Content Management Glossary
This content management glossary provides terms and definitions related to the creation, management, and distribution of digital content.

Whether you are new to the content management field or an experienced professional content creator, digital marketer, project manager, or executive, this content management glossary will serve as a useful reference to understand content management terminology and concepts used in the field and help you stay up-to-date on the latest developments and best practices in content management.
Agile Content Marketing
Agile Content Marketing is a flexible approach to creating and managing content. It involves continuously planning, executing, and reviewing content in short cycles, allowing for quick adjustments based on feedback and performance. This method helps businesses stay responsive to market changes and customer needs, ensuring their content remains relevant and effective.
Business Goals
Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives that a business aims to achieve.
Here are some examples of business goals:
- Increase revenue by 10% in the next fiscal year
- Expand into new markets by opening three new retail locations in the next two years
- Launch a new product line by the end of the year
- Achieve a net profit margin of 15% by the end of the quarter
- Increase customer satisfaction ratings by 20% within the next six months
- Reduce employee turnover by 50% within the next year
- Increase the number of social media followers by 50% within the next quarter
- Achieve a 90% on-time delivery rate by the end of the year
- Increase the number of recurring customers by 25% within the next six months
Business Mission Statement
A statement that describes the purpose and values of a business.
Here are some examples of business mission statements:
- “To provide the best products and services in our industry, and to always put our customers first.”
- “To create value for our shareholders by building a sustainable and successful business that makes a positive impact on the world.”
- “To be a responsible and innovative company that creates value for all of our stakeholders, including customers, employees, shareholders, and the communities in which we operate.”
- “To help people achieve their financial goals and live better lives through innovative, reliable, and accessible products and services.”
- “To be the leading provider of innovative, high-quality healthcare solutions that improve the lives of people around the world.”
- “To be the most trusted and respected company in our industry, known for our commitment to excellence and innovation.”
- “To be the global leader in providing sustainable solutions that improve the quality of life for all people.”
Business Plan
A document that outlines the goals, target market, and financial projections of a business.
Business Strategy
A plan for achieving the goals of a business, often involving the development of a unique value proposition and a competitive advantage.
Here is an example of a business strategy using content and content marketing:
Our company’s goal is to establish itself as the leading provider of healthy, convenient, and delicious food, helping people around the world to live their best lives.
To achieve this goal, we will develop a content marketing strategy focused on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to a clearly defined target audience. This content will include educational articles, recipe videos, and infographics that highlight the benefits of a healthy diet and the convenience of our company’s products.
The content marketing strategy will also include a strong social media presence, with regular posts showcasing the company’s products, highlighting customer success stories, and offering healthy living tips and inspiration. We will also partner with influential health and wellness bloggers and influencers to amplify its message and reach a wider audience.
Through this content marketing strategy, we will aim to attract and retain a loyal customer base, increase brand awareness and engagement, and ultimately drive sales and revenue growth.
Business Vision Statement
A statement that describes the long-term goals and aspirations of a business.
Here are some examples of business vision statements:
- “To be the most trusted and respected company in our industry, known for our commitment to excellence and innovation.”
- “To be the global leader in providing sustainable solutions that improve the quality of life for all people.”
- “To be the premier destination for all of your entertainment needs, offering the best content, experiences, and value.”
- “To create a world where everyone has access to high-quality education and the opportunity to reach their full potential.”
- “To be the go-to source for the latest and greatest products, services, and ideas that make life easier, better, and more fun.”
- “To be the leading provider of healthy, convenient, and delicious food, helping people around the world to live their best lives.”
- “To be the most admired and respected brand in the world, inspiring people to be their best selves and achieve their dreams.”
Buyer Journey
The buyer journey is the process that a potential customer goes through to become aware of, evaluate, and purchase a product or service.
Understanding this process will help you create a content strategy aligned with your target audience’s interests.
The stages of the customer buyer journey can include awareness, research, evaluation, and purchase.
The goal of the customer buyer journey is to understand the customer’s needs and preferences and to guide them through the process of making a purchase.
Learn more here: Understanding Your Customer’s Buyer Journey
Content Analysis
The process of examining and evaluating written or spoken material to extract meaningful insights and improve the quality of the content.
Content analysis is an essential part of content research, as it can help to ensure that your content is relevant, informative, and engaging to your target audience.
Content Audit
A review and assessment of the existing digital content within an organization, often with the goal of identifying areas for improvement or updating.
Learn how to perform a content audit.
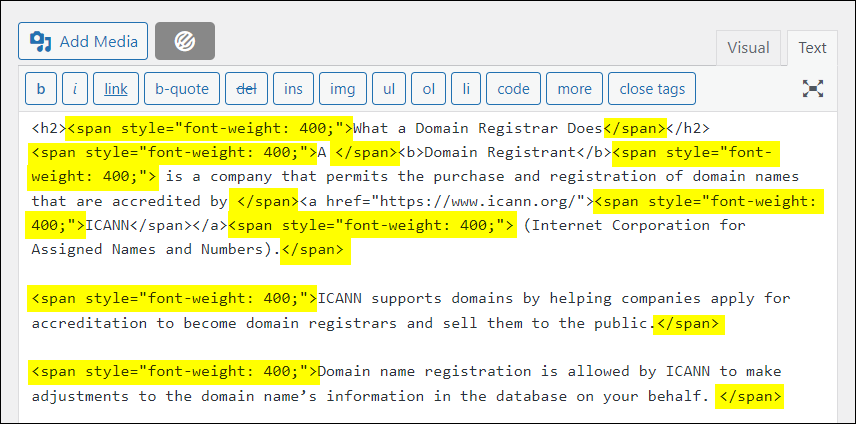
Content Authoring
The process of creating and writing digital content, often using a content management system or other tools.
Content Brief
A document that outlines the goals, target audience, and key messages of a specific piece of digital content.
- See an example of a content brief
Content Calendar
A schedule or plan for creating, publishing, and distributing digital content, often organized by date or topic. A content calendar (also known as an “editorial calendar”) can help organizations plan and coordinate their content creation efforts and ensure a consistent flow of content to their audience.
Content Creation
The process of creating and writing digital content.
Content Distribution
The process of making digital content available to a target audience, typically through a website or other online platform.
Content Documentation
The process of creating and maintaining records of digital content, including information such as the creation date, author, and any updates or revisions.
Content Governance
The policies, procedures, and standards that guide the creation, management, and distribution of digital content within an organization.
Content Link Management
The process of organizing and managing the links within digital content, often with the goal of improving navigation and user experience.
Content Management Audit
A review of an organization’s content management practices to identify areas for improvement.
Content Management Best Practices
Guidelines and strategies recommended by industry experts for managing content effectively and efficiently.
Content Management Governance
The processes and practices used to ensure that content is created, managed, and published in a way that is consistent with an organization’s policies and goals.
Content Management Lifecycle
The stages of content creation, management, and retirement within an organization.
Content Management Metrics
Data used to measure the effectiveness of an organization’s content management efforts.
Content Management Policy
A set of guidelines or rules governing the creation and management of content within an organization.
Content Management Strategy
A plan for creating, managing, and distributing content in a way that supports the goals of a business or organization.
Content Management System (CMS)
A software application, platform, or a set of tools used to create, edit, organize, store, manage, and publish content on a website or other digital media.
Additional useful CMS-related terms include:
- Asset – A digital file or piece of content that can be managed and reused within a CMS.
- Workflow – A set of steps or processes for creating, reviewing, and publishing content within a CMS.
- Metadata – Data about content, such as tags or keywords, that can be used to classify and organize it within a CMS.
- Permalink – A permanent URL that points to a specific piece of content within a CMS.
- User role – A set of permissions or privileges that determine what actions a user can take within a CMS.
- Taxonomy – A system for classifying and organizing content within a CMS, often using categories and tags.
- Content type – A category of content that is defined within a CMS, such as articles, products, or events.
- Revision history – A record of all the changes made to a piece of content within a CMS, along with who made the changes and when.
- API (Application Programming Interface) – A set of rules and protocols that allow different software systems to communicate and exchange data with each other.
Also, see these types of content management systems:
WCMS
A web content management system (WCMS) is a platform that facilitates the creation, publication, and management of website content.
ECMS
An enterprise content management system (ECMS) is a software solution that allows businesses to store, organize, and manage their digital content, regardless of format or location.
CCMS
A component content management system (CCMS) is a software solution that helps organizations create, manage, and publish modular content in a structured manner to be used across different products, services, or platforms.
DAMS
A digital asset management system (DAMS) is a platform designed to manage digital files such as images, videos, and audio files, allowing users to easily store, organize, retrieve, and distribute their assets.
Content Management Team
A group of individuals responsible for managing the content of a website or other digital media.
Content Management Workflow
The process of creating, reviewing, approving, and publishing digital content within an organization.
Content Marketing
A marketing strategy that involves the creation and distribution of valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience.
Content Marketing Plan
A content marketing plan is a strategy for creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a specific target audience, with the goal of driving profitable customer action.
Content Marketing Strategy
A content marketing strategy is a comprehensive plan for creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a specific target audience, with the goal of driving profitable customer action.
It outlines the overall goals and objectives for your content, your target audience, the channels through which your content will be distributed, and the metrics by which success will be measured.
Content Measurement Plan
A content measurement plan is a document that outlines the goals, objectives, key performance indicators (KPIs), measurement tools, and schedule for measuring and evaluating the performance of your content marketing efforts.
It helps to track progress and make data-driven decisions on how to optimize your content strategy.
Learn more: Content Measurement Plan
Content Metrics
Data and metrics used to measure the performance and effectiveness of digital content, such as website traffic, engagement rates, and conversion rates.
Content Migration
The process of moving digital content from one platform or system to another.
Content Performance
The effectiveness of digital content in achieving its intended goals, such as generating website traffic or driving sales.
Content Plan
A detailed plan for creating and managing digital content, typically including goals, target audience, and a content calendar.
A content plan is a document that outlines the content that your business will create and publish in a given period of time.
It helps your business align its content with its overall marketing and business goals, and ensures that you have a steady stream of relevant, high-quality content to share with your audience.
Learn how to create a content plan for your business.
Your content plan can be divided into smaller plans covering different aspects such as content production, content promotion, and content management, and distributed to different teams of departments responsible for managing and implementing these:
Content Production Plan
A content production plan is a detailed plan that outlines the specific actions and resources that your business will use to create and publish its content.
It is a more detailed version of a content plan and helps your business stay organized and on schedule when creating content.
Content Promotion Plan
A content promotion plan is a strategy for getting the word out about your business’s content.
It helps your business increase the visibility of your content and drive engagement and conversions.
Content Management Plan
A content management plan is a strategy for organizing, storing, and maintaining your business’s content over time.
It helps your business keep your content organized, ensure that it stays up-to-date and relevant, and make it easily accessible to the people who need it.
Content Planning
The process of organizing and scheduling the creation and distribution of digital content.
Content Production
The process of creating and publishing digital content, often involving research, writing, editing, and design.
Content Promotion
The process of increasing the visibility and reach of digital content, often through marketing efforts or partnerships.
Content Publishing
The process of making digital content available to a target audience, typically through a website or other online platform.
Content Repurposing
The process of adapting or reusing existing digital content for a new purpose or audience, often through formatting or modification.
Content Research
The process of gathering information and data to inform the creation of digital content.
Content SEO
The process of optimizing digital content for search engines, including keyword research and the use of tags and meta descriptions.
Content Strategy
A plan for creating and managing digital content, typically involving the development of goals, audience targeting, and a content calendar.
Content Tracking
The process of monitoring and collecting data on the performance and engagement of digital content, often using tools such as Google Analytics.
Core Business Values
The fundamental principles that guide the actions and decisions of a business.
Here are some examples of core business values:
- Integrity: honesty, transparency, and ethical behavior in all business dealings.
- Respect: treating all stakeholders with dignity and respect.
- Innovation: a commitment to continuous improvement and finding new and better ways of doing things.
- Excellence: a pursuit of the highest quality in all aspects of the business.
- Customer focus: a commitment to meeting the needs and expectations of customers.
- Teamwork: a belief in the power of collaboration and the importance of working together towards a common goal.
- Sustainability: a commitment to environmental and social responsibility, and to building a business that can thrive in the long term.
- Social impact: a desire to make a positive difference in the world through the business.
- Diversity and inclusion: a commitment to creating a workplace culture that values and supports diversity and inclusivity.
- Employee development: a focus on investing in and supporting the growth and development of employees.
Document Library
A collection of files, documents, or records that are systematically organized and stored in a digital format.
