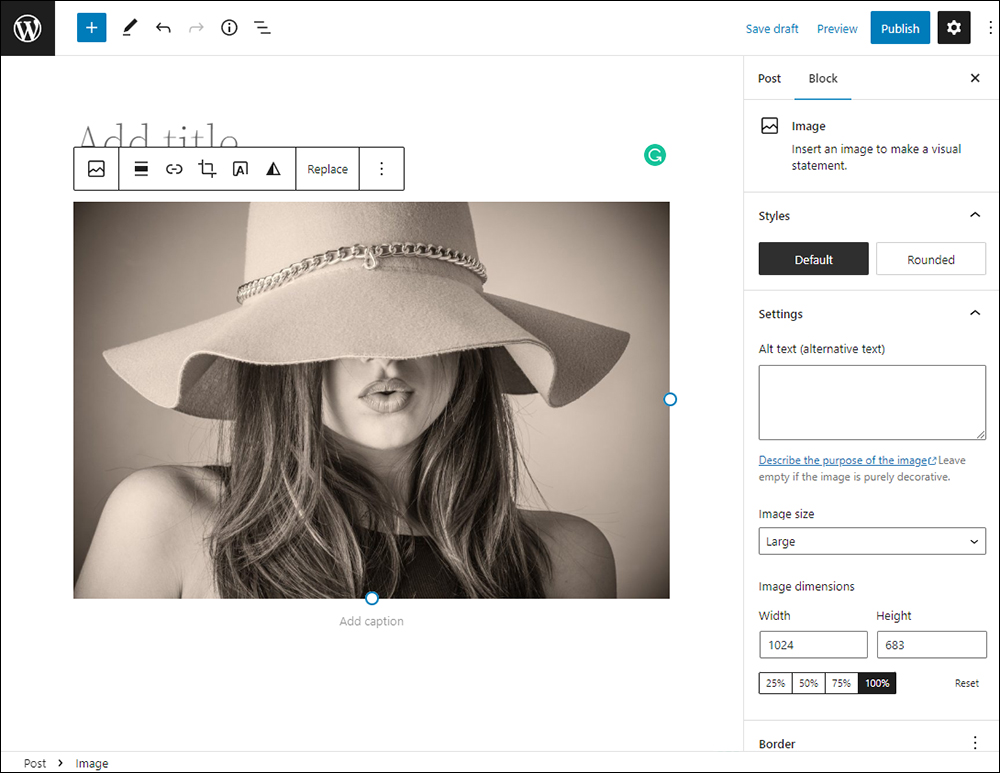
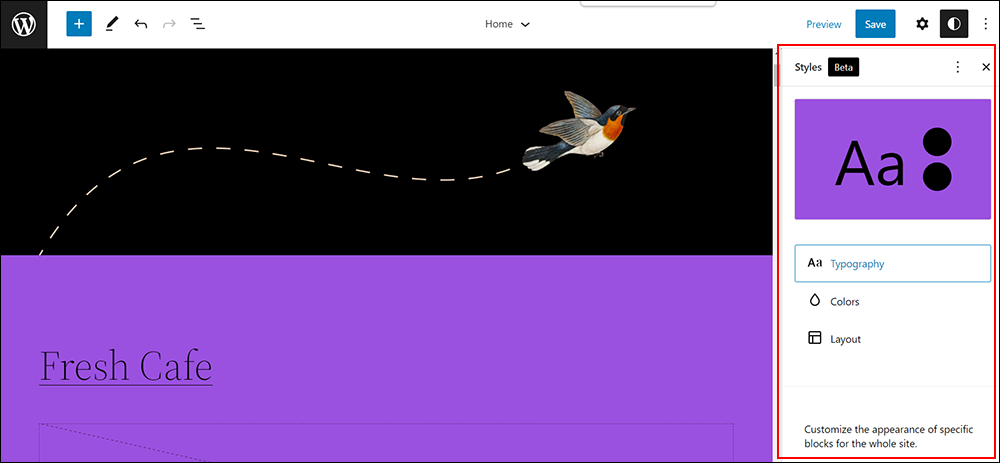
You can also turn repeatable content into reusable blocks, group different blocks together to form patterns, and apply global styles to control aspects of your content like typography, colors, and layout across your entire site.
Learn more about using blocks in WordPress.
Organize Your Content With Plugins
Plugins extend the functionality of your website.
WordPress offers a free plugin directory that includes thousands of useful plugins.
For example, earlier in this lesson, we mentioned that categories and tags are normally assigned only to WordPress posts, not WordPress pages. If you want to add categories (and tags) to your WordPress pages, however, you can easily do this by installing a plugin like Pages With Category And Tag.
We provide lists of some of the best WordPress plugins available for managing content on your website in the lessons below:
WordPress CMS Plugins
WordPress Content Plugins

WordPress SEO Plugins
WordPress Media Plugins
WordPress Engagement Plugins
![]()
The above section is another example of how plugins can be used to help keep your content organized. We created this list of tutorials using the plugin described below.
Content Views

Content Views is a free WordPress plugin that lets you organize, filter, sort, and display content from selected posts, pages, or custom post types using different views and layouts (e.g. grid, table, list) and insert these views anywhere on your site using a shortcode.