Document Management System
A Document Management System (DMS) is a software program that is designed to help organizations manage, store, and track their electronic and physical documents.
Learn more about Document Management Systems
Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix is a time management tool that helps prioritize tasks based on urgency and importance. It divides tasks into four quadrants:
- Urgent and Important: Do these tasks immediately.
- Important, Not Urgent: Schedule these tasks.
- Urgent, Not Important: Delegate these tasks.
- Not Urgent, Not Important: Eliminate these tasks.
This matrix helps businesses focus on what truly matters and manage their time more efficiently.
Evergreen Content
Evergreen Content refers to content that remains relevant and valuable over time. Unlike news articles or trend-based content, evergreen content addresses timeless topics and provides information that is consistently useful to your audience. Examples include how-to guides, tutorials, and FAQs. This type of content continuously attracts traffic and engagement long after it’s published.
Keyword Research
The process of identifying and analyzing the words and phrases that people use when searching for information on a particular topic.
Keyword research involves finding the terms that are most relevant to your content and that are likely to be used by your target audience. It is an essential part of content research, as it can help you to optimize your content for search engines and ensure that your content is being seen by the right people.
Learn more about keyword research tools.
Marketing Funnel
The marketing funnel is a framework used to describe the journey a potential customer goes through before making a purchase. It typically includes the stages of awareness, interest, consideration, and conversion.
The goal of the marketing funnel is to move potential customers through each stage, with the ultimate goal of converting them into paying customers.
Marketing Plan
A detailed plan for promoting and selling a product or service, including goals, target audience, and marketing tactics.
Marketing Strategy
A plan for promoting and selling a product or service, including an analysis of the market and the development of a unique selling proposition.
Metadata
Data about data, such as tags or descriptions, that can be used to describe and classify digital content.
Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method that breaks work into intervals, typically 25 minutes long, separated by short breaks. Each interval is called a “pomodoro.” After completing four pomodoros, take a longer break. This technique helps improve focus, reduce mental fatigue, and increase productivity by encouraging regular breaks.
Project Management
The process of planning, organizing, and overseeing the work of a team to achieve specific goals and meet specific success criteria. When managing content projects, this often involves using content production workflow tools.
Strategic Business Objectives
Long-term goals that a business aims to achieve to fulfill its mission and vision.
Here are some examples of strategic business objectives:
- To become the market leader in our industry within the next five years.
- To double the size of our business within the next three years.
- To establish a strong presence in the global market within the next decade.
- To develop a new product line that meets the needs of an underserved market segment.
- To improve our supply chain efficiency by 30% within the next year.
- To develop a customer loyalty program that increases retention rates by 50%.
- To implement a new sales and marketing strategy that increases conversions by 20%.
- To invest in research and development to create innovative products and services
- To diversify our product offerings to reduce reliance on a single product or market.
- To create a strong corporate culture that attracts and retains top talent.
You can also set specific content-related strategic objectives for your business.
Style Guide
A set of standards and guidelines that determine the writing, design, and formatting of your website, documentation, products, or brand.
A style guide serves as a reference for maintaining consistency and ensuring that the various elements of your website, documentation, products, or brand present a cohesive and professional image to your audience.
Additionally…
Content Style Guide
A document that outlines the guidelines and standards for creating and publishing content for your business.
It provides a set of rules and recommendations to ensure consistency and quality across all your content, from blog posts and social media updates to product descriptions and email newsletters, and standards for the writing, design, and formatting of your web content.
A style guide focuses on visual elements while a content style guide focuses on written elements. Both guides are essential tools for creating a consistent and recognizable brand identity.
Learn how to create a content style guide.
Trend Analysis
The process of using data to identify patterns and trends in the content that is being consumed by a particular audience. By analyzing trends, your business can gain insights into the types of content that are popular among your target audience, and use this information to inform your content creation and marketing strategies.
User Persona
A user persona is a fictional representation of a business’s ideal customer. It is based on data and research about the target audience, and it is used to help businesses create more effective marketing campaigns and design user-friendly products.
User personas provide a detailed and specific picture of who the target audience is, what their needs and goals are, and how they think and behave.
View a list of free online user persona generators.
***
Image: Wooden Letters
 Can AI really generate quality content that is engaging and valuable for human readers?
Can AI really generate quality content that is engaging and valuable for human readers?
















 Content management is a crucial aspect of running a successful business or organization. It involves creating, organizing, and distributing content across various channels and platforms.
Content management is a crucial aspect of running a successful business or organization. It involves creating, organizing, and distributing content across various channels and platforms.
 In this article, we will explore the importance of documenting procedures and how to effectively create and maintain them.
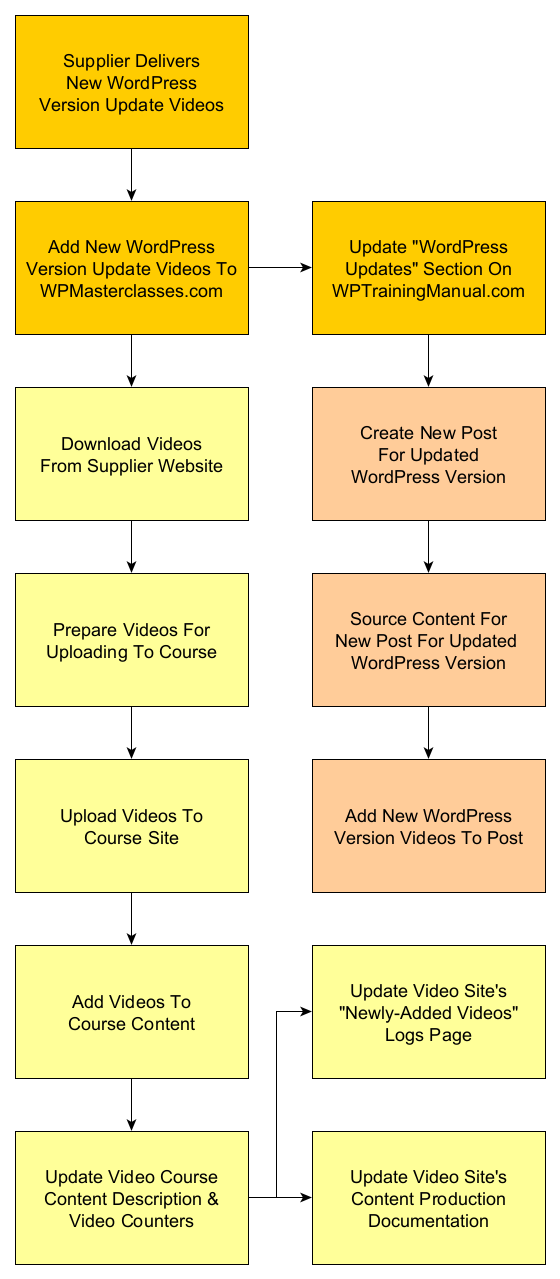
In this article, we will explore the importance of documenting procedures and how to effectively create and maintain them.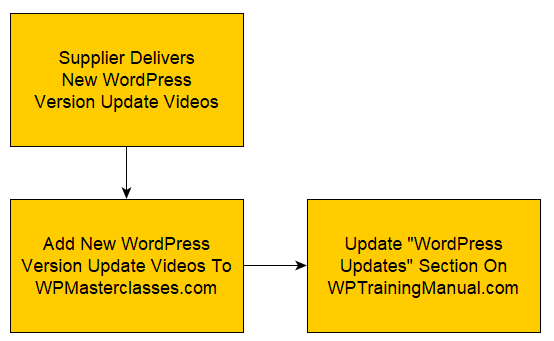
 While there is an abundance of information online about affiliate marketing, much of it is focused on how to succeed as an affiliate promoting products and services, not on how to manage your affiliate marketing content.
While there is an abundance of information online about affiliate marketing, much of it is focused on how to succeed as an affiliate promoting products and services, not on how to manage your affiliate marketing content.








 Managing content typically also involves managing many different accounts (e.g. other websites, social media platforms, subscription services, emails, membership sites, online banking, etc.).
Managing content typically also involves managing many different accounts (e.g. other websites, social media platforms, subscription services, emails, membership sites, online banking, etc.).
 RoboForm
RoboForm





 KeePass is a free portable password manager for PC (Windows, Linux, Mac OS X), with ports available for Android, iPhone, iPad, and more.
KeePass is a free portable password manager for PC (Windows, Linux, Mac OS X), with ports available for Android, iPhone, iPad, and more.


 Without a compelling post title or an attention-grabbing article headline, your site visitors may never get to see your message.
Without a compelling post title or an attention-grabbing article headline, your site visitors may never get to see your message.















 Your business needs content. Your website needs content. Your social media needs content. Your blog, newsletters, product descriptions, post headlines, sales copy, social media, ads, articles, promotional pieces, news releases, customer training sections, FAQs, forum signatures, SEO meta descriptions, etc. all need content.
Your business needs content. Your website needs content. Your social media needs content. Your blog, newsletters, product descriptions, post headlines, sales copy, social media, ads, articles, promotional pieces, news releases, customer training sections, FAQs, forum signatures, SEO meta descriptions, etc. all need content.


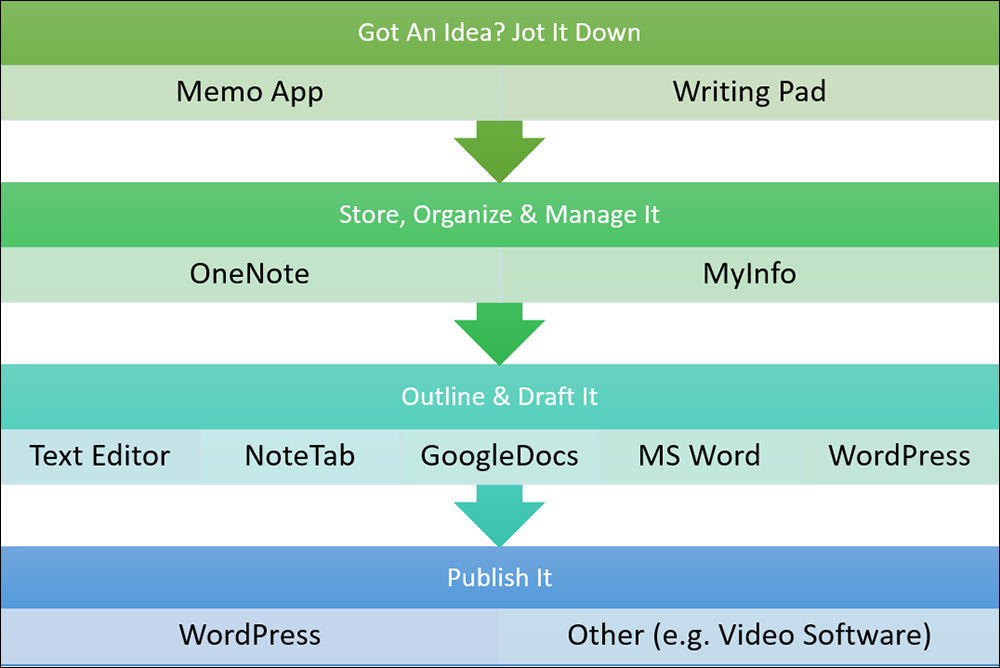


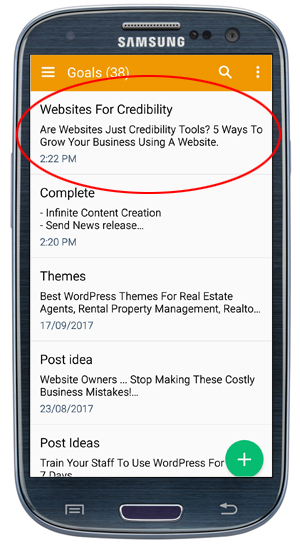
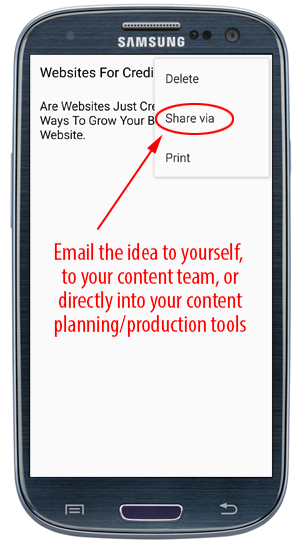
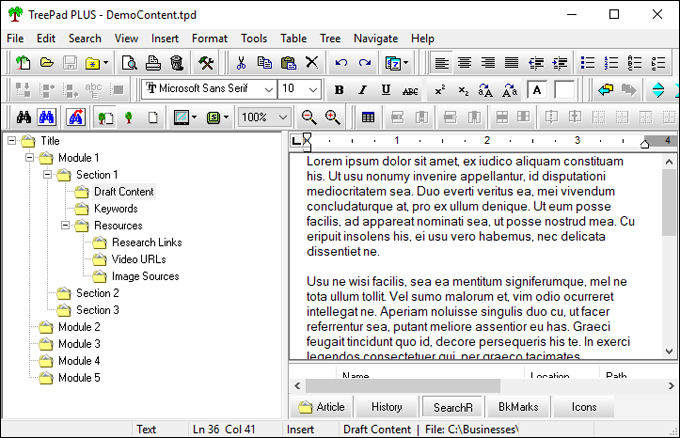
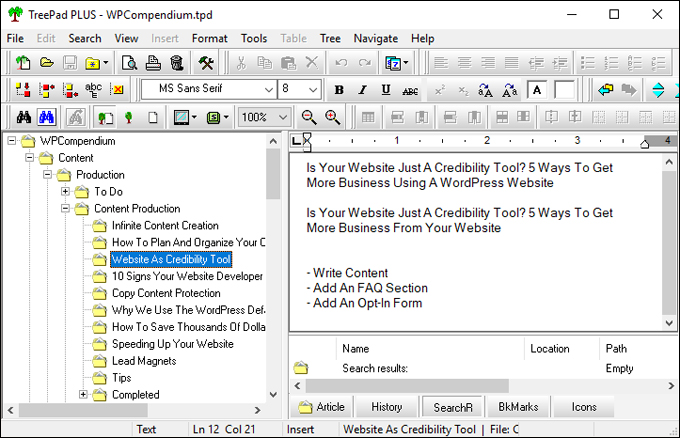



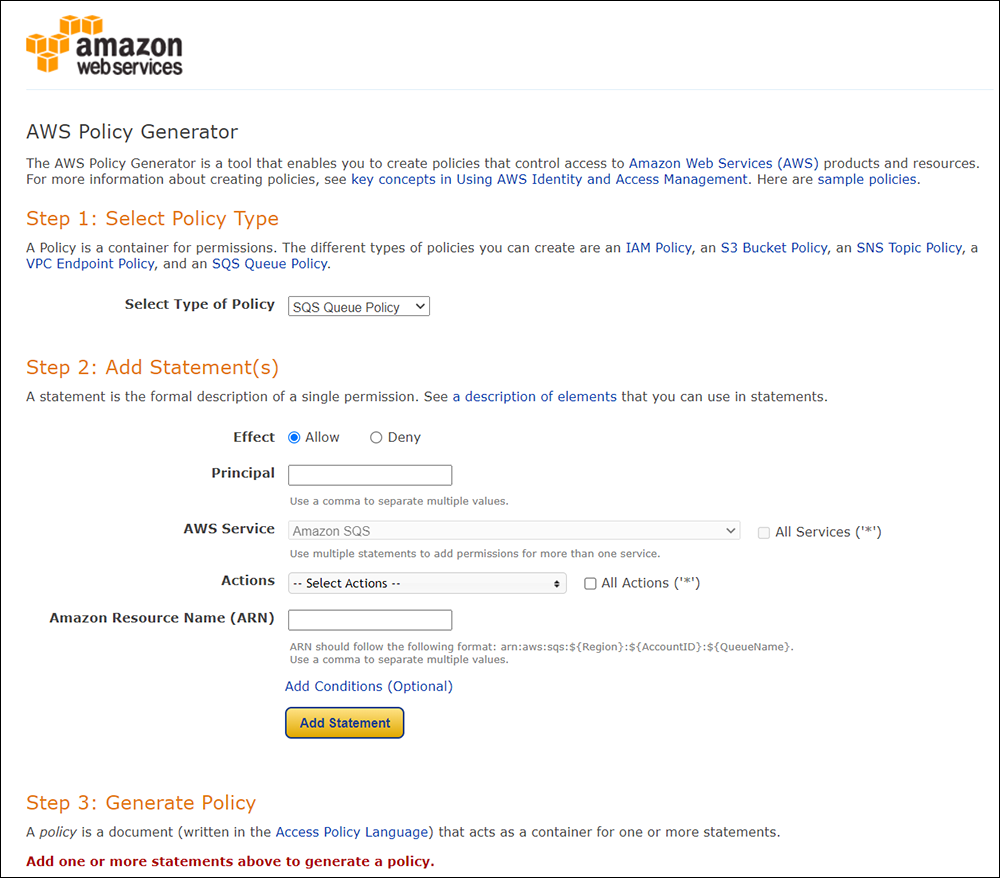
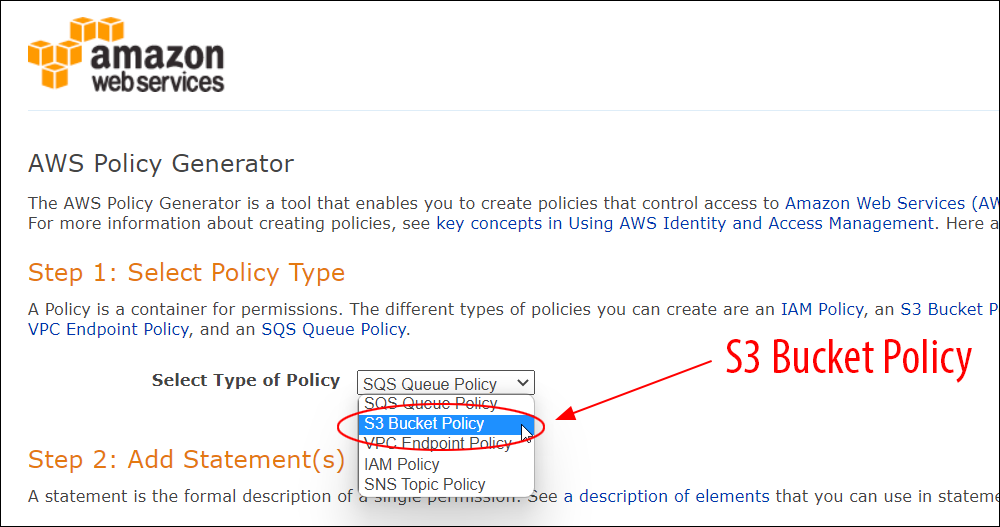
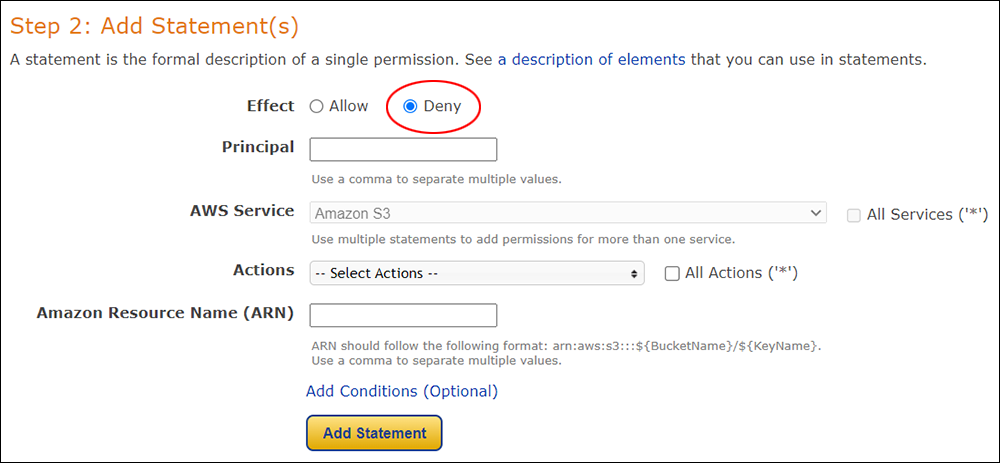
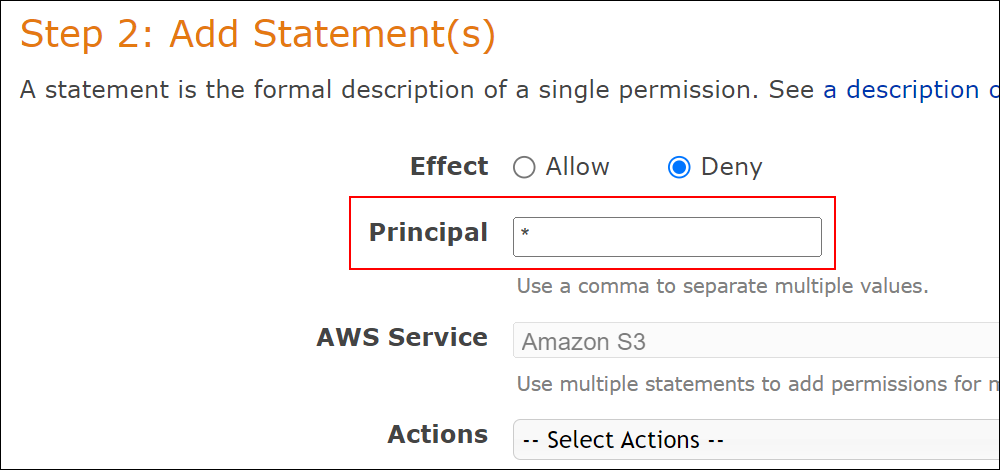
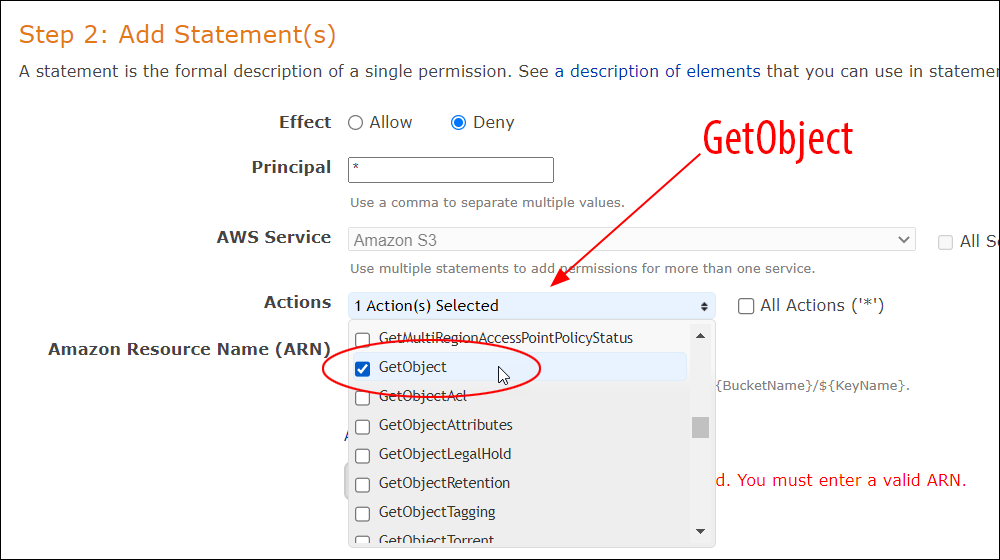
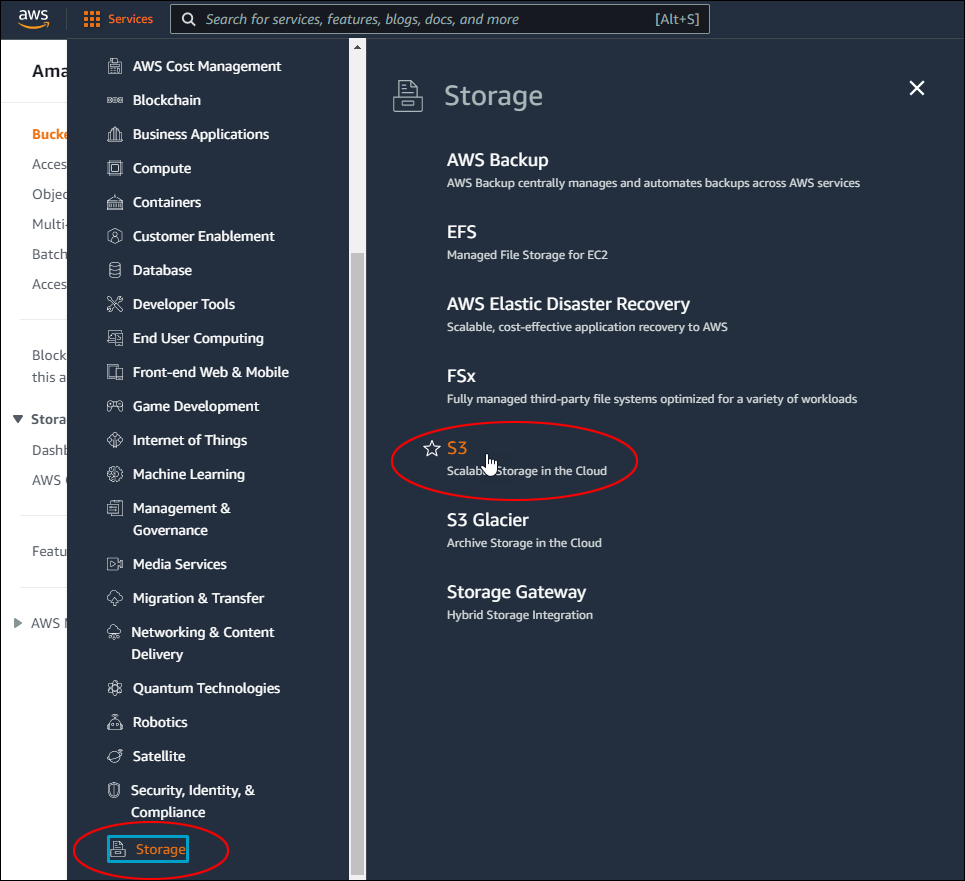
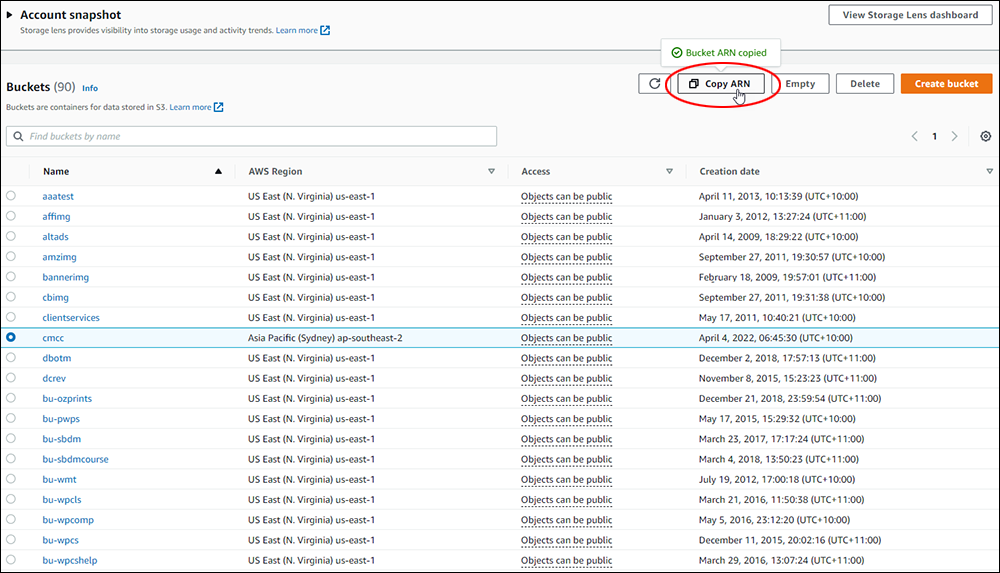
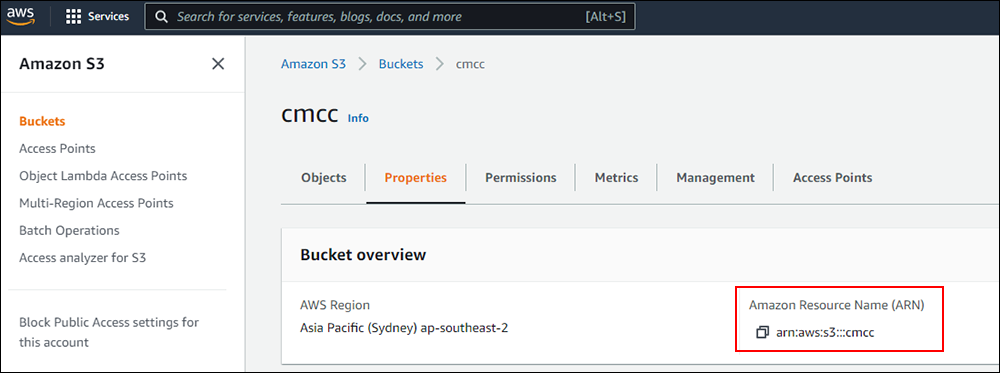