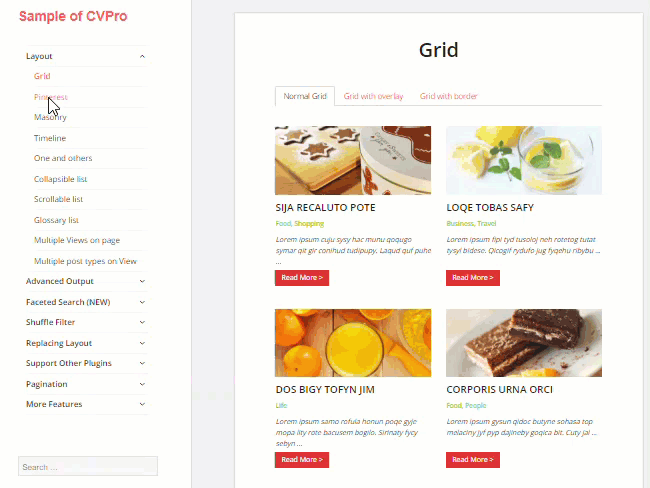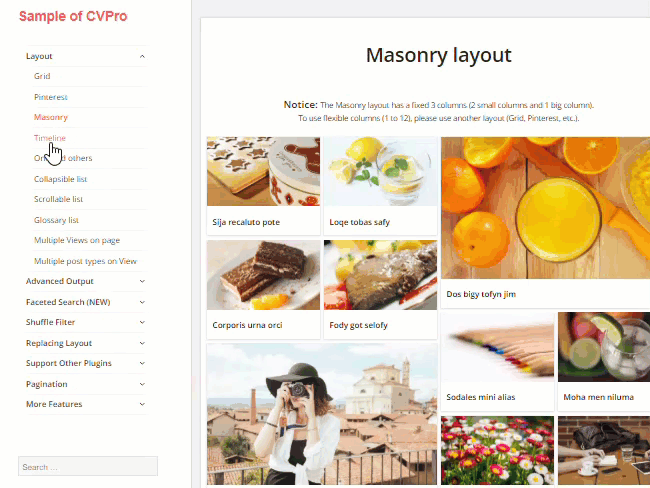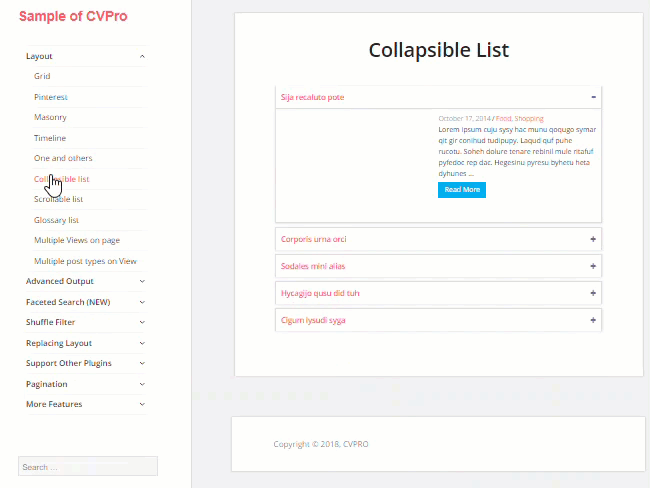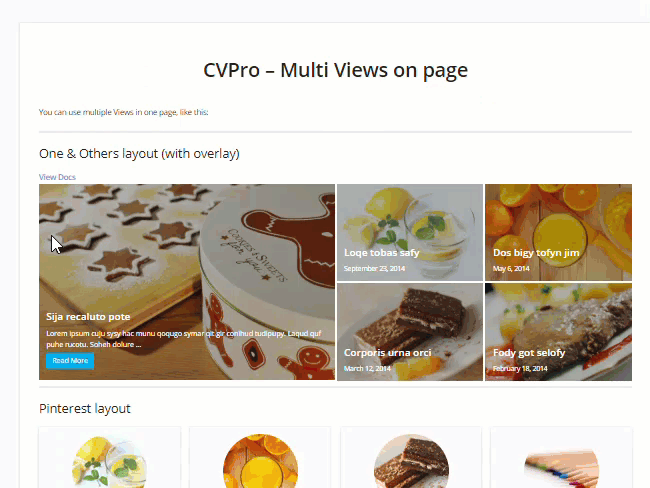
The plugin is very easy to use and lets you create unlimited custom views and layouts without touching code. It also gives you complete control over how your content is grouped and displayed to visitors. Views are 100% mobile responsive and the plugin is optimized to help improve SEO.
The free version of the plugin provides 3 basic layouts (Grid, Collapsible list, Scrollable list).
The premium version (Content Views Pro) provides the basic layouts and a lot more, including many advanced features.
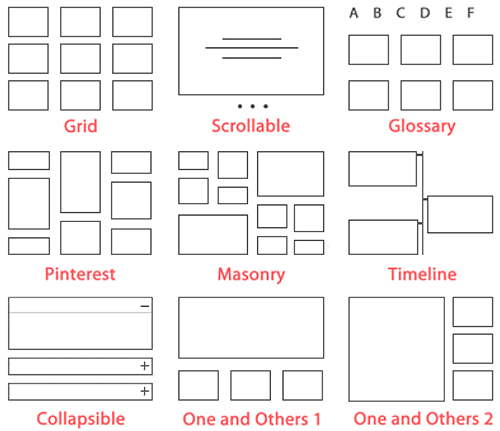
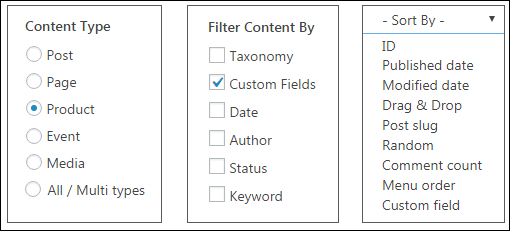
Although this tutorial focuses mostly on post categories, with Content Views Pro installed you can create different views using posts, pages, and custom post types and filter these using a combination of different criteria including post categories, tags, publish date, post author, keywords, and custom fields.
You can also sort and organize your content using a range of methods, including post or page IDs, published date, modified date, drag & drop, post slug, comment count, menu order, custom fields, and even random sort (content displays in random order every time the page is refreshed).
You then create Views by selecting different options in the view-building form …
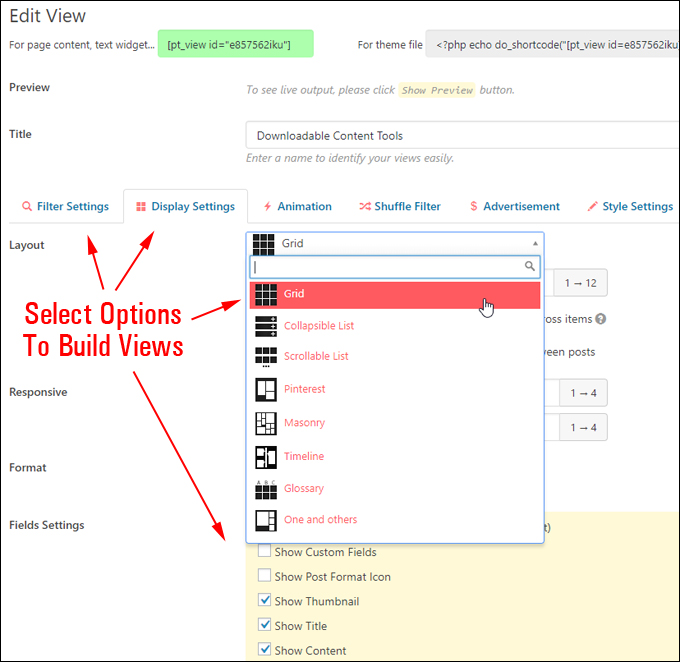
You can live preview your content as you build or edit your views.
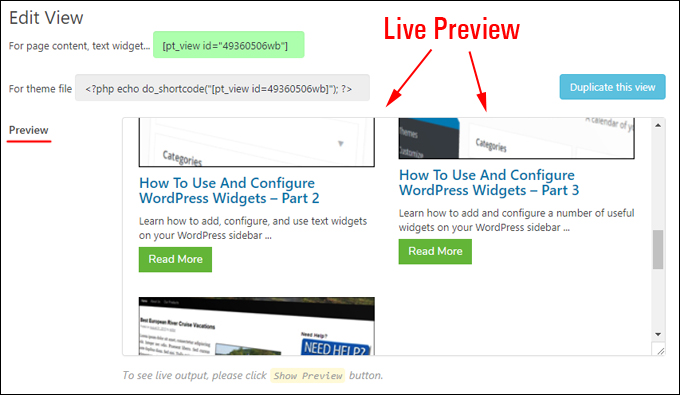
After creating and saving your views, the plugin generates a shortcode that you can use to insert into your posts, pages, widgets, etc.
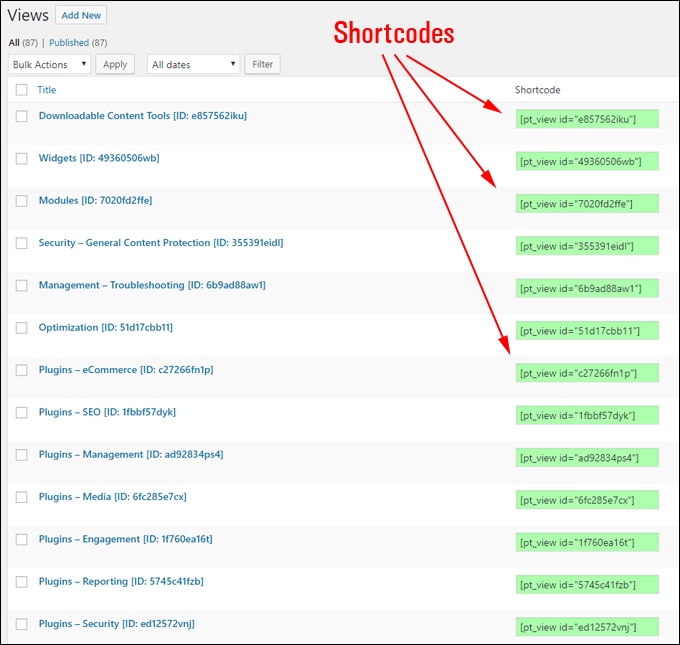
To add a view anywhere on your site, simply add the view’s shortcode to your content, wherever you want it to display. Republish your page and the plugin will automatically populate your content views with the content you have assigned to it.
You can control the content on all content views from the plugin’s settings area. As you add new content to your site, the plugin will automatically add it to the right content views, depending on your configuration settings.
![]()
You can also use the Content Views plugin to add an attractive site map for your visitors with post thumbnail images and descriptions. To learn more, go here:
For more details about using the plugin, check out the video below, and visit the FREE version plugin page here, or check out the Content Views Pro website for a full list of features, comprehensive demo site, premium plugin pricing, FAQ section, and more.
(Overview of WordPress Content Views)
Let’s show you now how you can use this plugin to keep your content organized in post lists, site indexes, course outlines, site maps, etc., and improve the layout of your content for your site visitors.
Tutorial: Organize Your Content Layout With The Content Views Plugin
We use Content Views Pro on all of our sites to organize, filter, and display content in our tutorial sections and lessons using mostly post categories and subcategories. We use the premium version of the plugin as it allows us to mix different content types (e.g. posts and pages) and use other advanced features when creating content display views.
Here is an overview of the process using this site as a real-life example:
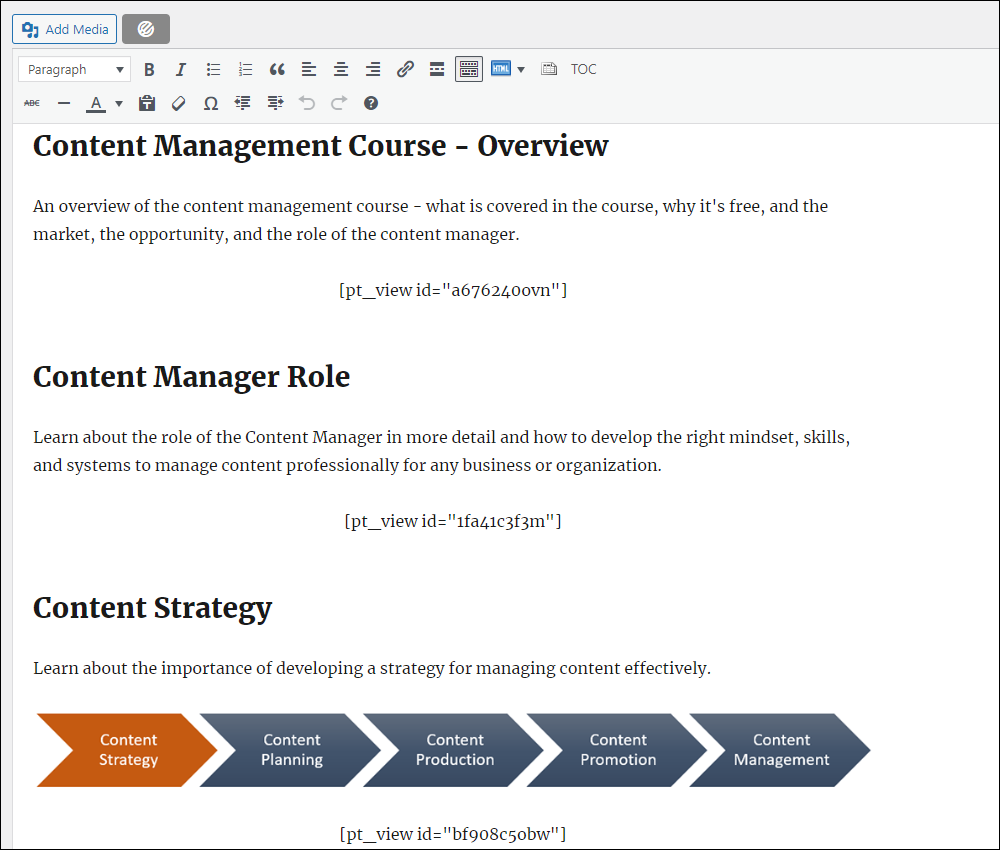
For our content management course, we wanted to create different training modules and submodules, so the course plan included lessons grouped into categories for each training module and subcategories for submodules.
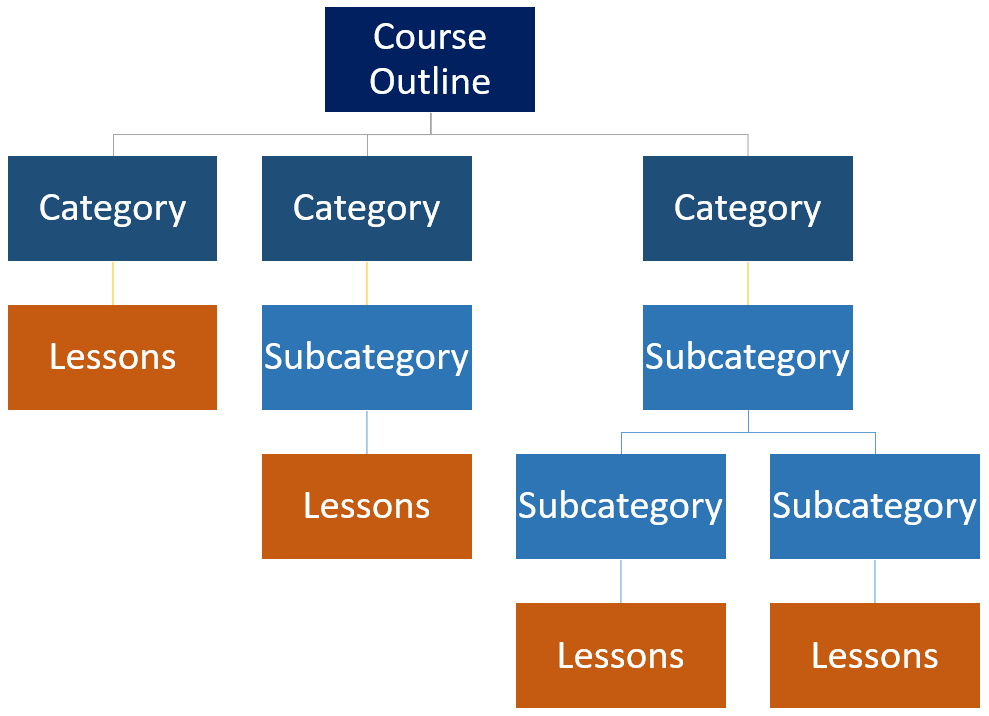
In the website planning phase, we decided to build this course using WordPress.