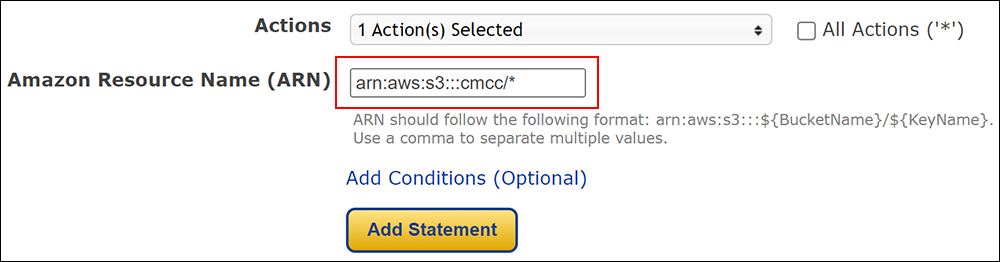
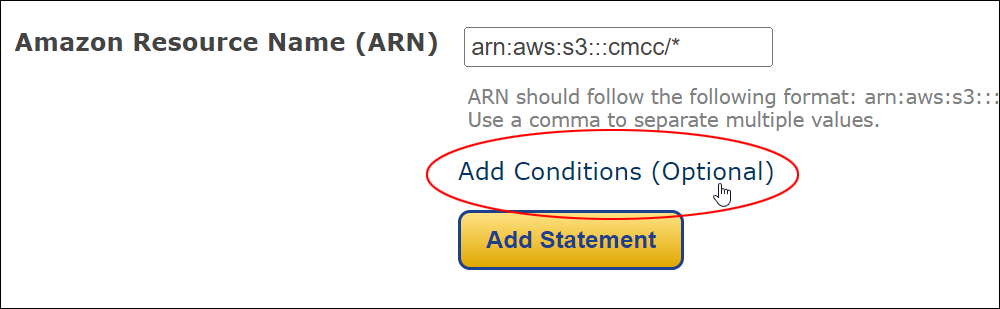
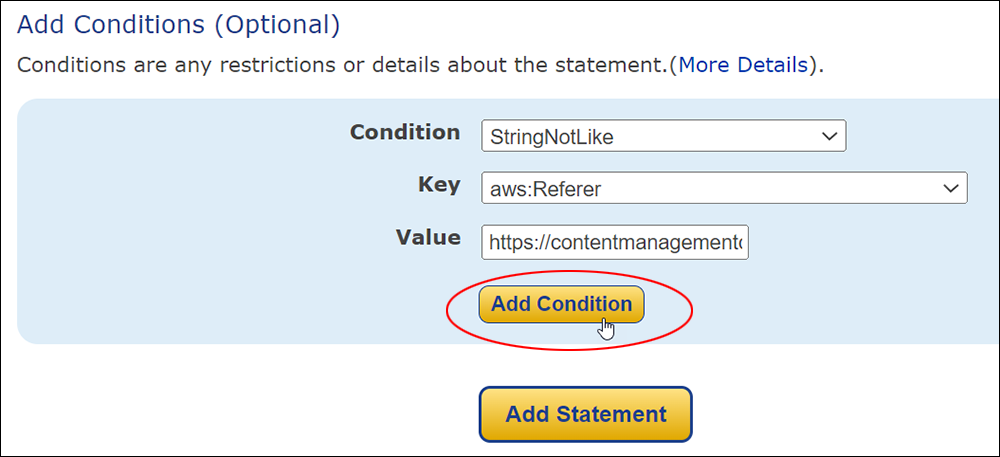
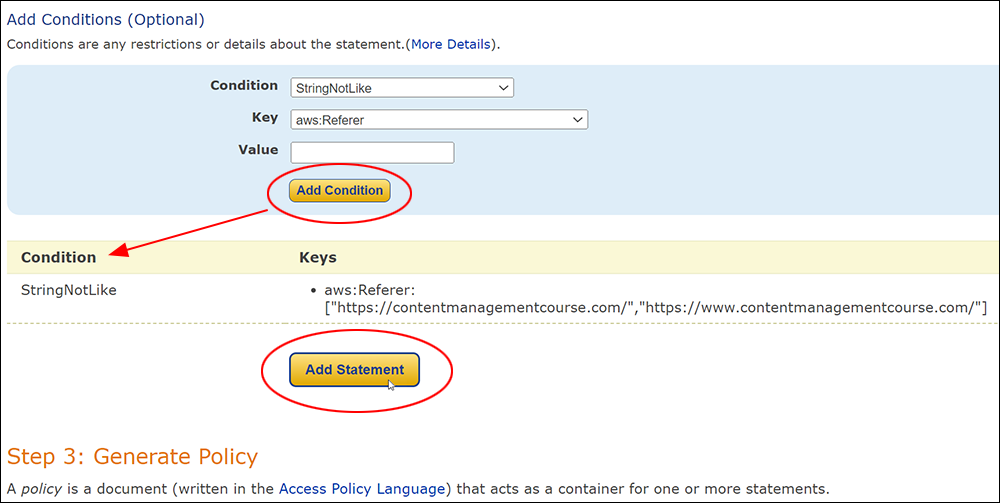
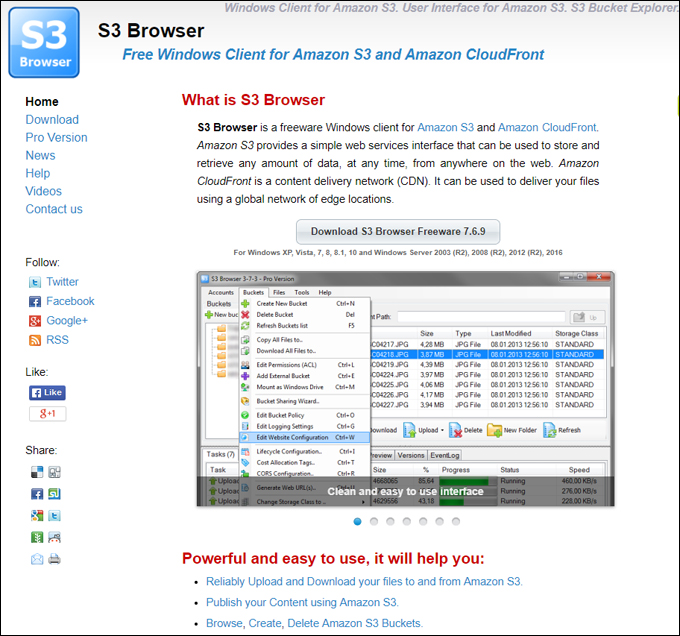
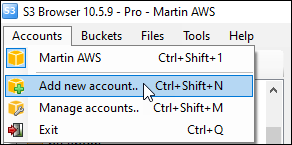
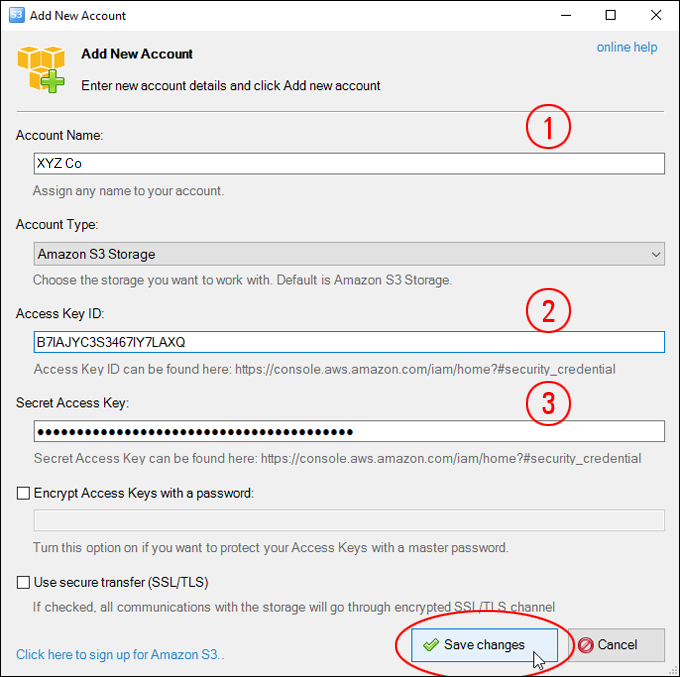
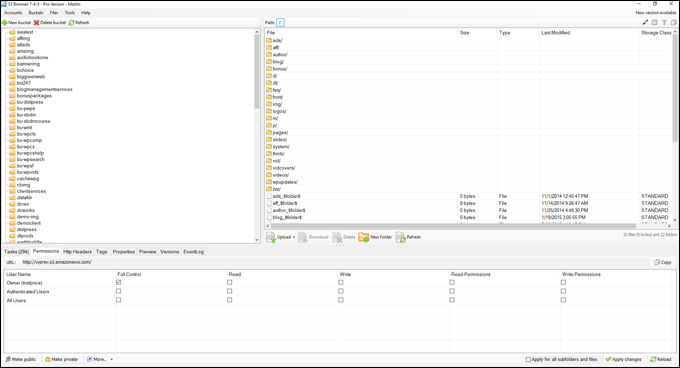
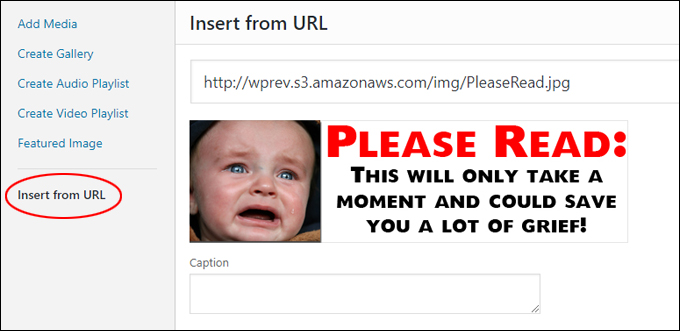
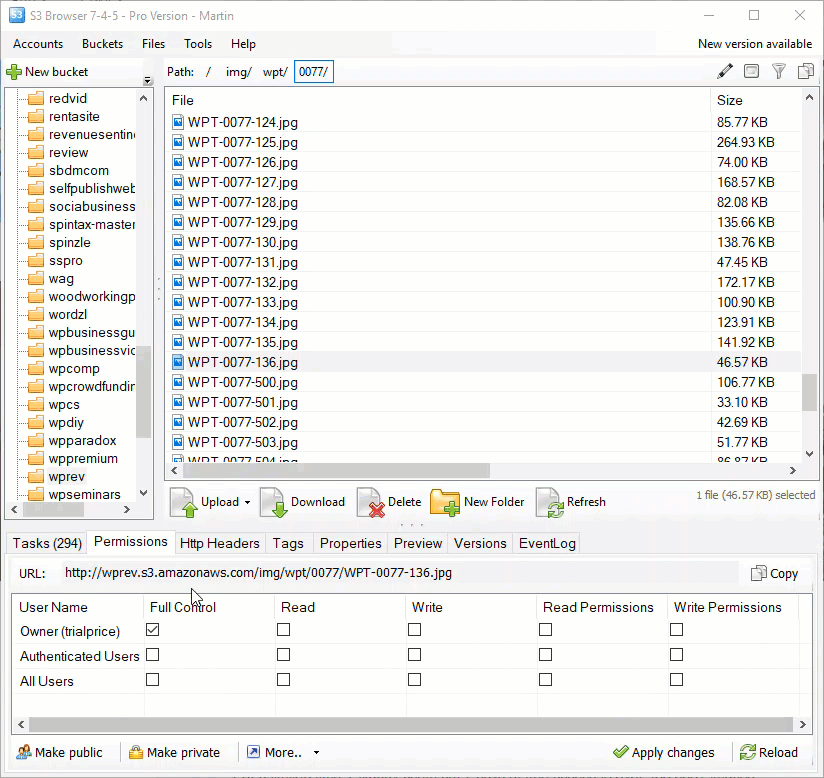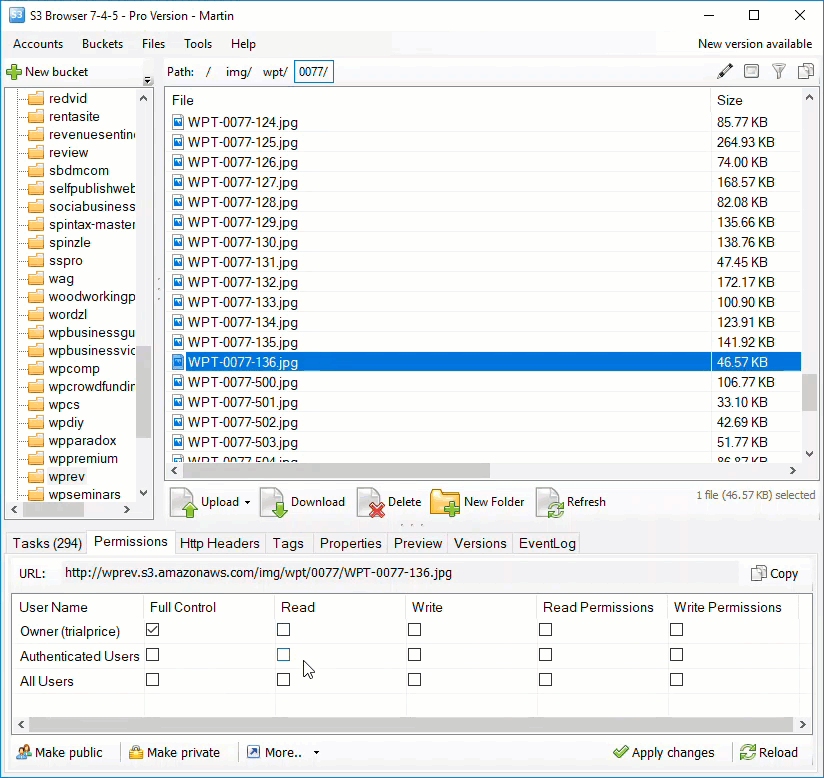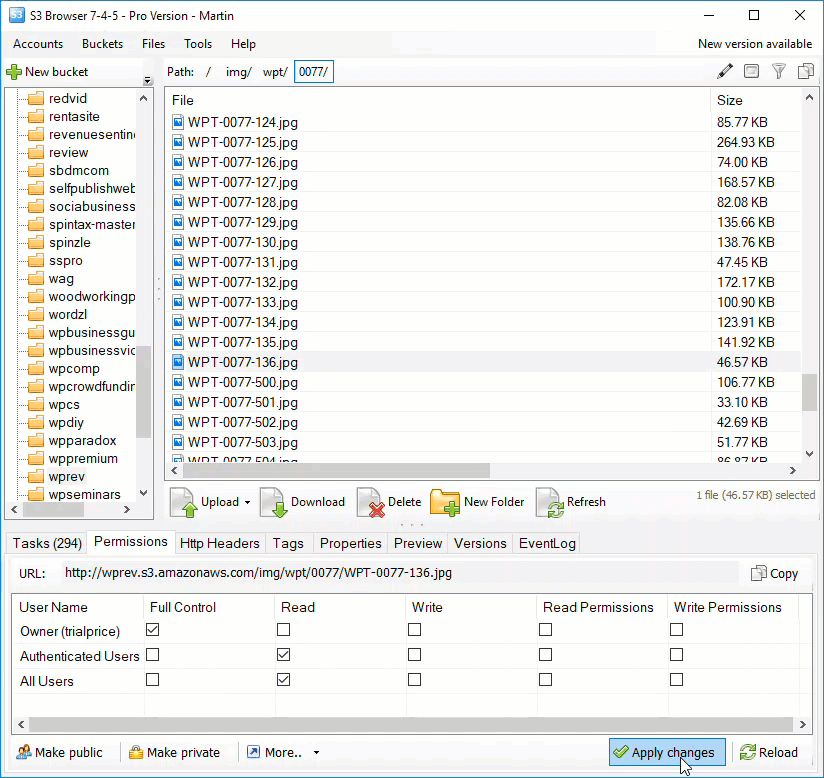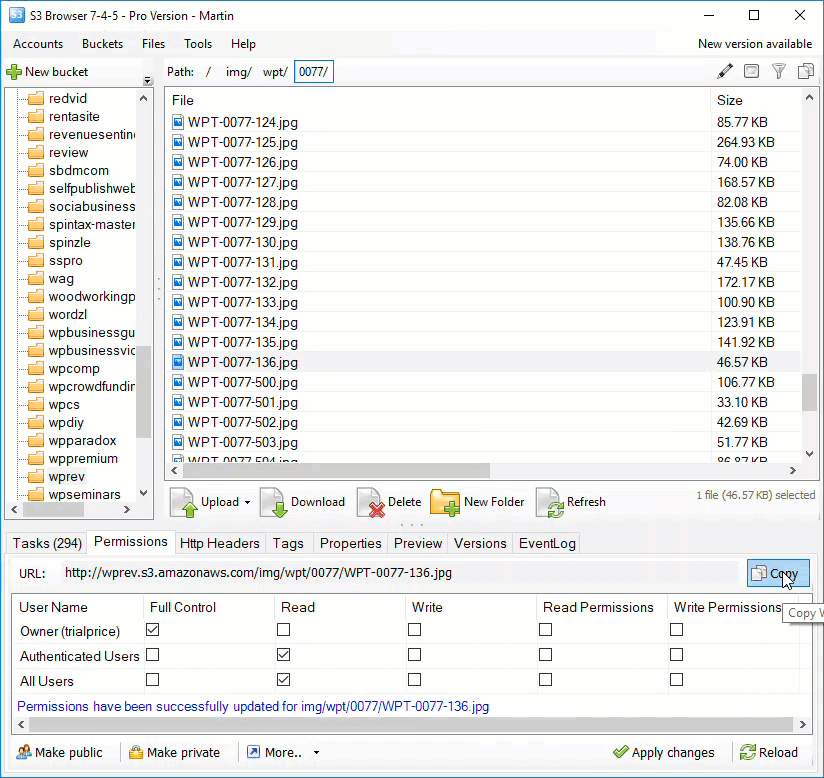