In the content planning phase, we worked out what the course would cover, and created an outline of the course’s training modules, content, and lessons using a spreadsheet. We also assigned categories and subcategories to each module.
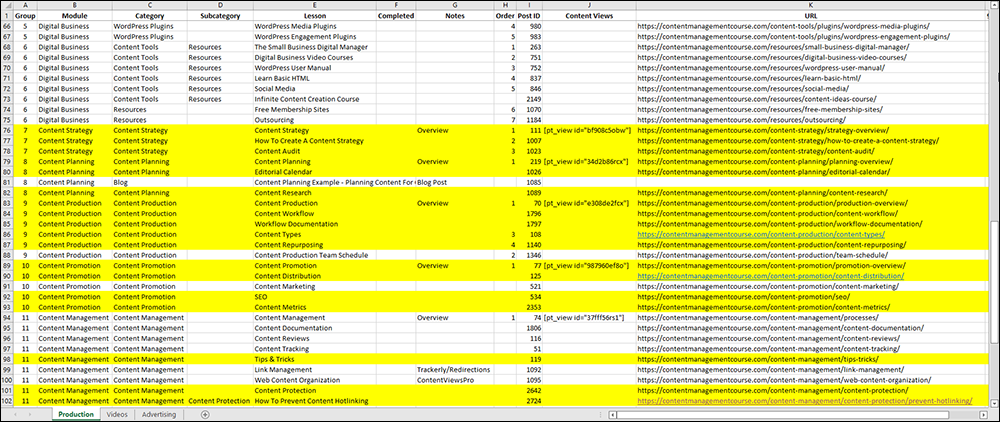
We used this spreadsheet to make sure that we were assigning the right categories and subcategories to all posts, tutorials, lessons, etc. as we created the content.
![]()
Keeping an accurate record of all the content we create for this site on a spreadsheet with additional related information like categories, post titles, post IDs, which content view it is assigned to, post URLs, etc. effectively helps to make other content management processes like running a content audit and scheduling content production easier.
***
After working out the course’s training modules and assigning a category to each module, we then added the categories and subcategories to our site in the Post Categories section of our WordPress admin area.
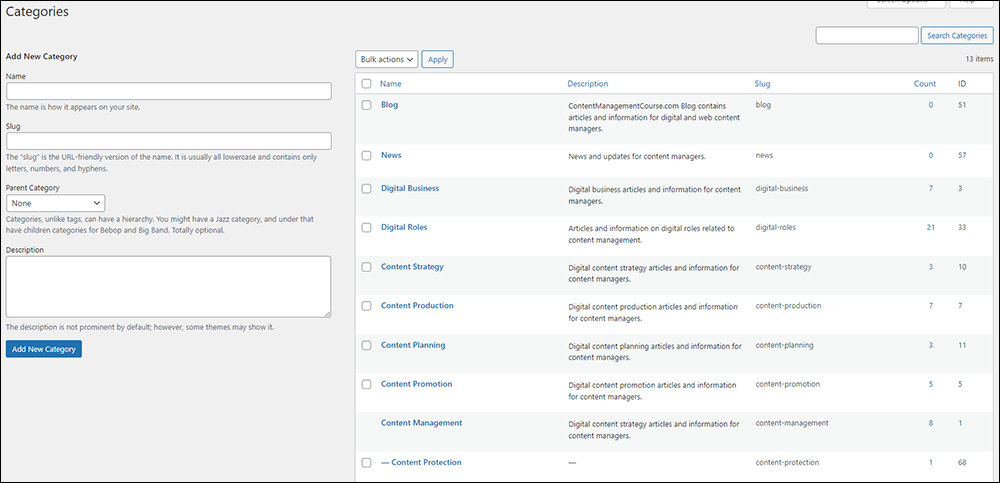
After installing the Content Views plugin, we then created all the site’s content lists (i.e. content views).
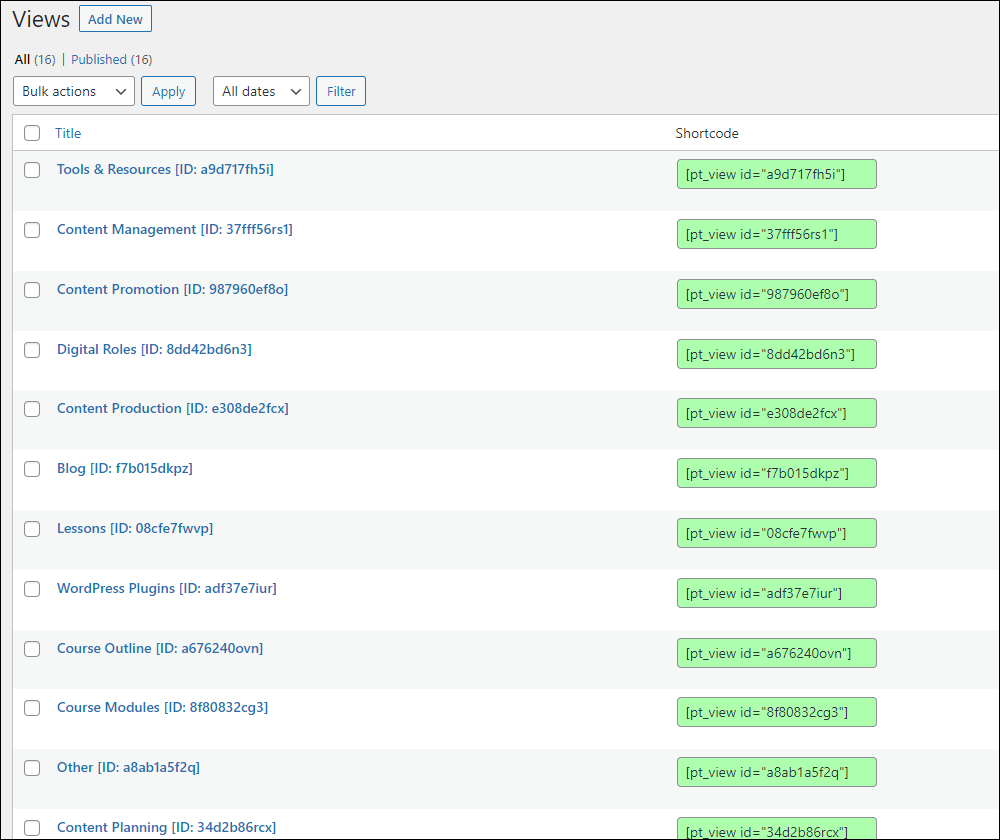
Next, we configured each view to list the right content and the information we wanted to display about each lesson.
As mentioned earlier, there are many ways to filter and organize views.
For example, we could have created a view of all content assigned to a specific category. This view would then automatically include any new content we create assigned to that category.
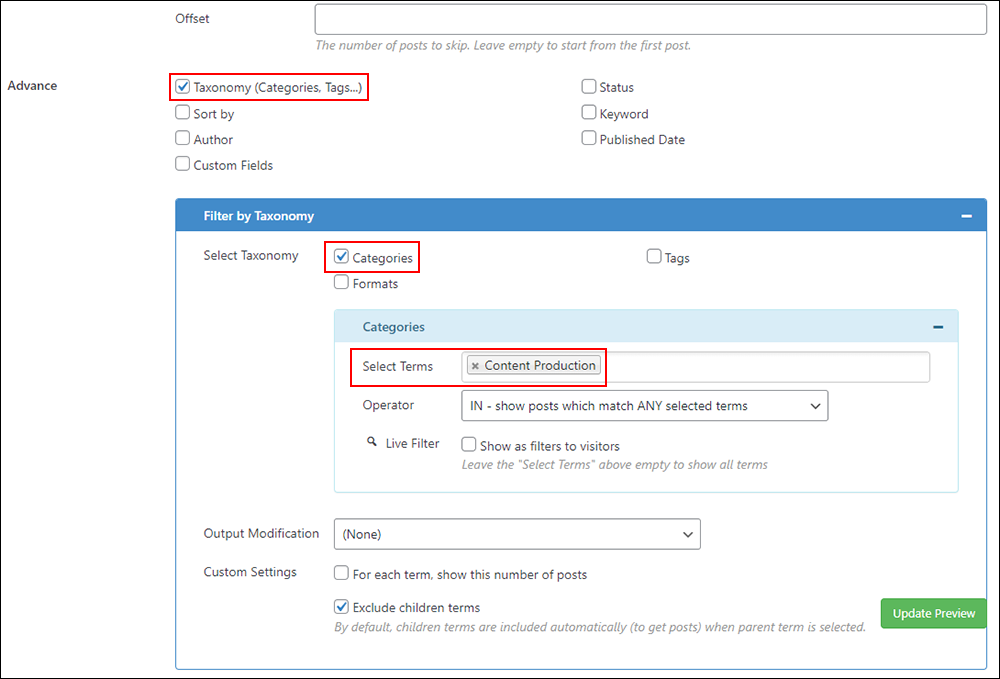
For this course, however, we wanted to display lessons in a particular order.
So, for each training module, first, we first filtered posts (i.e. lessons) by category (1), and then we recorded each post ID number (2)…
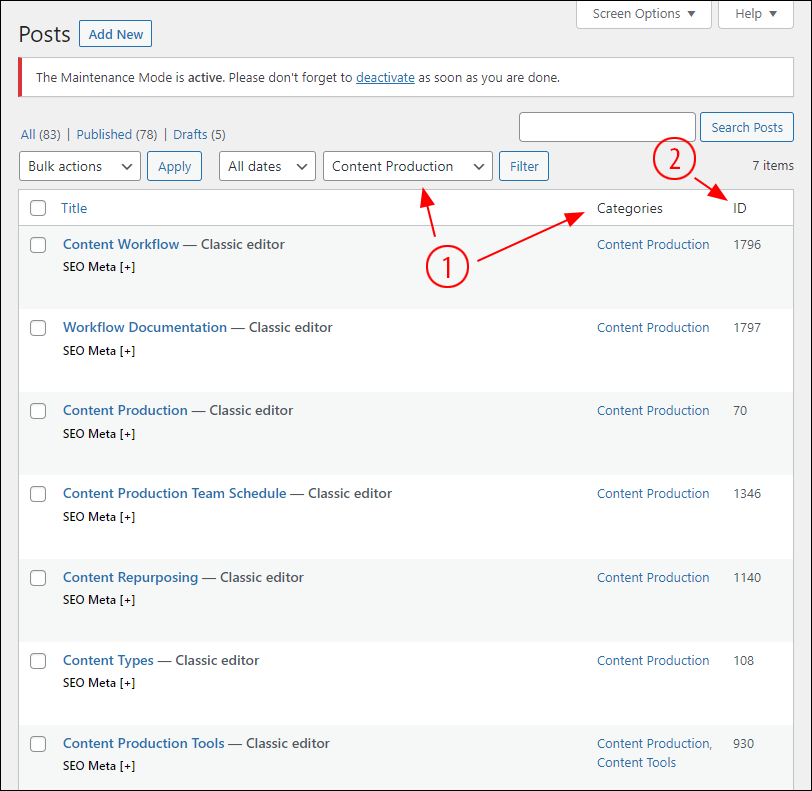
We then added each post (i.e. lesson) to the content view and arranged its order…
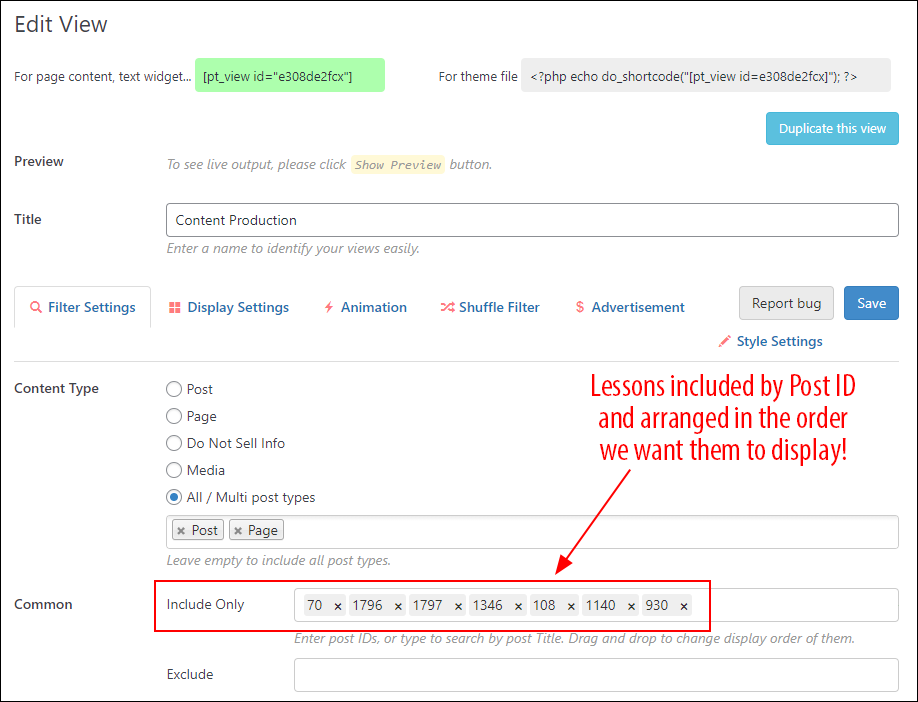
After creating the view, we added its shortcode to this page.
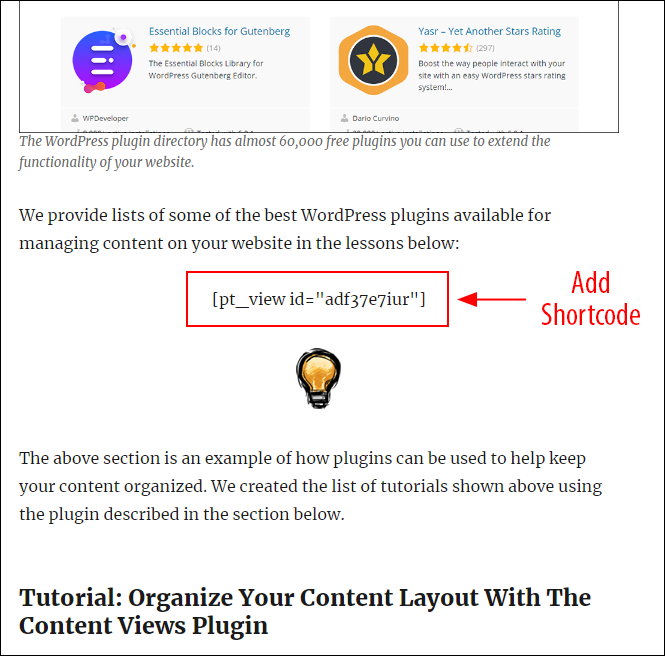
The plugin automatically populates the published page with the content we assigned to the content view.