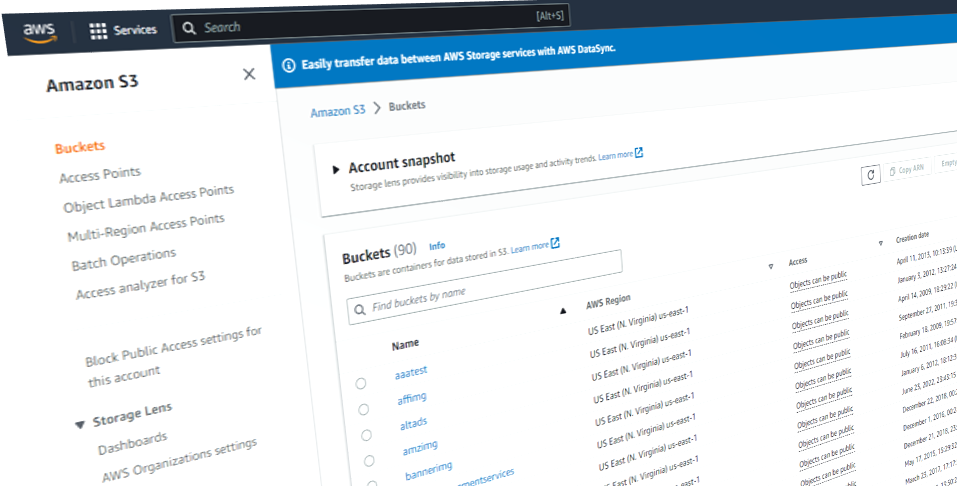
 Amazon S3 is an affordable and almost limitless cloud storage solution that lets you store your files and large amounts of data, including images, media files, and website backups securely and embed these in your web content.
Amazon S3 is an affordable and almost limitless cloud storage solution that lets you store your files and large amounts of data, including images, media files, and website backups securely and embed these in your web content.