Using the above method makes it easy to organize, automate and manage all the course information on this site from one central location.
![]()
If you know how you will organize your site’s content (from your content planning phase) but haven’t created all of the content yet, you can set up “empty” content views and add these as placeholders on your pages.
As you begin to add new content to your site, these “placeholder” content views will then automatically populate your pages with the right content.
***
Here are some additional examples of how we use this plugin to keep our content organized and manageable:
The main content shown on the content management course outline page was created using the plugin’s shortcodes.
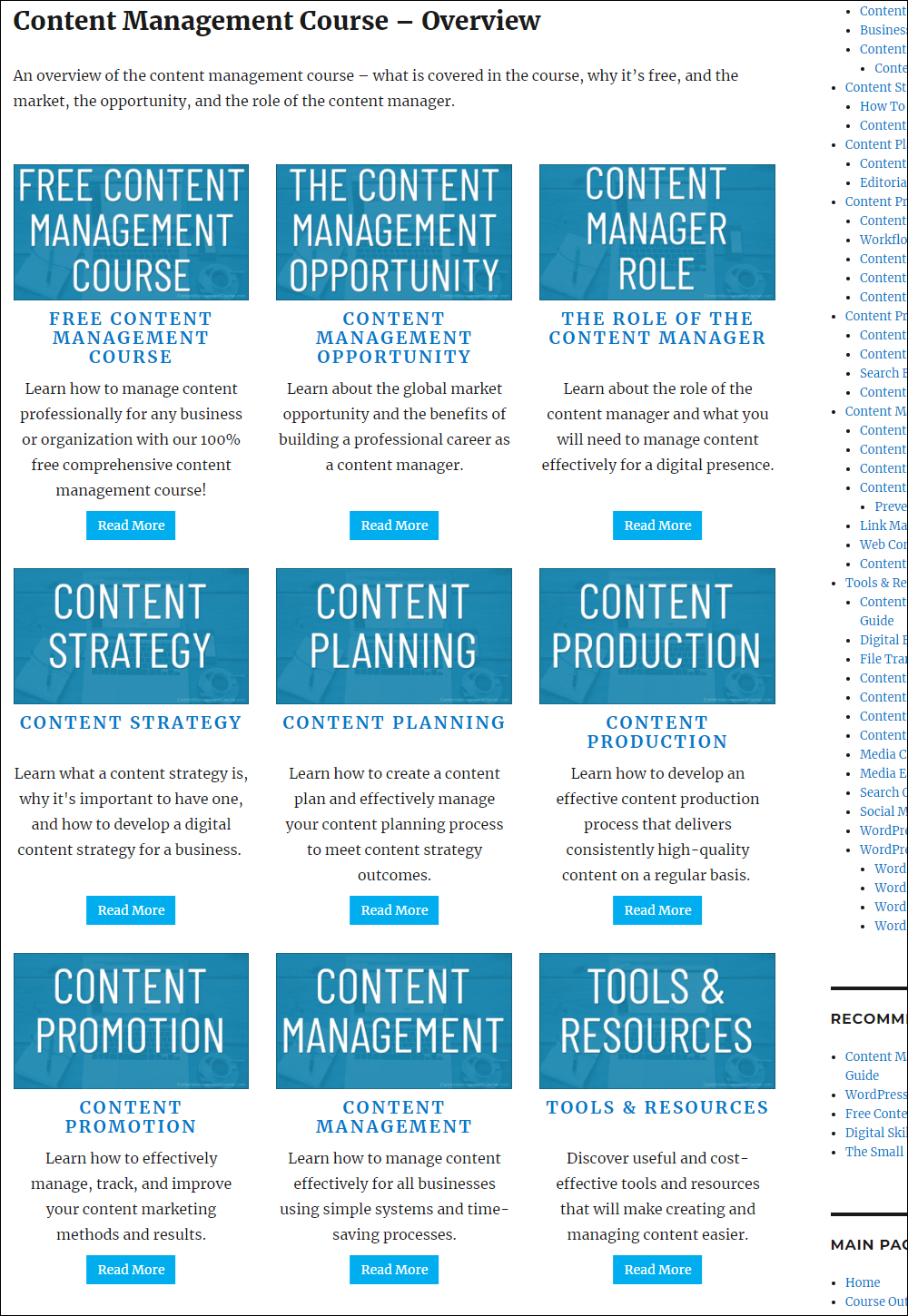
The only things we have added to the page are section titles and a brief description of the training modules with some graphic elements.
We also use this plugin on our WordPress training site to display a list of all of the site’s WordPress tutorials. Instead of displaying items by categories, however, we use Post IDs to display them in a logical sequence.

Similarly, we use the plugin on our video training site to list our video courses (using image thumbnails, the course title, and price fields only) in random order.

We also use the plugin on another site called WPCompendium.org to organize content by post categories and subcategories.
Each tutorial category has its own page.
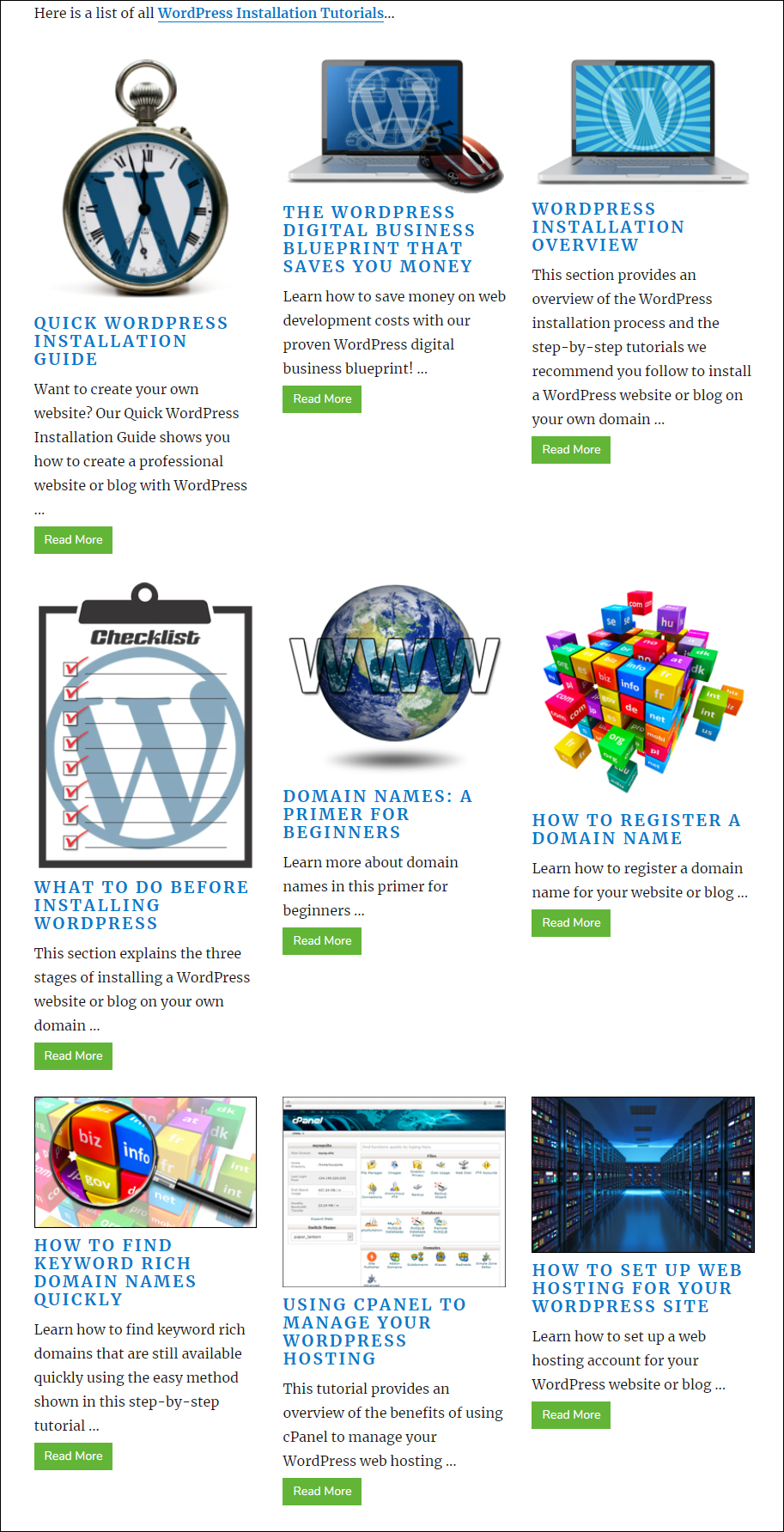
Some sections, however, display a list of subcategories on the page.