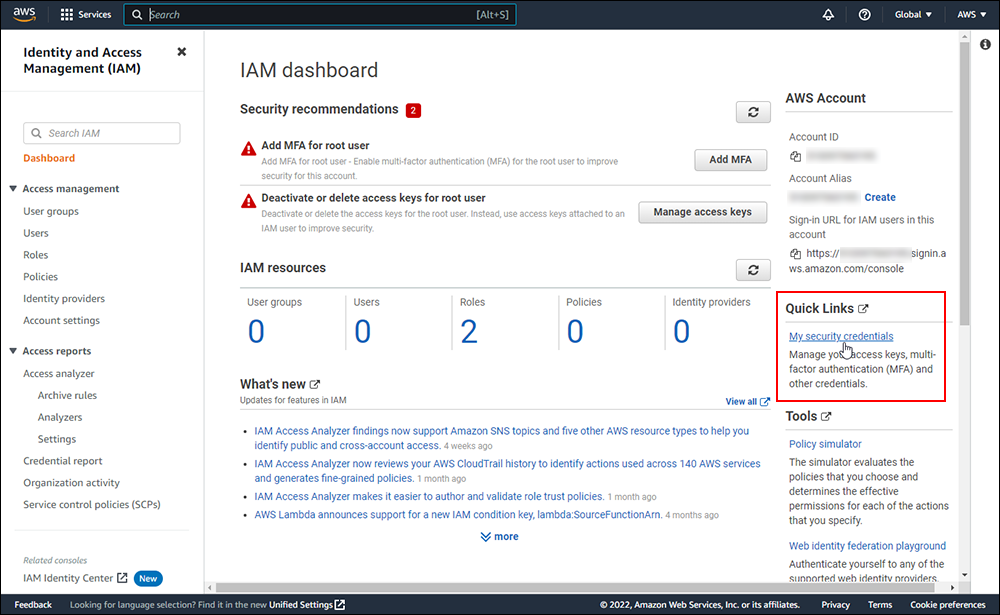
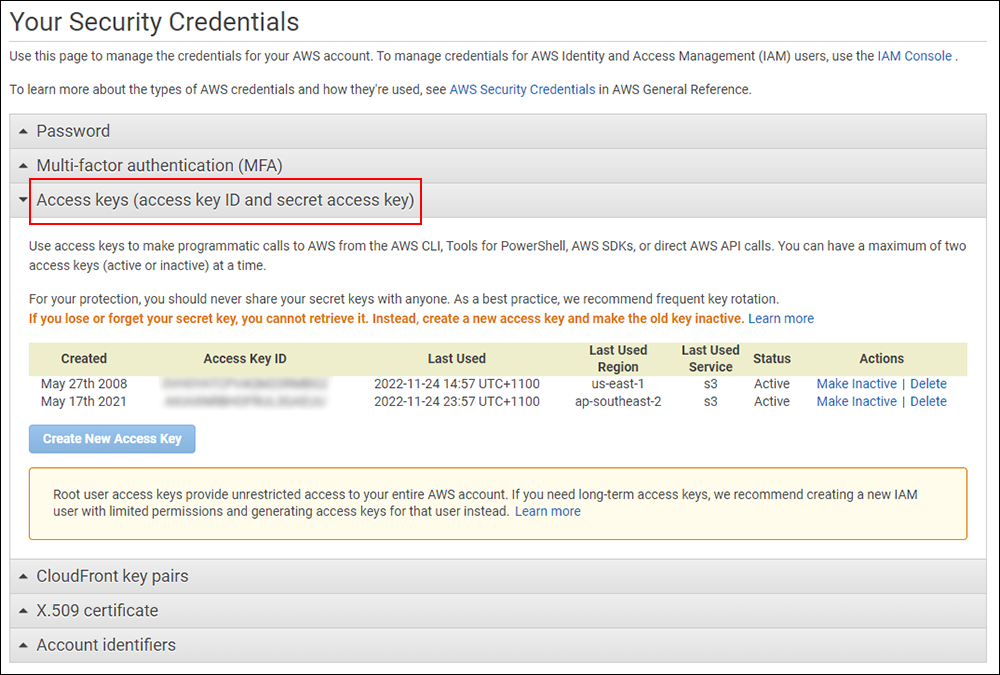


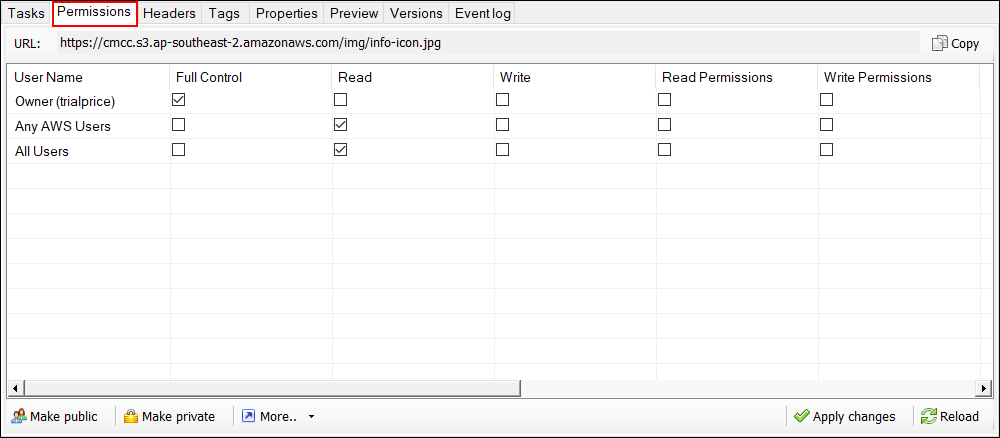
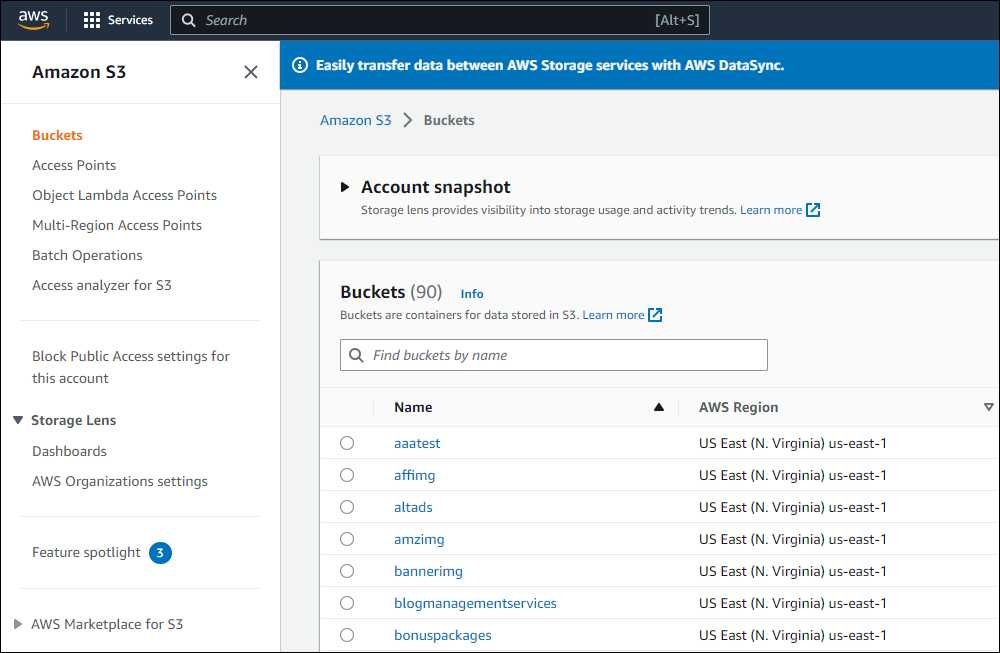
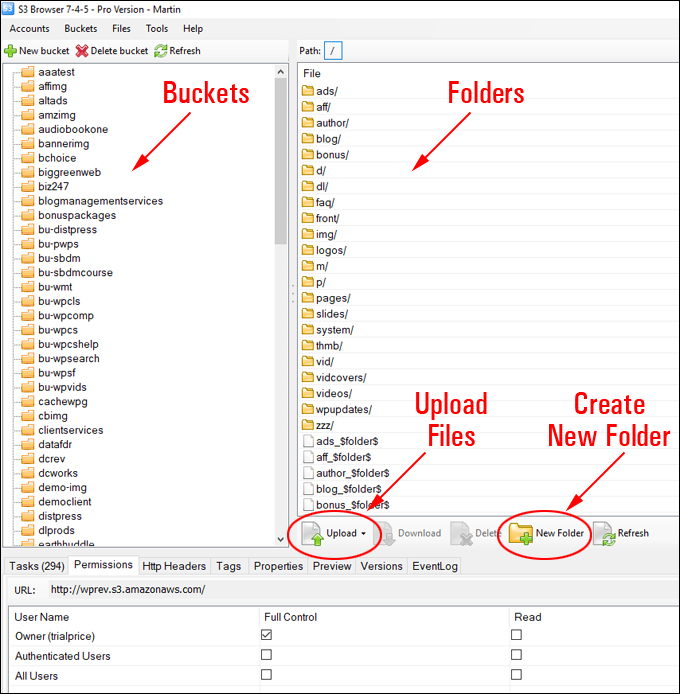
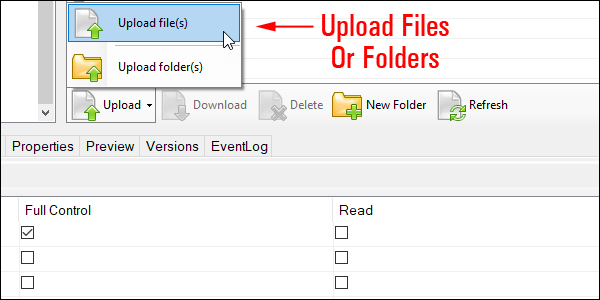
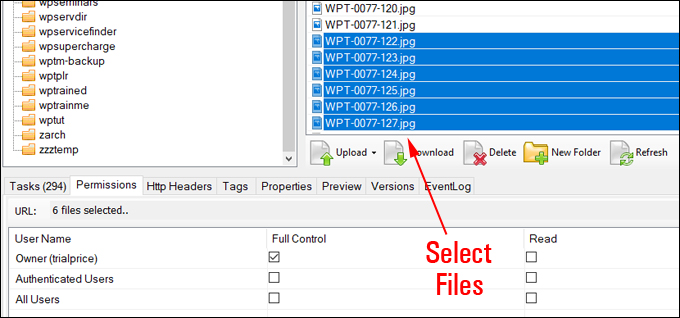
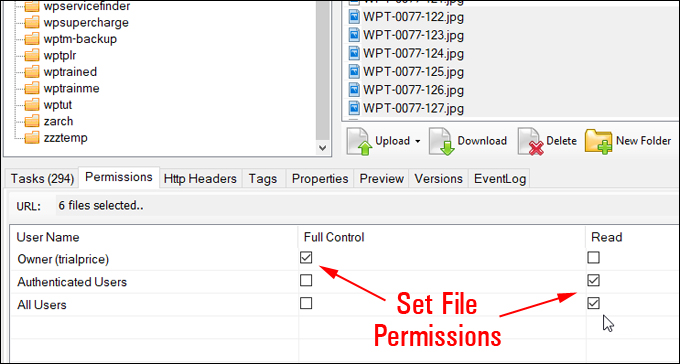
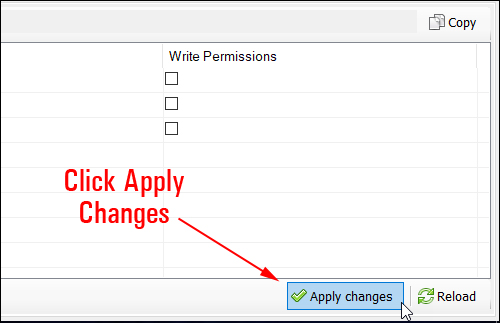
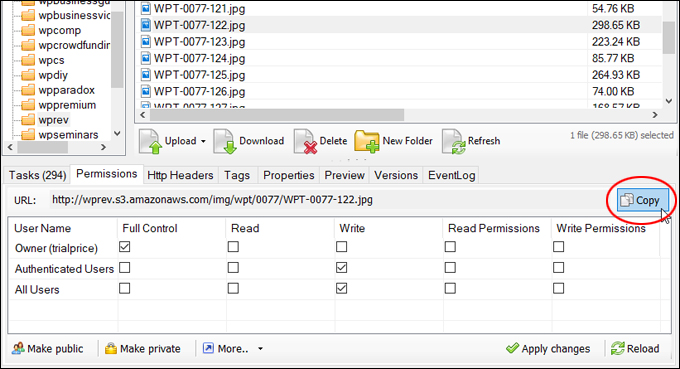
 We provide links to many useful tools, services, and resources throughout our course and the lessons.
We provide links to many useful tools, services, and resources throughout our course and the lessons.
 In this article, we show you how the right picture of what an effective content management framework looks like can help you fix and eliminate most of the content-related problems in your business.
In this article, we show you how the right picture of what an effective content management framework looks like can help you fix and eliminate most of the content-related problems in your business.



 The web has become so central to our lives that many people around the world today spend hours each day on average looking at screens on their digital devices searching for information, for work, or for entertainment.
The web has become so central to our lives that many people around the world today spend hours each day on average looking at screens on their digital devices searching for information, for work, or for entertainment.

 This troubleshooting guide will help you identify issues in your content that may be preventing your business from experiencing better results and presents fixes and solutions to improve your content management practices.
This troubleshooting guide will help you identify issues in your content that may be preventing your business from experiencing better results and presents fixes and solutions to improve your content management practices.












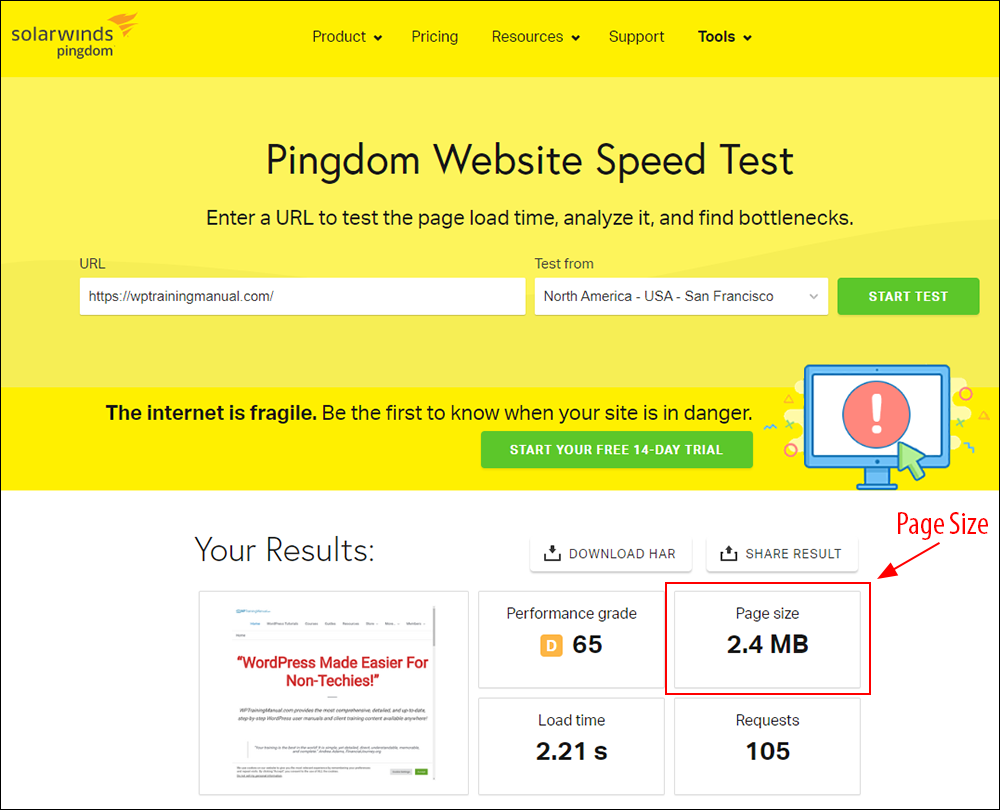
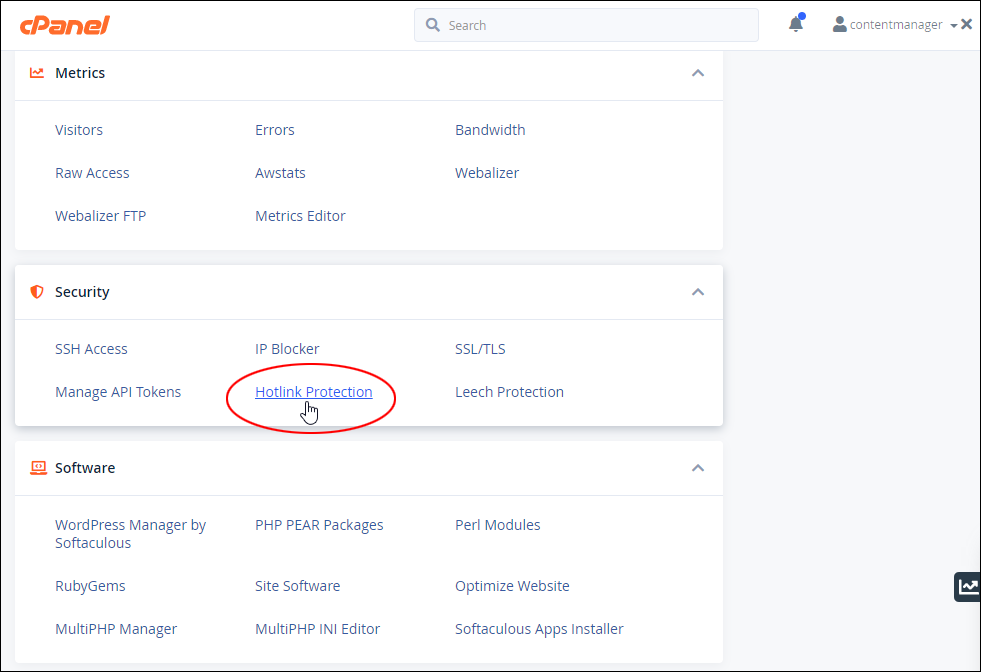
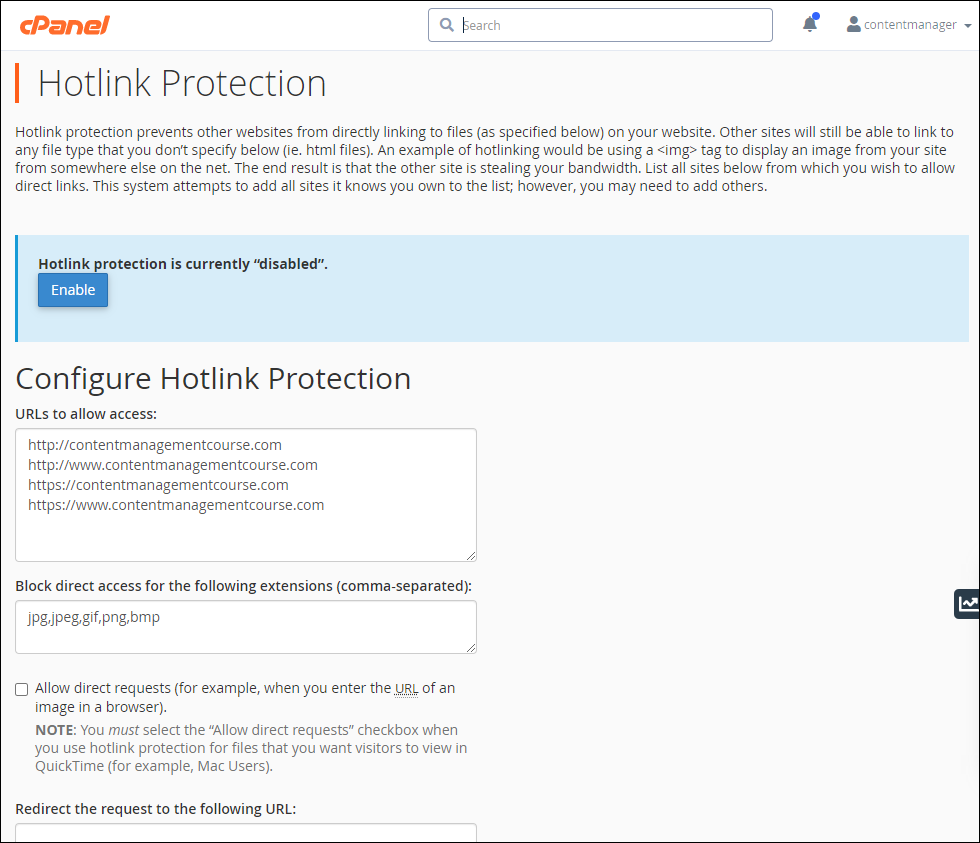
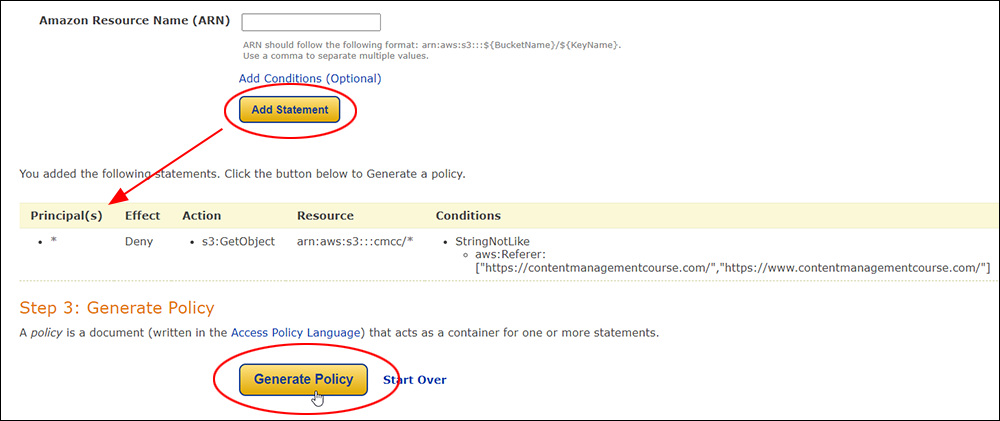
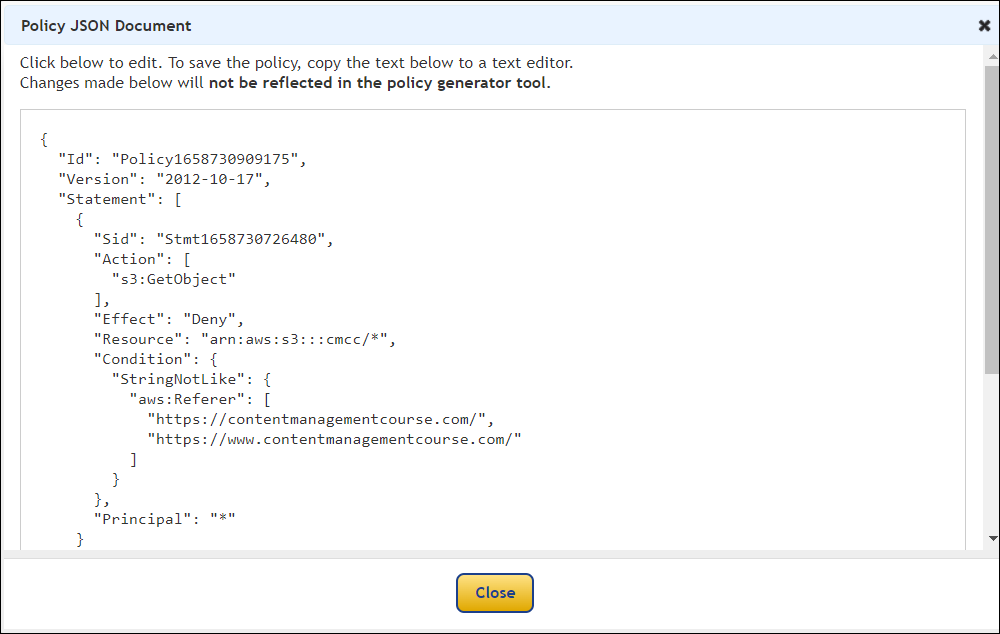
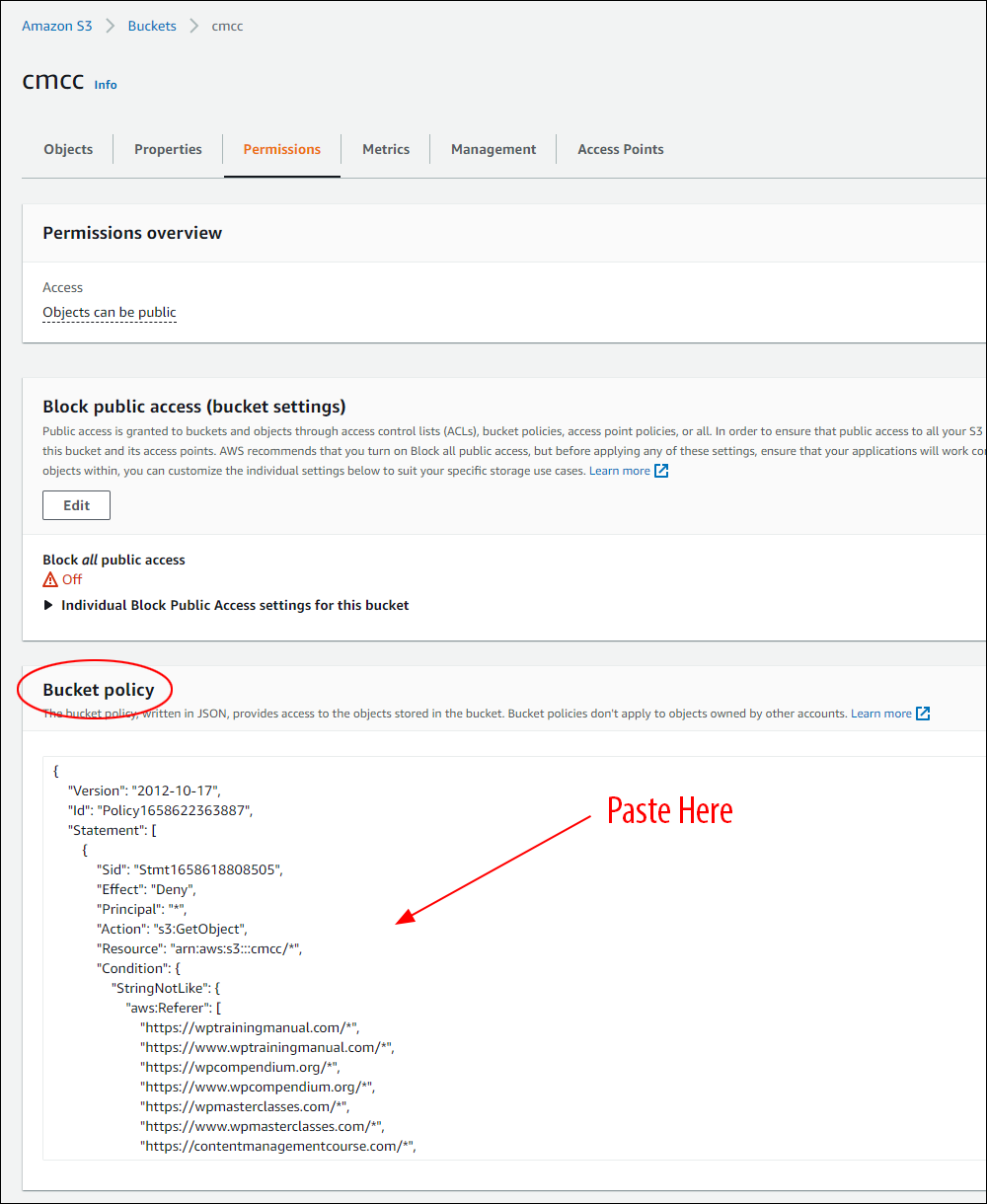
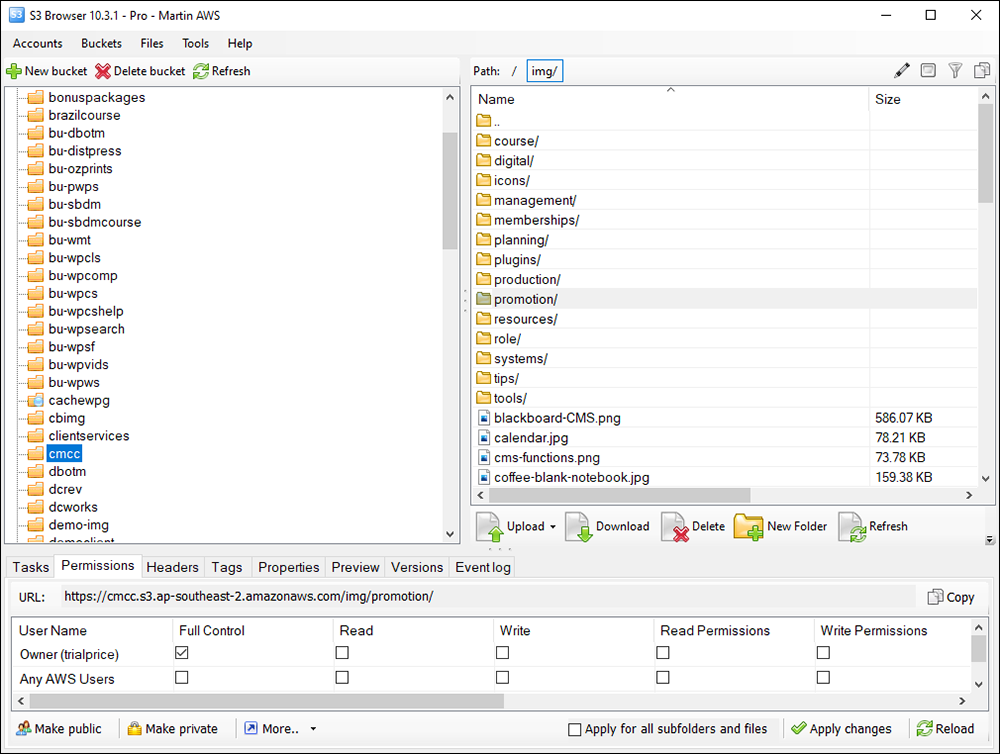
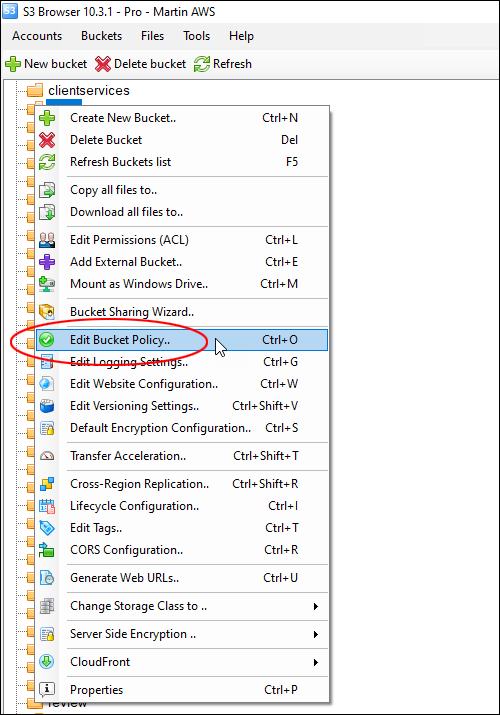
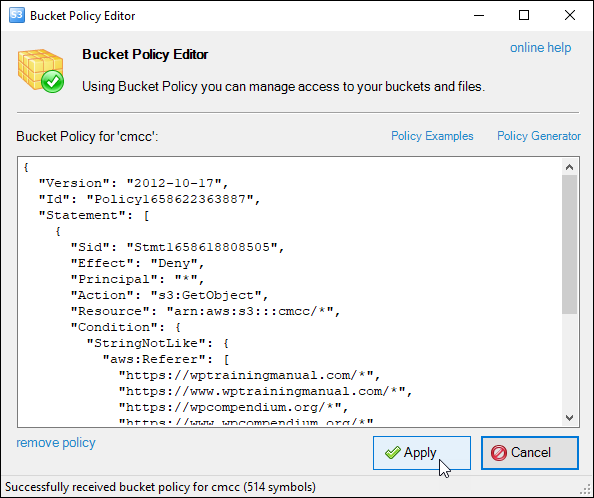
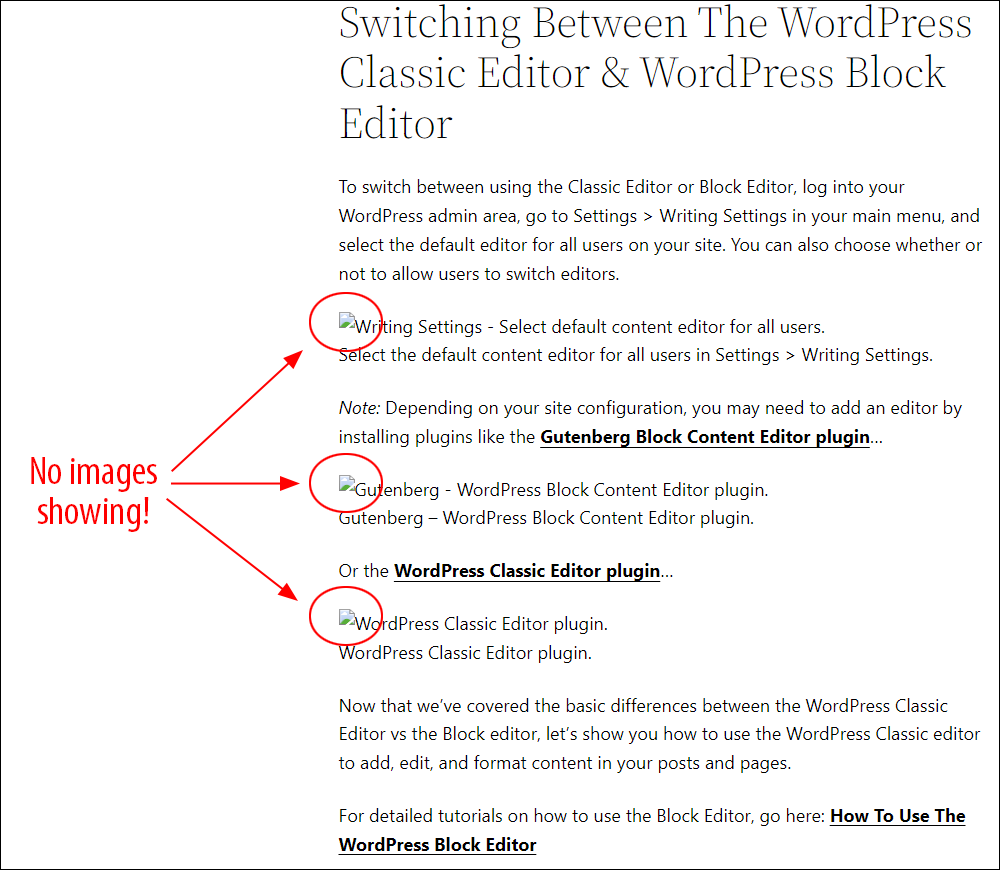
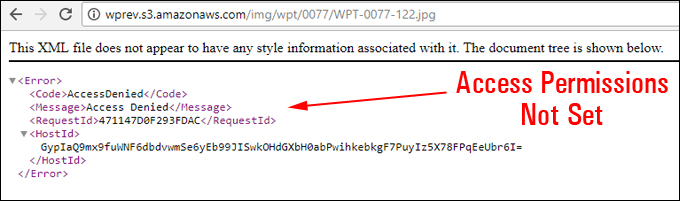
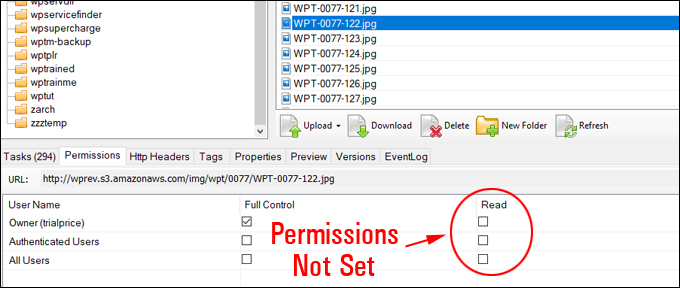
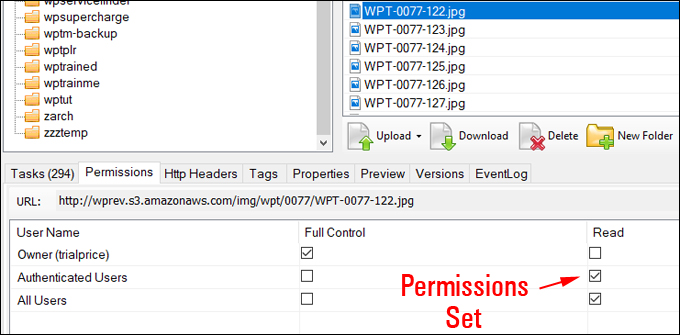
 Hotlinking is when someone links directly to assets on your website, such as images, videos, or downloadable documents.
Hotlinking is when someone links directly to assets on your website, such as images, videos, or downloadable documents.