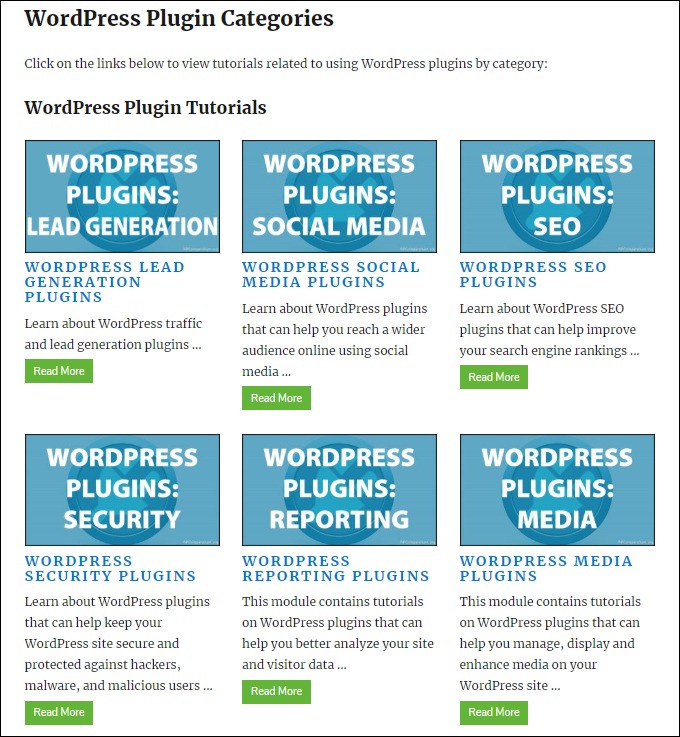
If a user clicks on any item listed on the category page (e.g. on the WordPress Plugin Tutorials list), they will be taken to other pages that list all the tutorials assigned to that subcategory, e.g. (Security Plugins, eCommerce Plugins, etc.)
Additional Content Organization Methods
In addition to using the above methods, here are some other tools we use to keep the content on this site organized and manageable:
Serve All Images From A Remote Service
We serve most images used on this site (and videos, downloadable files, etc.) from our Amazon S3 account.
Having all media files stored in one location not only makes things easier to manage but if the same files are used on different posts (e.g. an image banner or a downloadable PDF file), then all we need to do is replace the file on the Amazon S3 bucket where it is stored, and all instances of that file will automatically update on this site.
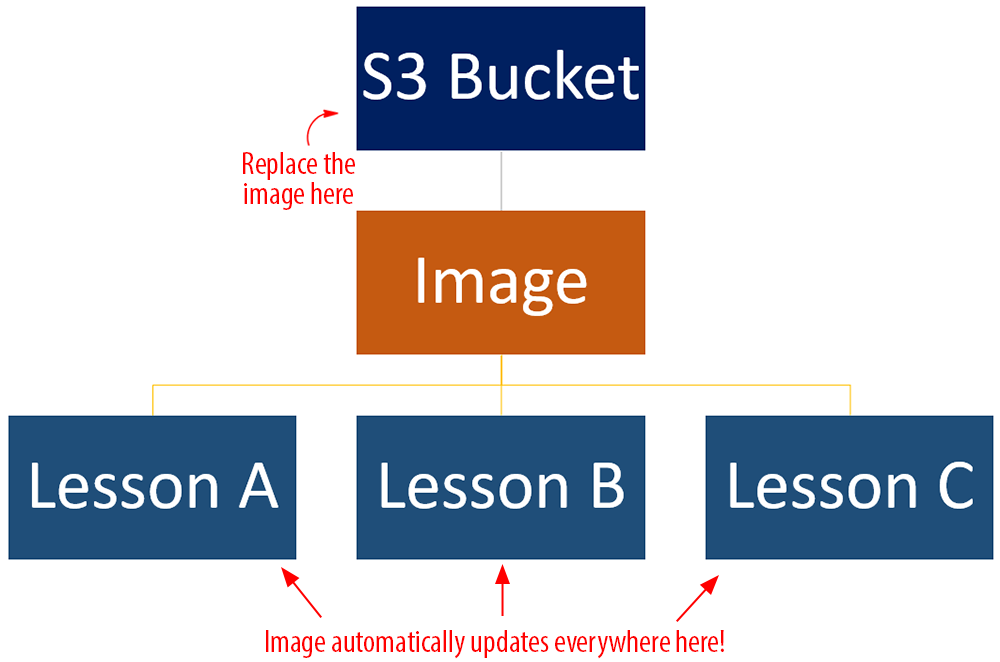
You can upload and manage all your media files to Amazon S3 (including protecting your content from image hotlinking) using a file transfer tool like S3 Browser.
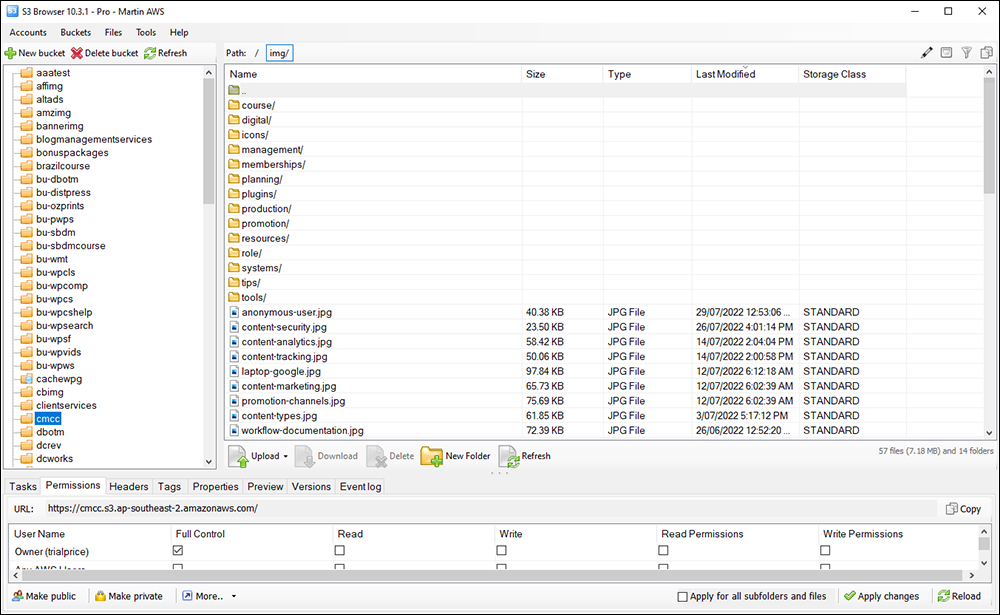
To learn how to set up an Amazon S3 account (and use the S3 browser tool), see this tutorial: How To Set Up An Amazon S3 Account and this Amazon S3 video course.
Note: Some media files in WordPress (like featured images in posts) need to be stored and managed in the WordPress Media Library. The WordPress Media Library stores media on your own server and also lets you easily manage your site’s media files.
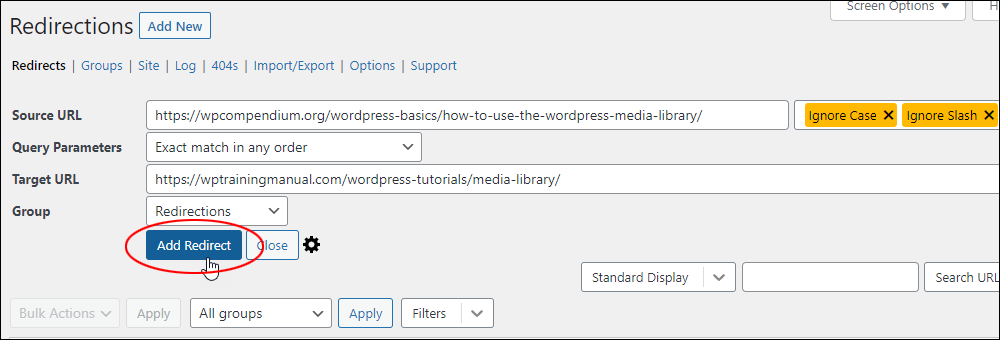
Use A Link Redirection Tool
Another method we use to help us manage and organize the content on our sites is to use a link redirection tool to point content to external sites, download files, etc.
This is useful because sites we link to can change their URLs (without informing anyone outside their organization of the change) and this can lead to broken links and a bad user experience.
For more information on using link redirection methods to manage your content see this lesson: Link Management
Final Tips…
Trash old posts and pages from your site when these are no longer used or whenever you redirect the URL of a post or page to another page or website (make sure to create a backup of your content first). This helps to keep things organized on the backend of your site and reduces the size of your database.
Organize your hard drive and external storage folders and choose “easy-to-search” naming conventions when storing your content, saving your files, choosing filenames for your images, videos, etc.
For additional ways to keep your content organized, see our Content Management Checklists section.
Also, for a list of useful content-organization tools and note-taking apps, go here: Content-Organizing Tools
Content Organization – FAQs
Here are frequently asked questions about content organization:
What is content organization?
Content organization refers to the systematic structuring and arrangement of digital content to make it easily accessible, navigable, and understandable for users. It involves categorizing, labeling, and structuring content elements to facilitate efficient retrieval and consumption.
Why is content organization important?
Effective content organization enhances user experience, improves navigation, increases search engine visibility, and facilitates content maintenance and scalability. It ensures that users can quickly find relevant information, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
What are the key components of content organization?
The key components include taxonomy creation, metadata implementation, content categorization, navigation design, information architecture, and content hierarchy establishment. These elements work together to create a cohesive and intuitive content structure.
How can I improve content organization on my website?
Start by conducting a content audit to assess the existing structure and identify areas for improvement. Develop a clear taxonomy, use descriptive metadata, implement intuitive navigation menus, and create a logical content hierarchy. Regularly review and update the organization based on user feedback and analytics.
What are some common strategies for organizing content?
Common strategies include categorization by topic or theme, tagging with relevant keywords, creating hierarchical structures (such as parent and child pages), and using metadata to help describe and retrieve the content more effectively.
How can I improve the searchability of my content?
To improve searchability, use clear and descriptive titles, utilize metadata and tags effectively, ensure that content is well-categorized, and regularly update content to maintain relevance and accuracy.
What role does metadata play in content organization?
Metadata provides additional context and information about content items, such as titles, descriptions, keywords, and tags. It helps search engines understand the content and improves searchability, aids in the automation of content processes like archiving and security settings, and helps users to quickly evaluate the relevance of the content.
How does content organization impact SEO?
Proper content organization enhances SEO by making it easier for search engines to crawl, index, and rank website pages. Clear taxonomy, optimized metadata, and logical content structure contribute to higher search engine visibility and better ranking for relevant keywords.
What are some best practices for organizing content across multiple channels?
Standardize your taxonomy and metadata conventions, maintain consistency in content presentation and labeling, and ensure seamless integration between different channels. Use cross-linking to connect related content across channels and provide a unified user experience.
What is content organization in a CMS?
Content organization in a Content Management System (CMS) refers to the way content is structured and managed within the system. This includes how content is categorized, tagged, archived, and retrieved to ensure efficient use and accessibility.
How does effective content organization benefit a CMS user?
Effective content organization improves navigation, enhances the user experience by making content easier to find, and increases the efficiency of content updates and management. It also plays a critical role in SEO performance.
How should FAQs be integrated into content organization?
FAQs should be organized to directly address common customer questions, grouped by themes or topics to facilitate easy navigation, and be easily accessible from related content areas or via site search features.
Summary
Keeping content on your website organized is an important area of content management.
Getting organized and systematized before you even publish content will also save you a lot of time later, especially when searching for content items that have already been previously created.
Using a CMS like WordPress and the various tools mentioned here will help you keep everything organized so you can access and manage your content more easily and more effectively.
Action Steps
Complete this lesson and spend some time carefully planning and reviewing ways to better organize your web content.
Resources
- WordPress Training Manual – A comprehensive WordPress training site for non-technical website owners and WordPress users with access to hundreds of detailed step-by-step tutorials, video tutorials, guides, resources, and more.
- WordPress Plugin Directory – Browse and access thousands of free plugins that help to extend the functionality of your WordPress website.
References
- How To Plan Your Website
- 50+ Reasons To Choose WordPress
- How To Tell If It’s A WordPress Site
- How To Use The WordPress Linking Tool
- How To Use WordPress Post Categories
- WordPress Posts Vs WordPress Pages
Next Steps
- Learn about different linking strategies to better manage your content: Link Management
- Learn ways to protect your content: Content Protection
- Learn how to track your content: Content Tracking
- Learn how to manage your content documentation: Content Documentation
- Learn how to perform a Content Review
- Return to this training module’s overview section: Content Management
- Return to the Course Outline
***
Image: Content views plugin